Animal Reproduction & Classification Worksheet
advertisement

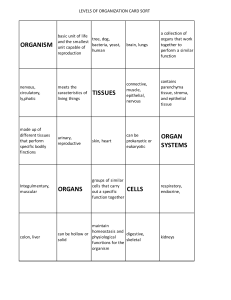
Name:________________________________________________ Date:_________________________ Reproduction in Animals: Sexual Reproduction Using teacher provided materials and your knowledge about reproduction, answer the following questions about sexual reproduction. 1. List an advantage and disadvantage of sexual reproduction. Match the following terms with their definitions by drawing a line from the term to the definition and writing the letter of the definition next to the term. 2. ____ Internal Fertilization A. Produces eggs and sperm. B. A hole in a hollow ball of cells. C. Process of two gametes fusing together resulting in a zygote D. A hollow ball of cells. E. Fertilization occurs inside of the body. F. The blastopore that will become the anus G. Produces the sperm. H. A fertilized egg. I. Fertilization occurs outside of the body. J. The blastopore that will become the mouth. K. Produces the eggs. 3. ____ External Fertilization 4. ____ Female 5. ____ Male 6. ____ Hermaphrodite 7. ____ Fertilization 8. ____ Zygote 9. ____ Blastula 10. ____ Blastopore 11. ____Protosome 12. ____Deuterostome In the chart below to describe the three types of chordate development after internal fertilization by placing an “X” in the boxes that apply. 13. Oviparous Develop inside of the body Develop outside of the body Nutrients obtained from yolk in an egg Nutrients obtained directly from mother 14. Ovoviviparous 15. Viviparous Name:_______________________________________________ Date:________________________ Animalia Graphic Organizer Using teacher presented lessons, books, or online resources fill out the graphic organizer with the two characteristics already listed and three more additional characteristics. 1. Type of Cells: __________ 5. ___________ ___________ ___________ ___________ 4. ___________ ___________ ___________ ___________ 2. Cell Walls Contain: ___________ Kingdom: Animalia 3. ___________ ___________ ___________ ___________ Name:_______________________________________________ Date:________________________ Body Plan and Symmetry Review Using teacher provided materials and your knowledge about body plans and symmetry, label each organism below with the type of symmetry it has. 1. ______________________________ 2. ______________________________ 3. ______________________________ 4. ______________________________ 5. ______________________________ 6. ______________________________ Name:_______________________________________________ Date:________________________ Comparing Vertebrates and Invertebrates Identify similarities and differences for vertebrates and invertebrates in the Venn Diagram shown below. Where there more similarities or differences? Explain. Name:_______________________________________________ Date:________________________ Phylum Description Chart Using knowledge obtained from teacher presented lessons, books, or internet research fill out the phylum characteristics listed below. Phylum Porifera Cnidaria Platyhelminthes Rotifera Nematoda Mollusca Annelida Arthropoda Echinodermata Chordata Body Symmetry Tissues & Body Cavities Digestive System Circulatory System Nervous System Examples Name:_______________________________________________ Date:________________________ Where Do I Belong? Animal Phyla Edition Using your knowledge of animal phyla, use the clues to determine the appropriate phyla each organism belongs to. Write the phylum’s name in the blank next to each clue. 1) I am a roundworm.___________________________________________________________ 2) I have a notochord.___________________________________________________________ 3) I am an insect._______________________________________________________________ 4) I have a blind gut and radial symmetry.___________________________________________ 5) I am a clam._________________________________________________________________ 6) I have three tissue layers and a blind sac-like gut.___________________________________ 7) I have a complete gut, a brain, segments, and a closed circulatory system._______________ 8) I am a sponge._______________________________________________________________ 9) I have a blind gut and bilateral symmetry._________________________________________ 10) I am a starfish._______________________________________________________________ 11) I am a “wheeled” animal.______________________________________________________ 12) I am an earthworm.___________________________________________________________ 13) I have three tissue layers and only small ganglia for a nervous system.__________________ 14) I am a vertebrate.____________________________________________________________ 15) I have a complete gut, a brain, and a radula. _______________________________________ 16) I am a flatworm._____________________________________________________________ 17) I have a complete gut, segments, and an open circulatory system._____________________ 18) I am a jellyfish._______________________________________________________________ Name:_______________________________________________ Date:________________________ Vertebrata Class Description Chart Using knowledge obtained from teacher presented lessons, books, or internet research fill out the class characteristics listed below. Phylum Agnatha Chondrichthyes Osteichthes Amphibia Reptilia Aves Mammalia Commonly Known As Nervous System Reproduction Circulatory Description System & Heart Chambers Endo- or Exothermic Examples: Name:_______________________________________________ Date:________________________ Where Do I Belong? Vertebrata Classes Using your knowledge of Vertebrata classes, use the clues to determine the appropriate class each organism belongs to. Write the class’s name in the blank next to each clue. 1) I am commonly referred to as a “jawless fish”. _____________________________________ 2) I am a mockingbird. __________________________________________________________ 3) I have fur or hair and mammary glands. __________________________________________ 4) I am a shark. ________________________________________________________________ 5) I have feathers. ______________________________________________________________ 6) I am a turtle. ________________________________________________________________ 7) I am commonly referred to as a “bony fish”. _______________________________________ 8) I am cold blooded and live on land and in water. ___________________________________ 9) I am a platapus.______________________________________________________________ 10) I have a three chambered heart and use internal fertilization. _________________________ 11) I have a skeleton made of cartilage and a jaw. _____________________________________ 12) I am a frog. _________________________________________________________________ 13) I have a four chambered heart and no fur. ________________________________________ 14) I undergo metamorphosis. _____________________________________________________ 15) I am a hagfish. _______________________________________________________________ Name:_______________________________________________ Date:________________________ Animal Symmetry and Phyla Chart Animal Frog Jellyfish Cat Fish Elephant Beetle Ant Shark Spider Anemone Starfish Coral Dog Alligator Monkey Parrot Earthworm Snail Scorpion Tiger Phylum Symmetry Name:_______________________________________________ Date:________________________ Nutrient Absorption In Animals Review 1. Intracellular digestion is digestion that takes place ___________________________ the cells. 2. Extracellular digestion is digestion that takes place ___________________________ the cells. 3. Blind guts consist of ___________________________ opening(s). 4. Cnidarians have a ___________________________ gut. 5. Platyhelminthes have a ___________________________ gut. 6. Nematodes have a ___________________________ gut. 7. Annelids have a ___________________________ gut. 8. Mollusks have a ___________________________ gut. 9. Arthropods have a ___________________________ gut. 10. Echinoderms have a ___________________________ gut. Match the following terms to their definitions. 11. ____ Choanocytes 12. ____ Archaeocytes 13. ____ Gastroderm 14. ____ Pharynx 15. ____ Crop 16. ____ Gizzard 17. ____ Intestine 18. ____ Nephridia 19. ____ Stomach 20. ____ Malpighian Tubules A. Grinds food into smaller pieces. B. Lines the body cavity of sponges and pull in water, oxygen, and food; engulfs the food. C. Specialized organ in the digestive tract that is used to absorb food and food nutrients. D. Food is stored in this specialized section in an earthworm as well as many other annelids. E. Saclike organs that extract wastes from the blood and adds them to feces that move through the gut. F. Specialized tube shaped organ that eliminates cellular waste containing nitrogen (found in annelids). G. Food is stored in this specialized section in mollusks as well as many other animals and begins the digestion process. H. Completes the digestion process and transport digested food to the rest of the sponge. I. In cnidarians as well as some other animals, partially digested food is absorbed by this. J. Muscular tube that pumps food into the digestive cavity. Name_________________________________________ Period__________ Date__________________ Sponge Anatomy Word Bank: Ostia Ectoderm Osculum Amebocyte Choanocyte Spicule Name:__________________________________________________________ Date:________________ Arthropod Coloring/Labeling Activity The kingdom Animals include many phyla, one of which is Athropoda. Athropods are considered the “segmented” animals with hard exoskeletons. Within the phylum Arthropoda, there are four main classes: Crustacea (the crustaceans), Myriapoda (millipedes and centipedes), Arachnida (the arachnids), and Insecta (the insects). First, label each animal below with which class it belongs to. Next, complete the coloring instructions listed as well. Note, each animal may not have all of the items listed to color as they belong to different classes within the phylum Arthropoda. Color all the legs blue. Color all the antenna brown. Color all wings grey. Color all the mandibles purple. Color all claws or pinchers purple. Color the head red. Color the thorax yellow. Color the cephalothorax orange. Color the abdomen green. Class: _______________________________________ Class: _____________________________ Class: _____________________________ Name:__________________________________________________________ Date:________________ Class: _____________________________ Class: _____________________________ Class: _____________________________ Class: _____________________________ Name:__________________________________________________________ Date:________________ Body Plan Vocabulary Words 1) Asymmetrical – The lack or absence of symmetry. 2) Bilateral Symmetry - Arrangement of an organism or part of an organism along a central axis, so that the organism or part can be divided into two equal halves. 3) Radial Symmetry - Arrangement of parts of an organism around a single main axis, so that the organism can be divided into similar halves by any plane that contains the main axis. 4) Body Cavity - Any fluid-filled space in a multicellular organism other than those of vessels (such as blood vessels and lymph vessels). The term usually refers to the space located between an animal's outer covering (epidermis), and the outer lining of the gut cavity, where internal organs develop. 5) Body Plan - A group of structural and developmental characteristics that can be used to identify a group of animals, such as a phylum. 6) Cell - The smallest structural and functional unit of an organism, typically microscopic and consisting of cytoplasm and a nucleus enclosed in a membrane. Microscopic organisms typically consist of a single cell, which is either eukaryotic or prokaryotic. 7) Organ - A part of an organism that is typically self-contained and has a specific vital function, such as the heart or liver in humans. 8) Organ System - A group of organs that work together to perform one or more functions. Each does a particular job in the body, and is made up of certain tissues. 9) Tissue - Any of the distinct types of material of which animals or plants are made, consisting of specialized cells and their products. 10) Nervous System - The network of nerve cells and fibers that transmits nerve impulses between parts of the body. Name:__________________________________________________________ Date:________________ Body Plan Vocabulary Words 11) Asymmetrical – 12) Bilateral Symmetry - 13) Radial Symmetry - 14) Body Cavity - 15) Body Plan - 16) Cell - 17) Organ - 18) Organ System - 19) Tissue - 20) Nervous System - Name:__________________________________________________________ Date:________________ Body Plan Fill-In-The Blank 1) _____________________________________ -- The network of nerve cells and fibers that transmits nerve impulses between parts of the body. 2) _____________________________________ -- Arrangement of an organism or part of an organism along a central axis, so that the organism or part can be divided into two equal halves. 3) _____________________________________ -- The smallest structural and functional unit of an organism, typically microscopic and consisting of cytoplasm and a nucleus enclosed in a membrane. Microscopic organisms typically consist of a single cell, which is either eukaryotic or prokaryotic. 4) _____________________________________ -- Any fluid-filled space in a multicellular organism other than those of vessels (such as blood vessels and lymph vessels). The term usually refers to the space located between an animal's outer covering (epidermis), and the outer lining of the gut cavity, where internal organs develop. 5) _____________________________________ -- A group of organs that work together to perform one or more functions. Each does a particular job in the body, and is made up of certain tissues. 6) _____________________________________ -– The lack or absence of symmetry. 7) _____________________________________ -- Any of the distinct types of material of which animals or plants are made, consisting of specialized cells and their products. 8) _____________________________________ -- A group of structural and developmental characteristics that can be used to identify a group of animals, such as a phylum. 9) _____________________________________ -- Arrangement of parts of an organism around a single main axis, so that the organism can be divided into similar halves by any plane that contains the main axis. 10) _____________________________________ -- A part of an organism that is typically selfcontained and has a specific vital function, such as the heart or liver in humans. Name:__________________________________________________________ Date:________________ Body Systems Vocabulary 1) Central Nervous System - The complex of nerve tissues that controls the activities of the body, in vertebrates it comprises the brain and spinal cord. 2) Circulatory System - The system that circulates blood and lymph through the body, consisting of the heart, blood vessels, blood, lymph, and the lymphatic vessels and glands. 3) Closed Circulatory System - The blood is closed at all times within vessels of different sizes and wall thicknesses. In this type of system, blood is pumped by a heart through vessels, and does not normally fill body cavities. 4) Muscular System - Organ system consisting of skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscles. It permits movement of the body, maintains posture, and circulates blood throughout the body. 5) Open Circulatory System - Blood is pumped by a heart into the body cavities, where tissues are surrounded by the blood. 6) Reproductive System - The system of organs and parts which function in reproduction consisting in the male especially of the testes, penis, seminal vesicles, prostate, and urethra and in the female especially of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, and vulva. 7) Nervous Tissue – Main component of the nervous system. 8) Peripheral Nervous System – The nervous system outside the brain and spinal cord. 9) Connective Tissue - Tissue that connects, supports, binds, or separates other tissues or organs, typically having relatively few cells embedded in an amorphous matrix, often with collagen or other fibers, and including cartilaginous, fatty, and elastic tissues. 10) Lymph - A colorless fluid containing white blood cells, that bathes the tissues and drains through the lymphatic system into the bloodstream. Name:__________________________________________________________ Date:________________ Body Systems Vocabulary 1) Central Nervous System ‘ 2) Circulatory System - 3) Closed Circulatory System - 4) Muscular System - 5) Open Circulatory System - 6) Reproductive System - 7) Nervous Tissue – 8) Peripheral Nervous System – 9) Connective Tissue - 10) Lymph - Name:__________________________________________________________ Date:________________ Body Systems Fill-In-The Blank 1) _____________________________________ - Blood is pumped by a heart into the body cavities, where tissues are surrounded by the blood. 2) _____________________________________ – The nervous system outside the brain and spinal cord. 3) _____________________________________ - The system of organs and parts which function in reproduction consisting in the male especially of the testes, penis, seminal vesicles, prostate, and urethra and in the female especially of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, and vulva. 4) _____________________________________ - The blood is closed at all times within vessels of different sizes and wall thicknesses. In this type of system, blood is pumped by a heart through vessels, and does not normally fill body cavities. 5) _____________________________________ - The complex of nerve tissues that controls the activities of the body, in vertebrates it comprises the brain and spinal cord. 6) _____________________________________ - The system that circulates blood and lymph through the body, consisting of the heart, blood vessels, blood, lymph, and the lymphatic vessels and glands. 7) _____________________________________ - Organ system consisting of skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscles. It permits movement of the body, maintains posture, and circulates blood throughout the body. 8) _____________________________________ – Main component of the nervous system. 9) _____________________________________ - A colorless fluid containing white blood cells, that bathes the tissues and drains through the lymphatic system into the bloodstream. 10) _____________________________________ - Tissue that connects, supports, binds, or separates other tissues or organs, typically having relatively few cells embedded in an amorphous matrix, often with collagen or other fibers, and including cartilaginous, fatty, and elastic tissues. Name:__________________________________________________________ Date:________________ Embryology Vocabulary Words - Part I 1. Reproduction – The production of offspring by sexual or asexual processes. 2. Sexual Reproduction - The production of a new living thing by two parent organisms, with each parent contributing half the material in the DNA of the offspring. 3. Asexual Reproduction - A type of reproduction by which offspring arise from a single organism, and inherit the genes of that parent only; it does not involve the fusion of gametes and almost never changes the number of chromosomes. 4. Gestation Period - Fetal development period from the time of conception until birth. 5. Reproductive System - The organs and glands in the body that aid in the production of new individuals. 6. Haploid - (of a cell or nucleus) having a single set of unpaired chromosomes. 7. Diploid - (of a cell or nucleus) containing two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent. 8. Fertilization - The action or process of fertilizing an egg, female animal, or plant, involving the fusion of male and female gametes to form a zygote. 9. Internal Fertilization - In mammals, reptiles, birds, and some types of fish the gametes meet inside of the female's body. 10. External Fertilization - A strategy of fertilization in which a sperm cell unites with an egg cell in the open, rather than inside a specialized organ within the body of a parent. Name:__________________________________________________________ Date:________________ Embryology Vocabulary Words - Part I 1. Reproduction – 2. Sexual Reproduction - 3. Asexual Reproduction - 4. Gestation Period - 5. Reproductive System - 6. Haploid – 7. Diploid - 8. Fertilization - 9. Internal Fertilization - 10. External Fertilization - Name:__________________________________________________________ Date:________________ Embryology Fill-In-The Blank - Part I 1) _____________________________________ - In mammals, reptiles, birds, and some types of fish the gametes meet inside of the female's body. 2) _____________________________________ - (of a cell or nucleus) having a single set of unpaired chromosomes. 3) _____________________________________ – The production of offspring by sexual or asexual processes. 4) _____________________________________ - Fetal development period from the time of conception until birth. 5) _____________________________________ - The action or process of fertilizing an egg, female animal, or plant, involving the fusion of male and female gametes to form a zygote. 6) _____________________________________ - The production of a new living thing by two parent organisms, with each parent contributing half the material in the DNA of the offspring. 7) _____________________________________ - A strategy of fertilization in which a sperm cell unites with an egg cell in the open, rather than inside a specialized organ within the body of a parent. 8) _____________________________________ - The organs and glands in the body that aid in the production of new individuals. 9) _____________________________________ - (of a cell or nucleus) containing two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent. 10) _____________________________________ - A type of reproduction by which offspring arise from a single organism, and inherit the genes of that parent only; it does not involve the fusion of gametes and almost never changes the number of chromosomes. Name:__________________________________________________________ Date:________________ Embryology Vocabulary Words - Part II 1. Ovum - A mature female reproductive cell, especially of a human or other animal, that can divide to give rise to an embryo usually only after fertilization by a male cell. 2. Gamete - A mature haploid male or female germ cell that is able to unite with another of the opposite sex in sexual reproduction to form a zygote. 3. Blastula - An animal embryo at the early stage of development when it is a hollow ball of cells. 4. Zygote - A diploid cell resulting from the fusion of two haploid gametes; a fertilized ovum. 5. Embryo - An unborn or unhatched offspring in the process of development. 6. Ectoderm -The outermost layer of cells or tissue of an embryo in early development, or the parts derived from this, which include the epidermis and nerve tissue. 7. Endoderm - The innermost layer of cells or tissue of an embryo in early development, or the parts derived from this, which include the lining of the gut and associated structures. 8. Mesoderm - The middle layer of an embryo in early development. 9. Placenta - A flattened circular organ in the uterus of pregnant eutherian mammals, nourishing and maintaining the fetus through the umbilical cord. 10. Differentiation - The process by which cells or tissues change from relatively generalized to specialized kinds, during development. 11. Hermaphrodite - An organism, as an earthworm or plant, having normally both the male and female organs of generation. Name:__________________________________________________________ Date:________________ Embryology Vocabulary Words - Part II 1. Ovum - 2. Gamete - 3. Blastula - 4. Zygote - 5. Embryo – 6. Ectoderm – 7. Endoderm - 8. Mesoderm - 9. Placenta - 10. Differentiation - 11. Hermaphrodite - Name:__________________________________________________________ Date:________________ Embryology Fill-In-The Blank - Part II 1) _____________________________________ - The innermost layer of cells or tissue of an embryo in early development, or the parts derived from this, which include the lining of the gut and associated structures. 2) _____________________________________ - An animal embryo at the early stage of development when it is a hollow ball of cells. 3) _____________________________________ - A mature female reproductive cell, especially of a human or other animal, that can divide to give rise to an embryo usually only after fertilization by a male cell. 4) _____________________________________ - An organism, as an earthworm or plant, having normally both the male and female organs of generation. 5) _____________________________________ - An unborn or unhatched offspring in the process of development. 6) _____________________________________ -The outermost layer of cells or tissue of an embryo in early development, or the parts derived from this, which include the epidermis and nerve tissue. 7) _____________________________________ - A flattened circular organ in the uterus of pregnant eutherian mammals, nourishing and maintaining the fetus through the umbilical cord. 8) _____________________________________ - A diploid cell resulting from the fusion of two haploid gametes; a fertilized ovum. 9) _____________________________________ - A mature haploid male or female germ cell that is able to unite with another of the opposite sex in sexual reproduction to form a zygote. 10) _____________________________________ - The middle layer of an embryo in early development. 11) _____________________________________ - The process by which cells or tissues change from relatively generalized to specialized kinds, during development.