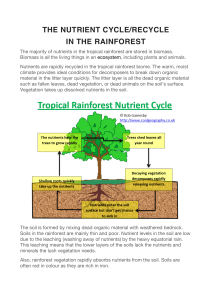
Example of a Small-Scale Ecosystem in the UK: Epping Forest, London TASK: Highlight abiotic in one colour and biotic in another Animals found in a woodland include many species of insects and birds, and mammals such as rabbits, squirrels and foxes. Plants include trees, wild flowers, grasses, mosses and algae. They provide food and shelter for many animals. Location Sunshine and rain are needed for photosynthesis, so they are essential in the ecosystem. Other climatic elements such as wind and frost are also important. Micro-organisms such as fungi and bacteria are decomposers. They help to break down dead plants and animals, releasing nutrients into the ecosystem so they can be recycled. Rocks help in the formation of soils and rock type is important. Weathering releases nutrients stored in rocks into the ecosystem. Soils store water and contain nutrients which plants can use. Soils are home to insects and decomposers. TASK: Highlight producers, consumers and decomposers in different colours. Key Facts: • It covers an area of 2,500 hectares. It is 19km long and 4km wide. • 70% of Epping Forest is deciduous woodland • 1,600 hectares has been protected as a Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) Fungi