Excel Skills Course Material: Functions, Analysis, Display
advertisement

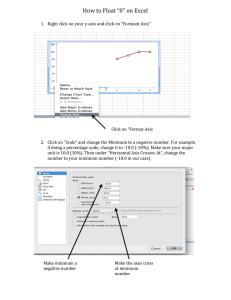
Module One: Fundamental Excel Skills Merge: Go to Alignment and Press Merge and Center ’Comma Style: Remove $ but keep in Accounting Mode =COUNT (counts the number of cells in a range) =COUNTA: to count the non-numerical AND numerical values in a range (counts the cells that aren’t empty) =SUM (summation of values) =AVERAGE Format Painter: copy style and format of a row Revenue = Volume* Unit Price Material Cost: Material Cost*Number Sold* Number per Box Fixed Cost: =SUM (Advertising + Overhead) FN--F4: Shortcut for Absolute Referencing Income Before Tax: Total Revenue - (Total Variable Cost + Total Fixed Cost) COUNTIF (range, “argument”) to count the number of cells that meet a criterion EX. # of locations that include an extra hydration. “>0”- to show that there is a number on the range Budget Summary: Include the number of items Sales volume, selling price (in this section make different columns for each company or service, for example, in the Ocean Ziploc assignment we had both online and in-store columns for each segment) Revenue: use the sales volume*selling price Variable cost: given in the table and is a separate chart. In this chart o Material: Number of items(fixed)*Material cost(letter is fixed)*sales volume(number is fixed) o Direct labor: Drag material equation to the rest of the cells. o Total variable cost: SUM(material + Direct labor) Summary: Use all the sales volumes from all the budget sheets Module Two: Solving Problems with Statistical Analysis AVERAGE: this is how you find the MEAN MODE.SNGL: finds the most frequently occurring mode Freeze a row: if you want to freeze rows 1-3, select A4 | view ribbon | freeze panes STDEV: standard deviation. He used STDEV.S. COUNTIF: (#rejected: # of cells in range that fail to meet criteria) | COUNTIF(A4:A6,”.>=265”) | must put “” SUMIF: (rejection cost: find total rejection costs given individual production costs in an adjacent column) | =SUMIF(B4:B6,”>=265”,A4 :A6) | if B is the Temp Test (values det P/F) and A is the production cost per unit RANK.EQ: (number, ref, order) rank of the cell in this row among the range | (H1,$H$1:$H$4,1) |1 is ascending, 0 is descending - Order: 0- descending (highest to lowest), 1 ascending (lowest to highest) Ref is fixed completely When it comes to order if we see < its descending and if its > its ascending COUNTIFS: more than one criteria | how many cells are 2100<x<2110: (A4:A6,”>2100”,A4:A6,”<2110”) LARGE (SMALL): returns largest cell in range | ($A$4:$A$:,k) where k=is the rank (ex. k=2 is second largest value) LARGE (array,k) Array means column and k is rank SMALL (array k) Array is fixed and k is rank “*” is a wildcard (example finding BLU) RAND Functions =RAND() gives # in [0,1) | RANDBETWEEN(1,5) will be integer (no deci) Example: Rand in [25,200): RAND()*175+25 Example: For a REAL NUMBER (deci) between bottom and top: =lo+(hi-lo)*RAND() Purchase Amount ($250-350): (350-250)*RAND()+250 is a random value between $250 and $350 ROUND: if you want ^ to have two deci, then ROUND((150*RAND()+250,2),2) Generate A Real number (continuous number) between Bottom and Top (High -Low)*RAND()+Low Round A number ROUND((high-low)*RAND()+low, 2) Count if: =COUNTIF(range, criteria(this should be in quotation marks “” with an = to the statement but it could also be a cell!, if it is a cell it doesn’t not need an = sign, if it is a number use >,>=,<,<= or =) Countifs: =COUNTIF(range, criteria(this should be in quotation marks, if it is a statement put an = sign, if it is a number use >,>=,<, <= or =), range, criteria 2) Sum if: =SUMIF(range, criteria(this should be in quotation marks, if it is a statement put an = sign, if it is a number use > or <),second range(numbers correlated to what you are trying to find)) Rank: =RANK(first cell(should be , Range(fixed),0 or 1(0 ranks highest value and 1 ranks the smallest value) Module Three: Effective Data Display Change bars into shape: Copy and paste any shape you create where the bar is Thicken bar and decrease white space: FDS, 3, gap width Add line on vertical axis: select vertical axis text, format axis, 1, solid line Change domain or range: FDS, select axis, 4, bounds Two outputs that have very different ranges (secondary scale): chart design, change chart type, combo, chart design-format, chart area drop down: select what you want as the secondary axis (smaller range), FDS, select secondary bars, secondary axis Sparklines : Go to Insert and Press Sparklines it is used to make small lines and graphs on cells Chart Design: Chart Elements HLC: date and HLC in that order Reformat date axis: format axis, axis options, 4, axis type: date axis, number O-HLC (Candlestick): the white up bars should be green and the black down bars should be red VHLC: lots of zeros to x million: format axis, axis options, 4, display units “millions” VC-COMBO: date, volume, close | show volume on primary and closing price on secondary axis Module Four: Solving Problems with Statistical Analysis AND: all statements are true (=AND(1 st statement, 2nd statement, etc) OR: one or more statements are true(=OR(1 st statement, 2nd statement, etc) NOT: =NOT(cell that is false) -> TRUE and NOT (cell that is true) -> FALSE Conditional formatting: Home, Conditional Formatting, Classic: ‘format only cells that contain...” IF= If all statements are true then the function is this or that (=IF(three statements in total, statement, result 1, result 2, *only three statements are allowed inside function, try to use another if statement inside for more arguments) Try to separate if statements if there is more than 1! How to put a drop down menu: Data ribbon→Data validation→List→add items (use commas for each separate item) Conditioning: Make new rules (use custom when it comes to highlighting a line) Module Five: Retrieving Data for Computation, Analysis, and Reference Index: =INDEX((all the graphs given or if it’s one graph just place that here), (=MATCH(cell, range or chart),(add more matches if n eeded)) VLOOKUP: =VLOOKUP(cell, chart, column of chart that contains that information, FALSE or TRUE) Only use true if it’s an approximation Label charts! If you made an error in naming your chart go to formula ribbon→Define name→select the name and press the “-“(minus sign on it) HLOOKUP: =HLOOKUP(cell, chart, row of chart that contains the information needed, FALSE or TRUE) MATCH-INDEX: