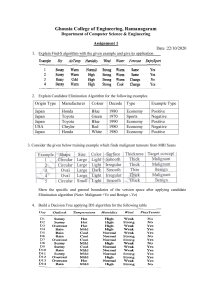
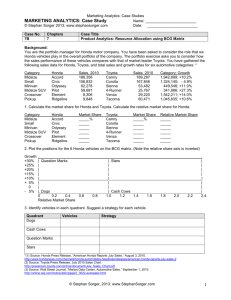
TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 3 MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING AND ESSENTIAL REQUIREMENTS OF DIFFERENT TYPES OF MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING SYSTEM 3 APPLICATIONS OF MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING: 3 MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING VS. FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING: 4 DIFFERENT METHODS USED FOR MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING REPORTING 5 COOPERATION AND PARTICIPATION OF EXECUTIVES REQUIRED BY VARIOUS DEPARTMENTS: 6 ORGANIZATIONAL PROCESSES IN KHAADI. 6 DIFFERENT TYPES OF MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING REPORTS. 6 EVALUATION OF BENEFITS OF MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING SYSTEMS AND THEIR APPLICATION WITHIN AN ORGANIZATIONAL CONTEXT 7 ACCOUNTING REPORTS FROM THE MANAGEMENT AND THEIR INTEGRATION WITH KHAADI. 7 LO2 APPLY A RANGE OF MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING TECHNIQUES 7 PRESENT COST CALCULATIONS TO PREPARE AN INCOME STATEMENT USING MARGINAL AND ABSORPTION COSTS.MARGINAL COSTING: 8 LO3 EXPLAIN THE USE OF PLANNING TOOLS USED IN MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING 16 CASH FLOW FORECASTING: 17 FORECASTING TECHNIQUES: 18 TWO FINANCIAL PROBLEMS FACED BY THE BUSINESS AND SLOUTION TO THOSE PROBLEMS. 18 TRACK THE SPENDING AND ADJUST AS NECESSARY. 1 19 FINANCING GOALS TO SOLVE THE PROBLEMS ARE EXPLAINED IN D3. 19 LO 4 COMPARE THE ORGANIZATIONS ARE ADAPTING MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING SYSTEMS TO RESPONSE TO FINANCIAL PROBLEMS 19 FINANCIAL INDICATORS: 20 REVENUE RATIOS 20 NON-FINANCIAL INDICATORS: 22 ANALYSE HOW IN RESPONSE TO FINANCIAL PROBLEMS MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING CAN LEAD ORGANIZATIONS TO SUSTAINABLE SUCCESS 22 FINANCIAL CONTORTS POINTS 22 LO3&4 23 DEVALUATE HOW PLANNING TOOLS FOR ACCOUNTING RESPOND APPROPRIATELY TO SOLVING FINANCIAL PROBLEMS TO LEAD ORGANIZATIONS TO SUSTAINABLE SUCCESS 23 TURNAROUND MANAGEMENT SOCIETY 2014 23 CONCLUSION: 24 REFERENCES 26 2 Introduction The report explains the various management accounting systems and the essential components of sound business operations that should be integrated to management accounting reporting. It also provides a meaningful discussion of management accounting and its techniques as more of a planning and measurement tool for the entire company to assess its achievement. It will give a better understanding of the same management accounting system. It frequently involves creating an income statement using marginal costing and cost of absorption. This study would also examine how different planning techniques are used as a gauge of organizational performance for budgetary management. This should help the client understand how many planning resources were used to prepare and forecast budgets. A comparison is made to demonstrate that companies should use accounting management to respond to financial problems. This would provide a better understanding as to how management accounting techniques develop organizational strategies and plans for consistent application as well as implementation. Khaadi is also involved in computer-aided production, one of the medium-sized clothing manufacturing companies in the Pakistan as well in Lo3 and Lo4 two multinational companies are discussed Honda and Toyota. Management Accounting and essential requirements of different types of management accounting system “Accounting management refers to the understanding, assessment, definition and reporting of financial accounting and cost accounting information. Accounting management supports industry managers in policy development, decision-making and day-to-day activities of the business”. i (Dr. Suhas Mahajan, Management Accounting, 18 December 2018) Applications of management accounting: Budgeting and Planning: Managers use management accounting analysis to decide what to produce, how much to sell, how much to pay to meet production costs, and how much to earn significant profits. They must also organize the funding of initiatives, the management of funds, etc. For the business's operations to continue to run smoothly, this is crucial. Capital planning or master financial planning are two essential matters in this profession which will explain. Decision Making: If managers have to assess to choose whether or not start a big project, they need financial reporting data from management to measure the advantages of multiple opportunities and determine which one to use. Somehow mangers generally use appropriate costing techniques. Measurement of Performance: In order to determine the business's performance, managers must match the real operating outcomes with budget figures. They use managerial accounting techniques such as normal costing to verify the 3 accuracy of specific projects. They then make improvements in all those units that are not doing well (xplaind, Mar 18, 2019). Accounting management's key roles and concepts are also described. Influence: Interaction is the primary source of great understanding. Accounting department are involved with better Interaction if it increases an option of all relevant information as of the different stages of public policy. It allows for logical thought and decision making to be likely to succeed. Relevance: Report can be essential. Management accounting measures its best appropriate data which can boost the user's decision-making efficiency and achieve maximum use of their decision-making style or system. Value Generation: Analysis of the impacts. Accounting management recognises assessing data when optimizing possibilities together with the direction of importance generation & efforts on price, threat and price generation possibilities. Trust: Instill faith in Khaadi. While upholding social and policy-making standards, it is crucial that the authorities involved in accounting management operations are knowledgeable, moral, and accountable. The decision-making process becomes more practical and accountable as a result. (Margaret Woods, 2017, p. 121) Management accounting vs. financial accounting: Main variations the following topics will be addressed among both management and financial accounting: Primary Users: Management accounting is primarily used internally for managers and staffs, while external purchasers are concerned with financial accounting, involving investors, lenders, banks, etc. Set of regulations: Beneath management accounting, neither implementation of accounting values or outside guidelines are enforced while Financial accounting covers variety of company laws and regulations. Sources: In management accounting, financial and non-financial records can be used, however financial accounting does use financial data from its company ( Khaadi ) main transaction-based accounting system. Nature: The definition to data in management accounting is largely historical, present and forward-looking, Whereas the source and purpose of every data has been traditionally linked in previous results of financial accounting 4 (Dr. Suhas Mahajan, Management Accounting, 2018) Different methods used for management accounting reporting The different forms in accounting management systems & the function of integrating to different structures related to Khaadi is covered. These last two management accounting systems are also described as discussed as follows including the main criteria: Job costing system: It is a method for allocating production rates to every individual product while controlling costs. Unless the products are identical, Khaadi could use this system that keeps control of an order costs. Certain method of accounting for work expenses includes. Receiving enquiry: Buyers have always been confused regarding the possible value of the fabric. Its cost of both the product as well as the time necessary to complete the Khaadi order. Estimate price of job: A work cost are managed by auditor of Khaadi, recognizing the wants and needs of the service provider. Order receiving: Unless the cost is permitted to a purchaser, the request will also be put in Khaadi. Production order: To initiate a production method, a request of distribution being set. Cost recording: Throughout the manufacturing process, for every cost object is widely reported. Completion of job: Once done, the invoice is sent to the account manager for all the final cost of the job. That comparison is based on price estimates. Price optimizing system: A rate optimization technique is being used to detect its prices in resources. Use the pricing optimization configuration to simultaneously verify various sales quantities. This technique will assist in calculating the volatility in supply at various Khaadi outlets. By carefully observing perspectives on various sales for more than just the client group pricing, Khaadi's specific system may now be applied. Khaadi has also utilised this type of accounting management system, despite the fact that it will support the business when deciding on advertising rates, genuine pricing, or cost-saving strategies. The pricing management method aids in establishing factors like lifecycle, class targets, or competition cost when determining prices for goods inside the Khaadi. Cost accounting system: That system will help the Khaadi predict a price of the product while the corporate efficiency, 5 production and cost management can be analyzed. Its two actual cost accounting systems are often the work order costs as well as the process costs. Their two key features of this effective cost accounting system are. Cooperation and participation of executives required by various departments: This will facilitate sufficient co-operation and involvement into the process of accounting that can help direct management throughout the correct assessment of manufacturing costs. Flexible and simple: It should also be adaptable or simple to understand and formulate a method designed to accounting. It should also identify numerous users i' requirements as well as adapt to Khaadi specific requirements. Inventory management system: Such method in accounting management system are completely compatible with about the control, management in Khaadi also non-capitalized stocks. Organizational processes in Khaadi. With such a type of system can often be implemented through achieving effective stock control within the business and by time of purchase. The two essential elements are. Strategies foreseen and replenished: It helps the Khaadi control and schedule the firm expense needs in time. Inventory management physically & monetarily: With this, multiple advantages are achieved, like cost savings and effective supply chain management. Different types of management accounting reports. The multiple management accounting reports assist management in preparing appropriate management reports that depend on the predictions to make sensible strategic decisions. Khaadi have reliable quantitative and financial info to managers. The different management reports and their advantages are addressed in the following paragraph. Comments ion results: The differences measured by comparing the real results with the forecast results are examined and data is described in the performance report. These are usually delivered per year. Indeed,they could be designed daily or weekly in Khaadi. Order information report: A form data report did help the administration to even see the patterns in Khaadi quickly and accurately. Various kinds of documents ready for such failure to report help coordinated workplace practices to achieve decreased placement costs via tactical plan forecasting. Khaadi situation or opportunity reports: A statement is programmed with senior managers to recognize the specific outbreak well. Actually, attempting to begin preparing the scenario and likelihood plan which is more excellently drafted works to help owners to make important financial judgements about either the events or their observation in Khaddi. 6 Evaluation of benefits of management accounting systems and their application within an organizational context Three benefits of management accounting system in context of Khaadi. System Advantages Price optimizing system of Khaadi (1) Khaadi may assess consumer attitudes on the basis of different prices (2) Helps boost operating profit at best prices (3) This allows consumer segmentation. (1) Inventory Management System of Khaadi Khaadi use this system to address effectiveness of all its inventory demand. (2) Then this will increase productivity, efficiency and to save resources and time. Accounting reports from the management and their integration with Khaadi. Performance reports: Implementing such Khaadi management and leadership operations testimony can inspire managers and serve as the cornerstone for long-term manufacturing, which can lead to cost reductions and healthy profits even in the face of rising expenses. Type of reporting Integration with organizational processes Order information report Introducing organizational methods with Khaadi by such monitoring can also provide a summary to public relations order information towards managers to produce different statistics to track and meet customers’ order in budget. Business situation or opportunity report Khaadi will be able to integrate business operations with any of these types of things. Administrators to evaluate situations critically and also to act on the decisions appropriately. LO2 APPLY A RANGE OF MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING TECHNIQUES What is cost? & explain different types of costs? Price relates to such money value used only to produce something and represents the monitoring of goods, capital, actions, threats, use of time and facilities, and the ability to produce and supply the product or service has been missed (Drury, i2013). 7 Demonstrate the specific costs as follows: Fixed and variable costs: Fixed costs are likely costs that remain constant over a specific level of output and do not rise or fall. As a result, just the salary rise reduces the modified value for each unit of the same product. Rent, depreciation, and other terms have a fundamental explanation. A variable value is just a cost that varies depending only on the variation of a certain production. It also has a direct relationship to the market because it grows and shrinks as the level of production changes. For instance, materials, labor, and so on. (Weygandt, et. al., i2015). Historical and replacement costs: This may be the sum of money pay in taxes at the time of reservation and which is known as just a source of personal accounts. The cost of replacement is a market value usually taxable for the trade of a resource. Opportunity and outlay costs: Expenditure as well as real expenses are the real and actual damages caused by Khaadi to machinery, employees, tools, etc. These expenses are described in the payment processing but are based on the principle of accounting costs. The cost of capacity, on the other hand, represents a cost by foregone income and select that next good option. Its value concept refers for long-term investments or capital budgeting judgments (Novas, iet. ial., i2017). Avoidable and unavoidable costs: The part of the price that cannot be avoided must be managed and reduced by limiting business operations associated with certain costs, thus Khaadi by managing those costs the manager involved The eventual cost, on the other hand, refers to costs that are recognised as fixed costs and cannot be minimised by scaling back business operations. For instance, perfect computer efficiency would come at a price. Total, average and marginal costs: A title's overall cost is determined by the fact that it really comprises a number of goods that are utilized in manufacturing. These products can be either variable or constant, and are referred to as total costs, or they can be average costs for each product. Without the accrual of additional unit value, the net cost or expense of a net unit generated. Incremental and sunk cost: Incremental costs are also defined when differential costs caused by changes well intothe level of financial operation or the essence of that same activity. This is expressed through calculating its costs in generating units in manufacturing. Hidden expenses were expenses who do not change the situation or remain in place Sunk cost was the part of the accrued expense and therefore cannot been returned. Sunk costs are not important to judgmentmaking criteria since they are past cost (Manyaeva, iet. ial., i2016). Present cost calculations to prepare an income statement using marginal and absorption costs. Marginal costing: Marginal costs can only be described here just for tactical judgment-making reasons as accounting system where the variable costs are assigned to a cost unit. Nevertheless, the total contribution was fully accounted by the fixed expenses for the entire length (Delis, i2015). 8 This can be defined as cost for a production manufactured marginal and last unit. It cost method is not the same as cycle costing or job costing, however it is a simple tactic for evaluating cost information chiefly through handling efforts to determine the impact in adjustments of manufacturing as well as level of output ion profits. In the Pakistan, the marginal costing process is common and involves the idea of financial contribution. INCOME STATEMENT (absorption costing) $ Sales 367200 (1200x306) Less: cost of sales 0 Opening stock 0 54600 Production cost (1400x39) (7800) Closing stock (46800) (200x39) Gross Profit 320400 Under/over (1000) absorbed overhead (W2) 319400 Gross profit Less : Non – Manufacturing (160000) Varaibale (60000) Fixed (50000) 159400 W2 Over/under absorbed O.H Fixed P.O.H 159000 9 16000/30000=5.3 5.3x30000=159000 160000 Actual 1000 Under absorbed INCOME STATEMENT (marginal costing) TOTAL $ Sales ( 1200x 306) 367200 Less: cost of sales 0 Opening stock Production cost (W1) 37800 (1400x27) Closing stock (5400) (32400) (200x27) Gross Contribution 334800 Variable POH (60000) contribution 274800 Variable (120000) NON Production Fixed POH (160000) Adminand distribution (50000) (210000) (55200) Profit/loss LIFO and FIFO Issue FIFO Method LIFO Method 10 Materials In most businesses, the actual flow of There are few businesses where the flow materials follows FIFO, which makes oldest items are kept in stock whiler this a logical choice. Inflation newer items are sold first. If costs are increasing, the first items If costs are increasing, the last items sold are the least expensive, so your sold are the most expensive, so your cost cost of goods sold decreases, you of goods sold increases, you report report more profits, and therefore pay fewer profits, and therefore pay a a larger amount of income taxes in the smaller amount of income taxes in the near term. Deflation near term. If costs are decreasing, the first items If costs are decreasing, the last items sold are the most expensive, so your sold are the least expensive, so your cost cost of goods sold increases, you of goods sold decreases, you report more report fewer profits, and therefore pay profits, and therefore pay a larger a smaller amount of income taxes in amount of income taxes in the near term. the near term. Financial There are no GAAP or IFRS IFRS does not all the use of the LIFO reporting restrictions on the use of FIFO in method at all. The IRS allows the use of reporting financial results. LIFO, but if you use it for any subsidiary, you must also use it for all parts of the reporting entity. Record There are usually fewer inventory There are usually more inventory layers keeping layers to track in a FIFO system, since to track in a LIFO system, since the the oldest layers are continually used oldest layers can potentially remain in up. This reduces record keeping. the system for years. This increases record keeping. 11 Reporting Since there are few inventory layers, There may be many inventory layers, fluctuations and those layers reflect recent pricing, some with costs from a number of years there are rarely any unusual spikes or ago. If one of these layers is accessed, it drops in the cost of goods sold that are can result in a dramatic increase or caused by accessing old inventory decrease in the reported amount of cost layers. of goods sold. FIFO (calculation) SCENARIO 3 A business had opening stock valuation going on. The following receipts and issues were recorded in May: Date Transaction Unit Cost Units £ Amount £ Purchased/(Sold) January 1 Opening 700 10 7000 12 1200 Inventory January 3 RECEIVE 100 January 8 ISSUE (500)W1 January 9 RECEIVE 600 14 8400 January 15 RECEIVE 200 15 3000 January 17 ISSUSE (400)W2 (4600) January 27 ISSUSE (100)W3 (1400) January 31 Closing Inventory 600 11800 (5000) W1 Value of sales January 1 500x10 5000 W2 Value of sales 12 January 19 200x10 2000 January 100x12 1200 100x14 1400 4600 W3 sales value 100x14 January 27 1400 W4 Value of closing stock January 1 January LIFO (calculation) SCENARIO 3 A business had opening stock valuation going on. The following receipts and issues were recorded in May: Date Transaction Units Unit Cost Amount 700 10 7000 12 1200 Purchased/(Sold) January 1 Opening Inventory January 3 RECEIVING 100 January 8 ISSUE (500) W1 January 9 RECEIVING 600 14 8400 January 15 RECEIVING 200 15 3000 January 17 ISSUE (400) W2 (6200) January 27 ISSUSE (100) W3 (1400) January 31 Closing Inventory 600 (5200) 14 W1 13 6800 Sales value January 100x12 1200 January 400x10 4000 200x15 3000 200x16 3200 400x14 1400 W2 sales value January 27 W3 Value of closing inventory January Standard cost overview The standard cost is the substitution of the actual cost in the accounting records. The differences are then recorded to show the difference between the expected costs and the actual costs. This approach represents a simplified alternative to cost overlay systems, such as FIFO and LIFO, in which large amounts of historical cost information must be kept for stock items in stock. Standard cost variance The variance is the difference between the actual cost and the standard cost at which it is measured. A difference can also be used to measure the difference between actual sales and expected sales. Thus, analysis of variance can be used to analyze income and expenditure performance. SALES PRICE VARIANCE Actual quantity x actual price – actual quantity x standard price 230 x 300 – 230 x 357 69000 – 82110 13110 (A) SALES VOLUME PROFIT VARIANCE Actual quantity x standard price – standard quantity x standard profit – 230 x 63 – 14490 14 200 x 63 12600 1890 (F) SALES QUANTITY VARIANCE Actual quantity x standard price – standard quantity x standard price – 230 x 357 200 x 357 – 82110 71400 107010 (F) DIRECT MATERIAL RATE VARIANCE Actual quantity x actual rate – actual quantity x standard rate – 230 x 104 230 x 63 – 23920 14490 9430 (A) MATERIAL EFFICIENCY VARIANCE Actual quantity x standard price – standard quantity x standard price 230 x 63 – 200 x 63 14490 – 12600 1890 (A) DIRECT LABOUR EFFICIENCY VARIANCE Actual hours x standard rate – standard hours x standard rate 230 x 63 – 14490 – 158 x 63 9954 4536 (F) DIRECT LABOUR RATE VARIANCE Actual hours x actual rate – actual hours x standard rate – 230 x 104 230 x 63 – 14490 14490 9430 (A) V.P.O.H VARIANCE Actual fixed O.H – budgeted fixed O.H 10,000 – 15 18900 8900 (F) Reconciliation of actual profit with budgeted profit. $ $ $ 000 000 000 FAV Adv 8300 Budgeted profit Sales volume profit variance 10710 Sales price variance (13110) Material price (9430) Material usage price (1890) labor rate efficiency 2400 Fixed OH 8900 Total 22010 (24430) (2420) 5880 Actual Profit /Loss RECOMMENDATION: Do the review only if there seems to be a clear case of huge costs. Investigate its analysis except in areas under which long-term costs are also not expected to change significantly (such as administrative functions) Carry out the study for purchased businesses to know regarding their cost structures and finish any furtherresearch. LO3 EXPLAIN THE USE OF PLANNING TOOLS USED IN MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING Explain the advantages and disadvantages of different types of planning tools used for budgetary control In business enterprises, budgeting tools were used to handle, plan or predicted its budget of the products or services, that is then introduced and tried to achieve targeted goals and results.Budget improves to facilitate the planning of operations by pushing managers to recognize how 16 circumstances could change or what steps must be taken now and empowering managers to consider issues before they occur. This also helps to arrange the Khaadi activities by convincing managers to look at interactions from their own operations from those of other departments. Advantages Disadvantages Coordinates activities across Khaadi There is a major problem with the Khaadi Departments of budgets Mechanical and rigid application Translate into action strategic plans. May discourage workers in Khaadi because of sudden loss of interference They specify the assets, revenues or tasks needed If the plans were implemented Khaadi the to support the growth strategy wrongly in workers will not of the expense budgeted and Khaadi know the reason. will not agree. Provide a good record of logistical actions in May contribute to perception of Khaadi would disparity in Khaadi helps to improve employee straggle for money and Khaadi. A restrictive communication in politics in Khaadi improve budgetary system levels of ambition or creativity distribution of resources by explaining eliminate almost impossible for receive money on new low and justifying all inquiries in Khaadi making ideas in Khaadi it. Provide re allocation framework for corrective measures in Khaadi (unknown, 2017; Michale, 2018) Some methods that could be used in a structured/ Budgeting Cash Flow Forecasting Budgeting: (Michale, 2018) When Khaadi know that plans for the future should mean, Khaadi would have to determine when to finance these plans preparing a plan is a necessary means of keeping the costs under control. Cash Flow Forecasting: Thus, financial planning is such a valuable resource, a cash flow forecast is much more relevant in terms with its definition It helps the business owner like Khaadi to identify bank finance peaks. A forecast of cash flow (“again if properly prepared”) can help identify the limitations to handle growth. Different types of Budgeting that is undertaken in a Khaadi are as follows: Khaadi financial budget applies towards calculating the summary of revenue, an assets and liabilities as well as the statement of income 17 towards coming years.Corporate Budgeting makes reference to a planning and implementation of such a Khaadi financial budgets on its operations.Cash budget leads to estimating for such a set period of time all expected money transactions & cash payments of the a Khaadi. Forecasting Techniques: 1.Qualitative Forecast: Based upon the assessment, its contributions to that of the forecasting system were collected across individual departments and different Khaadi workers. It utilizes a methodology outlined that obtain avoiding prejudice the predictions of experienced staff / executives in Khaadi 2.Time Series Forecast: It requires monitoring some particular factor in Khaadi through duration or creating forecasting programs based onto the variable's predicted motion throughout the upcoming cycle. The technique becomes helpful in Khaadi to research variables including repeated trends or seasonality with / without. 3.Causal Forecast: Some factors which cause motion in Khaadi factor were studied across time throughout this system. Examination of regression is really the best system of causal forecasting In Khaadi. TWO FINANCIAL PROBLEMS FACED BY The BUSINESS AND SLOUTION TO THOSE PROBLEMS. Budgeting Problems: They may also have problems with budgeting unless they constantly run out of money before even the month runs out and they find themselves having to rely on credit cards to meet objectives. They think about what they earn and wonder how, even though they earn a decent salary, it does not seem to have been enough to pay the bills. It may also have a written plan it tries to follow every month, but it never appears to work. This is a major indicator which has a problem with budgeting. Create a Budget: When they don't have one yet, begin to create a budget. Its simplest way to do that is to point a finger at and modify than what they spent last month from each category. Widely known categories of budget include: Accommodation (rent or mortgage) Resources 18 Saving (emergency fund, retirement fund and sinking fund) Utilities Insurance (auto, health, and life) Medical care Transportation (car payment and/or commuting expenses) Debt service (credit cards, personal loans, home equity loans, and other credit accounts) Health care Groceries Discretionary spending (entertainment, dining out, and "extras") Most of the costs are fixed. During a month, they continue to operate the same. Others could fluctuate other than the control — use costs may vary from season to season, or the childcare provider may have increased their rates. Some are still under the power, eg discretionary expenditure as well as grocery stores. If they have to spend very little on these stuffs. Track the Spending and Adjust as Necessary. Attach all the categories which they have listed in the budget. Unless the total is more than their quarterly give- home pay, they get some tweaking to do. Somewhere, usually from such expenditures they have control under, they will have to cut. When possible, they do not want to spend very little on the savings and otherwise debt service. Recognizing that it would be flexible seems to be the key to making the budget work. They could still take the money out of one category that can be used in another category unless they spend too much. Like, they could spend some money on festival tickets, and then they'll have to change the fund to cover that additional amount they spend in either the entertainment / discretionary category. Case study: Financial management and business success – A guide for entrepreneur’s management Financing goals to solve the problems are explained in D3. LO 4 Compare the organizations are adapting management accounting systems to response to financial problems Using benchmarks, financial and non-financial key performance indicators, & budgetary targets to identify financial problems and financial variances. Explain by using benchmarks and budgeting targets help identify financial problems and financial variances. Enterprise advances have emerged over the past few decades, whereby data is now seen as the most public resource of analyzing the Honda and Toyota stock price, acknowledging the financial problems associated with either the disparities discovered in the standardized range of performance 19 indicators. All of this reflected with the use of numerous leadership analysis strategies which set the benchmarks, use financial / non-financial result indicators that analyze the performance of the Honda and Toyota illustrating what it focuses on both the long-term profitability aspect. Use of such budgetary control throughout the design and implementation of its multiple business tasks of Honda & Toyota should allow the organization and keep the expectations for both the chosen data in order to meet the firm's objectives. (Parmenter, i2015). Key performance metrics are financial and non-financial factors used by most businesses like Honda and Toyota that demonstrate progress in achieving lengthy-term goals. Some of them will be listed below: Financial Indicators: Basis Liquidity, Solvency, Debt Ratio Key Performance Responses or use in identify indicators financial problems and variances Current Ratio Indicates payment ability. Short-term debts ion short-term assets in Honda and Toyota. Quick ratio Adequacy in assets for quickterm debt in Honda andToyota Working capital The skill of the Honda and Toyota.to stay solvent once the day to day criteria are available. Debt to equity A capital structure Honda and Toyota indicates the proportion of equity debt which is only like to finance assets. Profitability ratios Accounts payable to Percentage or accounts payable at inventoryGross profit the stage of both. The Honda and margin Toyota Inventory (Parameter, 2015). Selling cost Administrative Both Honda and Toyota cost, Total operating cost percentage left paying its working costs and to make a profit. Net profit margin Like to set benchmarking targets and budgeting in Honda and Toyota Revenue ratios Sales Indicates the both Honda and 20 Toyota net income. Include monitoring in part of Calculation of revenue through a CRM system that provides the information required to influence it in Honda & Toyota. (Bai & Sarkis, i2014). Sales growth Assessment and advancement of industry innovation. 21 Non-financial indicators: Management of human resources Employees of Honda and Toyota also began to look like some kind of major asset throughout today's world but recognize this as an important element to ensuring that company's success. Which comprises turnover for workforce, percent in approved job opportunities, suitability studies, etc. (Podgorski, i2015). Product and service quality Its been found that perhaps the issues identified in the both Honda and Toyota product reliability of the firms get a long-term effect in its sustainability or natural consequences in customer. Brand awareness and company profile Its scope of both the brand as well as industry profile can also be their long-term success, growth. Should include measures like wide allegiance, acknowledgement, performance but also characteristics of a trademark and product. (Bai & Sarkis, i2014). Analyse how in response to financial problems management accounting can lead organizations to sustainable success The role of management accounting in sustainable success of a business organization can be summarized in points discussed below: Financial contorts points The managers will be required to support the strategic and sustainable goals with the strategies and policies to be developed Honda and Toyota. Management accounting tools and techniques like marginal costing, standard costing, break analysis etc. will help Honda and Toyota in integration of sustainable matters into the various decision-making processes. Management accounting helps in the production of Honda and Toyota reports that include information ion sustainability impacts which will help in understanding pricing and budgeting decisions and strategic planning. Honda and Toyota Management Helps in development of reporting strategy that will integrate sustainability issues which in turn will allow reporting of financial and non-financial information. By developing effective strategies and systems which require effective and timely reporting, which also requires disclosure of all financial positions that are governed and owned responsibly by those who hold them Honda and Toyota. Strategic planning works with those of the development and business strategy decisions onto the types of markets, industries where the company operates which involves competitive market 22 performance decisions. Thus, strategic planning utilizes financial data from multiple frameworks e.g. costing, financial planning, performance processes and other internally and externally organizational sources (Noordin, et. al., 2017). Company auditors from Honda and Toyota. These techniques can be implemented using different techniques usingplanning as well as control systems mentioned below. Budgeting systems: Similar programs have to be linked to long-term budget development strategies which can sustain organizational tactics. Performance measurement systems: This could be used to correlate actual results to relevant expenditures or various certain goals that rely on organizational policies. (Rothaemal, i2015). Rules governing banks, investment firms, and insurance firms were also financial regulations. They protect you against financial risk and fraud of Honda and Toyota. Law is an issue if it inhibits its free market. That’s the most efficient way to set prices. It increases business efficiency as well as reduces buyers ' costs. It distorted the economy by wage price controls in the 1970s which induced stagflation. Regulations can dampen economic growth. Rather than investing in factories, machinery, even assets, businesses need to use their resources to follow federal law laws. Such rules complement its Financial Regulations and have been limited by them. LO3&4 Devaluate how planning tools for accounting respond appropriately to solving financial problems to lead organizations to sustainable success 50% within five years, start-ups fail (OECD, Entrepreneurship at a Glance, 2015) 36% Inadequate financial management is responsible for business failures Turnaround Management Society 2014 Different strategy methods assist managers recognize financial challenges for both financial management tools and techniques. Its information collected from these techniques in preparing sort of takes tactical moves as well as investment decisions which can cause to a success of both the organization. A method will be intended to implement tracking or even decisions could be taken properly. Review as well as interpretation in financial data may help to external reporting, that in turn can ensure sustainable growth for both the company. The business will have a significant impact in its climate issues with both the implementation of planning techniques. Management accounting as closely connected with different levels in preparation, decisions throughout the waydescribed below: Planning and controlling: This would be the key component in management accounting, as well as Honda and Toyota can adopt plans to build the path both the firm as well as the control unit to make 23 sure that some operations are conducted to accordance with those of the plans (Manyaeva, et. al., i2016). Implementing plans: Management teams are now using planning techniques and collect essential information on even a daily basis, eg forecasts, performance ratings products cost, to meet the goal set during budget process. This really allows that management at Honda and Toyota should assign of each process as per the needs on each unit or department. Competitive edge: Would see that, through both the strategies and goals, the excellently run businesses focus on building the competitive advantage of both the business. A business develops a strategy through the use of accounting to management strategies strive to achieve the competitive market added benefit and therefore maintain low cost and product image. (Rothaemal, i2015). Those are protecting you toward financial risk as well as fraud. But they have to be balanced by the need to allow the efficient operation of capitalism. Financial strength. That you are going to need to make sure you can learn how to deal like your business will be less successful financially than you assume, or if you face a sudden one-off cost. Financing cost. They would like to reduce financing costs, whether it really requires the interest you pay or even the share of the company you abandon for funding. Financial flexibility. For e.g., the company should always be flexible so that you can get extra funds to help you seeknew future opportunities. Business control. You're going to have to maintain market leverage, including creditors and investors having as few constraints as feasible about what you can do; and now you're going to want to limit their right to a part in decision making. Financial risk. That you are going to have to restrict that personal financial risk as well as the risks towards any family and friends which have invested in the company, reducing the risk of losing as much as you can handle when things go bad. Personal finances. Any investment strategies will consider the amount of business income that need and the degree in which you are prepared to reduce the income to reinvest throughout the business. Business strategy. The ability to generate funding can decide how much you can afford to invest in development, as well as whether you have to concentrate on cost control and cash generation. Conclusion: It can include a fact that various management accounting methods and methods help a company to obtaining as well as retrieving its information essential for the company managers to perform their duties. Honda and Toyota may very well adapt & integrate such methods but also strategies for the sustainability & growth throughout the manufacturing industry therefore generates decision-making leaders of data-driven insights as well as allows that reliability for decisions to also be enhanced. Using marginal costs and absorption costs also helps companies to plan financial statements that reflect to customer priorities Implementing specific management accounting tools, frameworks helps managers towards good business techniques, plans which can focus from both long-term 24 sustainability of the business whilst maintaining profitability as well as success. so, it allows an organization could prepare various financial reports onto the basis of reliable information, which will in turn ensures the firm's examination, quality of legalities and strategy. 25 References Armstrong, S.O., Amorosi, S.L., Garfield, S.S., & Stein, K., 2014. Medicare Budget Implications of Left Atrial Appendage Closure for Stroke Risk Reduction in Non- Valvular Atrial Fibrillation. Circulation, vol. 130,no. 2, pp. A16185-A16185. Bai, C., & Sarkis, J., 2014. Determining and applying sustainable supplier key performance indicators.Supply Chain Management: An International Journal, vol. 19, no. 3, pp. 275-291. Chenhall, R.H., & Moers, F., 2015. The role of innovation in the evolution of management accounting and its integration into management control. Accounting, Organizations and Society, vol. 47,pp. 1-13. Collier, P.M., 2015. Accounting for managers: Interpreting accounting information for decision making.John Wiley & Sons. Delis, M., Iosifidi, M., &Tsionas, E.G., 2014. On the estimation of marginal cost. Operations Research, vol. 62,no. 3, pp. 543-556. Drury, C.M., 2013. Management and cost accounting. Springer. Fagundes, V.O., Zaniboni, R., & Garcia, R., 2017. Cost Estimate Methodology in procurement processes of ME. InVII Latin American Congress on Biomedical Engineering CLAIB 2016, Bucaramanga, Santander, Colombia, October 26th-28th, 2016 ,pp. 177-180. Hart, J., Wilson, C., & Fergus, C., 2012. Management Accounting: Principles & Applications, New South Wales: Pearson Higher Education AU. Hugh, C., David, H., & Ellis, J., 2016. Management Accounting-Principles and Applicat io ns. Kaplan, R.S., & Atkinson, A.A., 2015. Advanced management accounting. PHI Learning. Manyaeva, V., Piskunov, V., &Fomin, V., 2016. Strategic Management Accounting of Company Costs. Noordin, R., Zainuddin, Y., & Mail, R., 2017. Competitive Strategy, Elements of Strategic Management Accounting Information, and Performance Consequences-A Conceptual Link. Journal AkuntansidanBisnis, vol. 8,no. 1. Novas, J.C., Novas, J.C., Alves, M.D.C.G., Alves, M.D.C.G., Sousa, A., & Sousa, A., 2017. The role of management accounting systems in the development of intellectual capital. Journal of Intellectual Capital, vol. 18,no. 2, pp. 286-315. Parmenter, D., 2015. Key performance indicators: developing, implementing, and using winning KPIs. John Wiley & Sons. Parmenter, D., 2016. The Financial Controller and CFO's Toolkit: Lean Practices to Transform Your Finance Team. John Wiley & Sons. Podgórski, D., 2015. Measuring operational performance of OSH management system–A demonstration of AHP-based selection of leading key performance indicators. Safety Science, vol. 73, pp. 146-166. 26 Rothaermel, Frank T. Strategic management. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2015. Shepherd, R.W., 2015. Theory of cost and production functions. Princeton University Press. Tsofa, B., Molyneux, S., & Goodman, C., 2016. Health sector operational planning and budgeting processes in Kenya—“never the twain shall meet”. The International journal of health planning and management, vol. 31, no. 3, pp. 260-276. Weygandt, J.J., Kimmel, P.D., &Kieso, D.E., 2015.Financial & Managerial Accounting. John Wiley & Sons. Robinson, T.R., Broihahn, M.A., Henry, E. & Pirie, W.L. 2012, International Financial Statement Analysis Workbook (CFA Institute Investment Series), 2. Aufl.;2;2nd; edn, Wiley, Hoboken. Ruckova, P. 2015, "Dependency of return on equity and use of finance sources in building companies in V4 countries",E+M Ekonomie a Management, vol. 18, no. 3, pp. 73. Schmidlin, N. 2014, The Art of Company Valuation and Financial Statement Analysis: A value investor's guide with real-life case studies, 1st edn, John Wiley & Sons Inc, GB. Yakhshibaev, G. 2011, "Sources Of Short-Term Finance And Investment Opportunaties", European Journal of Business and Economics, vol. 2. Zaman, H. & Akbar, M.I. 2013, "Exploring non-traditional sources of development finance: The case of remittance in Bangladesh", Progress in Development Studies, vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 105-116 Bhimani, A., Horngren, C.T., Datar, S.M. (2013), Management and Cost Accounting. Financial Times Prentice Hall, Harlow. Drury, C. (2012). Management and Cost Accounting (8th ed.). Andover, Cengage Learning EMEA. Dyson, J. R. (2010). Accounting for non-accounting students (8th ed.). Harlow, Financial Times Hansen, D.R. and Mowen, M.M. (2006), Cost Management: Accounting and Control, Thomson Higher Education, Ohio. Sangster, A. and Wood, F. (2012), Frank Wood's Business Accounting Volume 1, Financial Times Prentice Hall, Harlow. Sangster, A. and Wood, F. (2013), Frank Wood's Business Accounting Volume 2, Financial Times Prentice Hall, Harlow. (Noordin, et. al., 2017). 27 The report of the international company and they follow those accounting systems https://www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/320187/000032018718000142/nke-5312018x10k.htm https://www.bloomberg.com/profile/company/TFCOZ:JP Honda financial report Please follow the link. https://www.atlashonda.com.pk/financial-reports/ 28