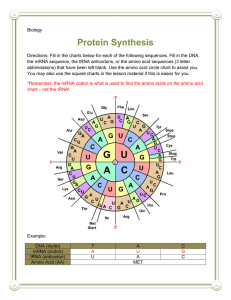
Adventures in Protein Synthesis è Go to: BioMan Protein Synthesis Race at http://bit.ly/2k2y287 You will work through Protein Synthesis as you answer the following questions: WORD BANK (you can expect to use terms more than once) ribosome enzyme triplet gene nucleotides double helix mRNA DNA sequence folds Transcription unzip amino acid one DNA RNA polymerase two function codon protein Translation polypeptide peptide shape DNA PROTEIN SYNTHESIS - TRANSCRIPTION 1. ____________________ is the copying of a ______ (a section of _____) to make ______. It is the FIRST process that must happen in order to make a ___________. In order for transcription to occur DNA must ________. 2. Notice that the DNA molecule has unzipped to make _____ strands. Only _____ strand is used for _____________________. 3. An _______________ called _____ ___________________ is used to add new RNA ____________________ to make _________. 4. Now _____ _____________________ is ready to add new ____________________. RNA polymerase is touching the first ________________ of the _____ ______________. DNA: mRNA: TAC AGT TAC AGT TTT CTG GCT TTT CTG GCT AGT TAC TTT ACT 5. When transcription is done, you have made ______ (____________________ RNA), which carries the information needed to make a _______________. 6. _______ zips back up to reform a ____________ _________. _______ must leave the _______________ and travel to the site of protein synthesis, the __________________. LEARNING CHECK 1. Both DNA and RNA are made of subunits, or building blocks, called ___________________. 2. What is the name of the enzyme that adds new nucleotides to build mRNA? ____ _________________ 3. How many strands does DNA have? _____How many strands does mRNA have? _____ 4. Which mRNA nucleotide is complementary to guanine? ______________ to adenine? ___________ to thymine? _______________ 5. What is the function of mRNA? 6. What happens to DNA once transcription is done? PROTEIN SYNTHESIS - TRANSLATION 1. Once mRNA is made, what is the location where mRNA must go for translation to occur? 2. What exactly is produced during translation? 3. In order to understand translation, you must understand that a _______________ is a chain of ___________ __________. The order of the amino acids in the chain and the length of the chain determine what _________ of protein it will _____ and what it will _____. 4. You must also understand that mRNA ________________ the instructions for how to make a protein as ________________, which is a ______________ of _______________________ bases on mRNA. Each codon ________ for one _____________ ________. For example, the codon AUG codes for the amino acid _______________________ (_____) 5. What type of codon is AUG, specifically? ____________ 6. What is the name of the cart used to determine which amino acid the mRNA codon is coding for? 7. Translate the following mRNA sequence: mRNA tRNA AUG UCA AUG UCA AAA GAC CGA AAA GAC CGA UCA AUG AAA UGA ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ amino acids 8. Notice you have a chain of amino acids, with each amino acid connected to another by a ________________ bond. For this reason, chains of amino acids are often called __________________, which is a simple __________________. Once the polypeptide chain is made, it __________ to make a 3-dimensional ____________. This shape is unique to one specific protein and gives the protein its _____________. DID YOU GET IT? CIRCLE and LABEL EACH of the following in the image below: mRNA tRNA ribosome codon anticodon amino acid LEARNING CHECK 1. Define translation? 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Match the following terms: ______ 2. Translation A. triplets of tRNA _____ 3. mRNA B. brings amino acids to the ribosome ______ 4. tRNA C. copies DNA code to take it from the nucleus to the ribosome ______ 5. Codons D. triplets of mRNA ______ 6. Anticodons E. another name for a protein ______ 7. Polypeptide F. building blocks of proteins 9. How many nucleotides make up a codon?____ 10. The “start” codon is: 11. Each codon codes for an ____________________ 12. If the mRNA codon is CGA, the tRNA anticodon that binds with it is: 13. What organelle assists tRNA in translating the mRNA in the cytoplasm?