Uploaded by
dyannecapili
Population Dynamics Mind Map

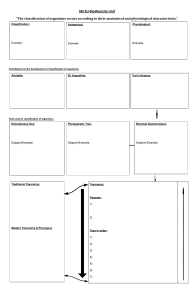
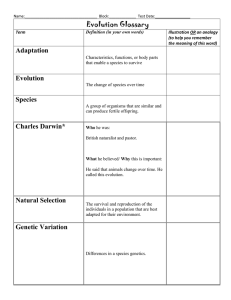
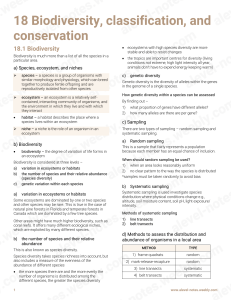
• increase in numbers without any limits to their growth • J-shaped curve • ex. bacteria DEMOGRAPHY statistical study of population changes EXPONENTIAL GROWTH LO N G TER M C O N SEQ U EN C ES • degradation of natural environment • inequality in resource access • climate change DYANNE DANE D. CAPILI SCIENCE11 (CK) LIFE TABLES - mortality rate - life expectancy at each interval - life history of organism GROWTH 1. competition for food 2. ability to find a mate - compare the life histories of different populations POPULATION DENSITY FORMULA number of individuals per unit area TYPES No. of individuals dying x 1,000 No. of individuals surviving FORMULA • EFFECTS ON INTERACTIONS WITHIN A POPULATION SURVIVORSHIP CURVES Type I (humans) Type II (birds) Type III ( trees) DEMOGRAPHICS Population growth = r N LOGISTIC GROWTH r = birth rate – death rate POPULATION SIZE VALUE CAN BE: ( + ) = increasing ( - ) = decreasing ( 0 ) = unchanging • limits to reproductive growth • S- shaped curve • ex. yeast total number of individuals P O P U L AT I O N DY N A M I C S • BIRTH AND IMMIGRATION increases population size • DEATH AND EMIGRATION lead to the decline in population size FORMULA [ rN K–N K ] SPECIES DISTRIBUTION K = carrying capacity RANDOM R E G U L AT I O N • density-dependent factors (biotic) • density-independent factors (abiotic) CLUMPED ESTIMATING POPULATION SIZE • COUNTING UNIFORM most accurate way, but not feasible for large areas. • QUADRAT immobile organisms or for very small and slow-moving organisms example: - dandelions with wind-dispersed seeds example: - oak trees - schools of fish example: - sage plants - penguins • MARK AND RECAPTURE smaller mobile organisms, such as mammals