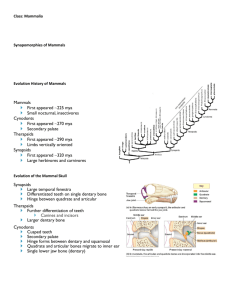
Mammals Chapter 34 What is a mammal? Endothermic vertebrate Amniotic egg Four chambered heart Synapomorphies of Mammalia Mammary glands Hair _____ inner ear bones Neocortex region of brain Single ________ bone (mandible) Differentiated teeth _________ dentition Two occipital condyles Anapsids, Synapsids and Diapsids Based on number of temporal openings (fenestra) Orbit (eye socket) Jaw muscle attachment Anapsid: no temporal openings Turtles Synapsid: single temporal opening Mammals Diapsid: two temporal openings Reptiles including birds Temporal fenestra Evolutionary History of Mammals Mammals First appeared ~225 mya Small ________, insectivores Cynodonts First appeared ~270 mya Secondary palate Therapsids First appeared ~290 mya Limbs ________ oriented Synapsids First appeared ~320 mya Large herbivores and carnivores Evolution of the Mammal Skull Synapsids Large temporal fenestra Differentiated teeth on single dentary bone Hinge between quadrate and articular Therapsids Further differentiation of teeth Canines and incisors Larger dentary bone Cynodonts _______ teeth Secondary palate Hinge forms between dentary and squamosal Quadrate and articular bones migrate to _______ Single lower jaw bone (dentary) Mammal Dentition Differentiation of teeth led to success in mammals Size and arrangement of teeth associated with diet Cusps Four distinct tooth types Incisors: cutting _______: tearing Premolars: grinding Molars: crushing, grinding Diversification of Mammalian Dentition A. Hedgehog K. Raccoon B. Mole L. Coyote C. Armadillo M. Mountain lion D. Anteater N. Horse E. Giant Anteater O. Deer F. Marmoset P. Jackrabbit G. Peccary Q. Woodrat H. Bear R. Porpoise I. Fruit-eating bat S. Right whale J. Nectar-eating bat T. Walrus Digestive Tracts of Carnivores and Herbivores Carnivores Large, expandable _________ _____ digestive tract Herbivores Large ______ with symbiotic bacteria break down plant material _____ digestive tract Modes of Locomotion Plantigrade Most ambulatory (walking) mammals Walk on _____ of hands and feet Bears, primates, lagomorphs Digitigrade Many cursorial (running) mammals Run on one or more _____ Canids, felines Unguligrade Ungulates Walk or run on _____ (nails) Horses, pigs, camels Timing of Activity Diurnal: animals active during daylight Many mammal species Squirrels, ungulates, primates _____________: animals active during twilight (dawn and dusk) Predator avoidance Skunks, rabbits, mice, deer, bear, bobcats, coyotes Nocturnal: animals active at night Reduce competition, escape heat, avoid predators Highly developed senses Large eyes (more rods, tapetum lucidum) Large ears (greater hearing range) Vomeronasal system Bush babies, bats, wolves, cats, raccoons, opossums hours Lactation Lactation: secretion of milk from mammary glands Modified sweat glands ________: stimulates milk production Oxytocin: stimulates milk ________ Milk: nutritional liquid comprised of fats, proteins, and lactose Nutrition for newborn Transmits passive immunity Supports growth of intestinal flora Major lineages of Mammals Monotremes Lack a placenta Leathery eggs similar to reptiles Body temp ~ 32°C Marsupials Rudimentary, ________ placenta Body temp ~ 35°C Platypus, echidnas Marsupials Golden moles Elephant shrews Aardvarks Elephants Hyrax Manatees Armadillos, sloths, anteaters Flying lemurs Tree shrews Apes, monkeys, humans Rabbits and hares Rodents Eutharians Well-developed placenta Body temp ~ 38°C Hedgehogs, moles, true shrews Canines, felines, bears, seals, weasels Pangolins Horses, tapirs, rhinos Camels, pigs, whales, dolphins, antelope Bats Biogeography of Mammals Early Jurassic (~ 200 mya) • Monotremes and marsupials in southern Pangaea Early Cretaceous (~ 135 mya) • Marsupials and monotremes isolated in “Australia” • Marsupials isolated on “South America” Late Jurassic (~ 180 mya) • Eutheria diverge from Marsupials in “South America” Early Paleocene (~ 65 mya) • Dinosaurs extinct • Mammal radiation • Separation of primates • New world/old world • Lemurs • Eutheria northern distribution Mammal Reproductive Tracts Monotremes • Single vagina • Two uteri Marsupials • _____ vagina • Two uteri Eutherians • Single vagina • Single uterus Monotremes Prototherians (“first wild beast”) Single platypus species and four species of echidna Milk glands Lack _______ Egg laying Lack _____ as adults Reptile like gate Low metabolic rate All found in either Australia or Papua New Guinea Body temp. ~32°C Single vagina, two uteri Cloaca Marsupials Limited to Australia and the Americas Yolk sac placenta High metabolic rate __________ (pouch) often present Scrotum anterior to penis No baculum We have an exam.. Females have bifurcated reproductive tract Body temp. ~35°C Three vagina and two uteri Male penis bifurcated at tip Small braincase (relative to body size) Minimal neocortex development No corpus callosum .. on Monday?! Major Marsupial Orders Didelphimorphia (~100 species) Opossums New world distribution Most semi-arboreal omnivores ~50 teeth Didactylous: unfused toes Polyprotodont: small, unspecialized incisors Diprotodont 2 large lower incisors Polyprotodont Multiple small lower incisors Dasyuromorphia (~75 species) Carnivorous marsupials (Quolls, numbats, Tasmanian devil) Australasia Didactylous Polyprotodont Diprotodontia (~137 species) Kangaroos, wallabies, wombats, koalas, possums Australasia Syndactylous: fusion of second and third digits Diprotodont dentition: shortened mandible, enlarged lower incisors Syndactyl Eutherians Worldwide distribution Scrotum posterior to penis One vagina with uterus High metabolic rate Baculum sometimes present Female have single reproductive tract Introduced to ________ Body temp ~38°C Large braincase (relative to body size) Neocortex Complex neocortex: higher functions including sensory perception, language, spatial reasoning, motor commands Corpus callosum: connects left and right hemispheres of brain Corpus callosum Placental Mammals Placenta: organ that connects developing fetus to uterine wall and facilitated transfer of gases, nutrients and wastes. _______: outermost membrane that develops chorionic villi, which facilitates exchange between mother and fetus Umbilical cord: vascularized cord connecting fetus to placenta Differences in the Placenta Marsupials Rudimentary connection between yolk sac and maternal tissue Large ______ provides nutrients to developing embryo Allantois: avascular; storage of nitrogenous waste Marsupial Eutherian Chorion Amnion Embryo Eutherians ____________ connects fetus to uterus Umbilical vein and artery Efficient exchange of nutrients, gases and waste Reduced yolk sac Allantois connects fetal bladder to yolk sac, which drains into umbilical cord Allantois Yolk Sac Fetal portion of placenta Maternal portion of placenta Umbilical cord Marsupials Dependency on yolk sac for nutrition Young born in very immature state Short gestation period Prolonged lactation period Eutherians Placenta facilitates nutrient transfer between embryo and mother Young born in well developed state Long gestation period Short lactation period Days after conception Lactation versus Gestation Times 500 Gestation 400 Lactation 300 200 100 0 Grasshopper mouse Marsupial mouse Thomson's gazelle Wallaroo Return to Water Three mammal clades returned to water Cetartiodactyla Carnivora Afrotheria Characteristics that support terrestrial origin Lungs and a need to breathe air from the surface Limb bones homologous with land mammals Vertical movement of spine Vestigial pelvic bones in cetaceans Cetacea Mysticeti ______ whales Odontoceti Humpback whales, blue whales, right whales, minke whales Krill, small schooling fish 15 species ____ blow holes Lack echolocation _______ whales Sperm whales, porpoises, dolphins, killer whales Fish, squid, marine mammals >70 species ____ blow hole Echolocation Cetacea Mysticeti Odontoceti Baleen Brain Tongue Fat-filled cavity Melon Ungulates (Hoofed Animals) Artiodactyla Perissodactyla Cannon bone Metapodials 3 and 4 Fused metapodials 3 and 4 3rd Metapodial Tapir Horse Peccary Camel Deer Perissodactyla Odd-toed ungulates Equidae (Zebra, Asses and Horse) Tapiridae (Tapirs) 8 species 4 species Rhinocerotidae (Rhinos) 5 species Dominant ungulates from 50 mya to mya Upper _______ present (except rhinos) Hind gut fermentation Large _______ Fibrous vegetation 25 Artiodactyla Even-toed ungulates 10 families, ~220 species Pigs, hippos, camels, antelope, deer, giraffe, bovines Radiation during Oligocene and Miocene epochs ~33 to 5 mya Closely related to cetaceans Cetartiodactyla Upper incisors and canines __________ _______ Ruminant fermentation (except pigs) “Double pulley” astragalus (ankle) bone Greater extension and flexion Canine Deer Digestion in Ungulates Ruminants Artiodactyla, kangaroos Food chewed several times Complex, multi-chambered ________ Rate of passage ~ 80 hours Cellulose utilization ~ __% Hindgut Fermenters Perissodactyla, lagomorphs, rodents Food chewed once Simple stomach, large ______ Rate of passage ~ 48 hours Cellulose utilization ~ __% Simple stomach Reticulum Omasum Rumen Food chewed, regurgitated, then chewed again Cecum Abomasum Large intestine Cecum Small intestine Food chewed once Small intestine Large intestine Antlers and Horn Horns Bovine family Outgrowth of frontal bones Unbranched Covered by epidermal horny, keratinized sheath ___________ Antlers Deer family Dermal bone of antler attaches to skull bone Branched in most Outside layer of highly vascularized skin _______ Shed annually Proboscidae Elephants Two genera Elephas – Asiatic elephants Loxodonta – African elephants Horizontal _____ replacement Similarities to Manatees and Hyrax Tusks derived from incisors Flattened nails Internal ________ Two teats near armpits Low-frequency sounds Long distance communication African elephant Large ears Three nails on hind feet Single dome on head Dip in back Two lips on trunk 9 -13ft tall 8,000 - 15,400lbs Asian elephant Small ears Four nails on hind feet Two humps on head Arched back Single lip on trunk 7-9ft tall 6,500 – 13, 200lbs Sirenia Manatees and dugongs Only ____________ marine mammal Three manatee and one dugong species All four species considered threatened Indefinite molar replacement Found in shallow bays, estuaries, and inland river systems Long lungs and dense bones help regulate buoyancy Steller’s sea cow extinct 27 years after discovery by Europeans Rodentia Beaver, squirrels, mice, rats, capybara Largest mammalian order Worldwide distribution Wide range of habitats Most are small (<100g) Single pair of upper and lower ________ Open rooted (ever growing) Canine teeth _______ Diastema Lagomorpha Rabbits, hares, and pika Two pairs of upper incisors Grow constantly Strictly herbivorous ___________: poo eating Large ears and hind limbs in rabbits and hares Chiroptera Bats Second largest order of mammals Diverse diets Insectivorous, carnivorous, piscivorous (fish), insectivorous, frugivorous, sanguinivorous (blood) ___________ foraging Approx. 920 species Diurnal roosting Most with single litter per year One or two young per litter Two Suborders Megachiropterans (1 family) Large, nectivorous and frugivorous No echolocation Microchiropterans (16 families) Small, primarily insectivorous Ecolocation Primates Lemurs, lorises, monkeys, apes, humans Most found in tropical regions _____ instead of claws Clavicle Two lower limb bones Opposable thumb Reduced snout Greater movement Reduced smell, but better vision ____________ vision Depth perception Carnivora Weasels, pinnepeds, cats, dogs, bears Most are carnivores Large brain to body mass ratio Camouflage fur Hunting Ambush predators Large canines __________ pair Shearing