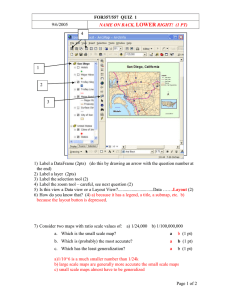
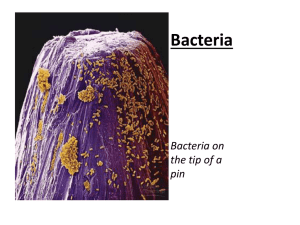
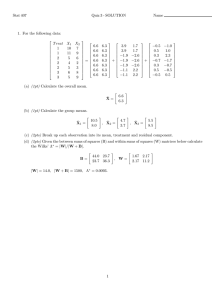
MICROBIOLOGY 1: BACTERIOLOGY GRAM POSITIVE BACILLI ANSWER SHEET 15 (GRAM POSITIVE BACILLI) NAME: CONOGANA, YETTA C. SCORE: ______________________ COURSE AND YEAR: BSMT-3A DATE: _______________________ STUDENT ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS SAQ#1: A 59-year-old male patient was admitted to Kocaeli University Hospital with a history of bilateral vision loss for five months. Bilateral severe carotid stenosis was diagnosed and carotid arterial stent placement was planned by the Radiology clinic. He had no history of any known disease, except for diabetes mellitus and hypertension for the past four and eight years, respectively. He was a taxi-driver, but had not worked for one month prior to hospital admission. During this period, he spent his time at home with his wife. On admission to the ICU, physical examination revealed the following: body temperature 39 °C; pulse rate 110/min; blood pressure 180/80 mmHg; respiratory rate 32/min. He was in a toxic condition, with abdominal tenderness, distension and rebound positivity. No skin lesion or skin infection was observed. Laboratory results were as follows: white blood cell (WBC) count 11.4 × 109/l (65% neutrophils, 20% lymphocytes); hemoglobin 12.79 g/dl; platelet (PLT) count 279 000/ul. Endotracheal intubation was performed and mechanical ventilation was started, in addition to continuous arteriovenous hemofiltration (CAVH). Cultures tracheal aspirates were obtained. The tracheal aspirate gram stain shows: 1. Describe cells and organisms seen on Gram stain. (2pts) - Short chains of large Gram-positive rods, erythrocytes, and polymorphonuclear leukocytes - B. anthracis (Encapsulated bacilli on the methylene blue stain of the mouse spleen imprint.) 1 MICROBIOLOGY 1: BACTERIOLOGY GRAM POSITIVE BACILLI 2. Growth on Blood agar shows ground glass appearance. What is most likely the causative agent? (2pts) - Bacillus anthracis 3. What are the biochemical tests to be used to identify the organism? (2pts) - Motility testing - Catalase testing 4. The confirmation of this organism is based on the presence of capsules on defibrinated sheep blood. What other method can be used for confirmation of the causative agent? (2pts) - Antimicrobial susceptibility testing 5. What is the diagnosis/disease of the patient? (2pts) - The patient has a pneumonia caused by Bacillus anthracis SAQ#2: A 6years old fully immunized male child presented with chief complaints of fever for 6 days, painful swallowing for 6 days and swelling of neck glands to ENT Department. On examination, the patient is of average built, well-nourished but looked toxic. General examination reveals multiple, enlarged, matted, sub in the left side of neck. On local examination white membrane on both tonsils and posterior pharynx was seen which bleeds on touch and difficult to remove. His chest x-ray reveals normal study. Throat swabs were taken from both the tonsils and the posterior pharyngeal wall and processed according to standard microbiological procedure. Gram stains shows: 1. Describe the organisms seen on Gram stain. (2pts) - Gram positive bacilli arranged in Chinese letter pattern (Corynebacterium diphtheria) 2. What other staining method use to identify the organism showing the bacilli with metachromatic granules? (2pts) - Albert staining 3. Give at least 2 biochemical tests used in identifying the organism. (2pts) 2 MICROBIOLOGY 1: BACTERIOLOGY GRAM POSITIVE BACILLI - Catalase testing (catalase positive) - Cystinase test (cystinase production) 4. What is the causative agent (2pts) and the disease(2pts)? - Corynebacterium diphtheria, Diphtheria bacterial disease SAQ#3: The patient was a 28-year-old Filipino male with a medical history significant for newly diagnosed human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and AIDS. he was admitted to the hospital for persistent fever of unknown origin. He was found to have HIV on this admission, and the CD4 cell count was 42/mm3. The initial workup included sputum Gram stain, silver stain, and culture, which showed only normal flora. In addition, sputum acid-fast bacillus (AFB) stain and culture were negative for Mycobacterium spp. and routine urine and blood cultures were also negative. During this admission, he was noted to have a pleural effusion, which prompted a thoracentesis. Direct Gram and AFB stains on the pleural fluid were negative, and no significant growth was detected on routine bacterial cultures. However, the AFB culture of the pleural fluid subsequently became positive at week 6. Both the AFB and modified AFB stains were partially acid fast positive. Modified AFB shows: 1. Describe the result of the modified acid fast stain? (2pts) - modified AFB stains is positive - branching of gram- positive bacilli 2. Give at least 2 biochemical tests to identify the organism. (2pts) - decomposition of casein, tyrosine, and xanthine 3. What is the causative agent (2pts)? - Nocardia asteroides 4. If the organism is weakly acid fast and does not exhibit branching, what other bacteria should be considered as causative agent? (4pts) 3 MICROBIOLOGY 1: BACTERIOLOGY GRAM POSITIVE BACILLI - Rhodococcus Tsukamurella Gordonia Dietzia spp. EVALUATION MATCHING TYPE: (7PTS) __c__1. Reverse CAMP test positive rhusiopathiae a. Erysipelothrix __d__2. diphtheriae b. Corynebacterium Bacterial Vaginosis __a__3. Butcher’s disease perfringenes __b__4. Black colonies on Potassium tellurite __f_ _5. Biological indicator for autoclave __g__6. CAMP test positive-rectangular stearothermophilus __e__7. Farmer’s lung c. Clostridium d. Gardnerella vaginalis e. Nocardia spp f. Bacillus g. Listeria monocytogenes MULTIPLE CHOICE: (8PTS) 8. Which of the following is not a characteristics of Corynebacterium diphtheriae? a. Pleomorphic morphology b. Gram-positive bacillus c. Spore former d. Nonmotile 9. To differentiate bacillus anthracis from Bacillus cereus: a. B. anthracis is a beta hemolytic on blood agar and non motile; B. cereus is nonhemolytic and motile b. B. cereus is beta hemolytic on blood agar and motile; B. anthracis is nonhemolytic on blood agar and nonmotile 4 MICROBIOLOGY 1: BACTERIOLOGY GRAM POSITIVE BACILLI c. B. anthracis produces acid from glucose and maltose; B. cereus does not. d. B. anthracis is lecithinase positive; B. cereus is lecithinase negative. 10. Bacillus cereus has been implicated in which of the following disease? a. b. c. d. Anthrax Pseudomembranous colitis Gastroenteritis Meningitis 11. On potassium tellurite medium, Corynebacterium diphtheriae produces: a. b. c. d. Beta-hemolytic colonies Enhanced pleomorphic properties Black colonies Pink to red colonies 12. What species of Corynebacterium was characterized in 1976 as a multidrug-resistant agent in a variety of clinical infections? a. b. c. d. C. diphtheriae C. ulcerans C. pseudotuberculosis C. jikeium 13. “Partial acid fastness” is a characteristic of: a. b. c. d. Listeria monocytogenes Nocardia Lactobacillus acidophilus Bacillus anthracis 14. A gram-positive bacillus isolated from the spinal fluid of a 1-month old infant is catalase positive, beta hemolytic and bile-esculin positive and exhibits tumbling motility in a wet preparation. The organisms is most likely: a. b. c. d. Lactobacillus acidophilus Listeria monocytogenes Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae Corynebacterium jeikeium 5 MICROBIOLOGY 1: BACTERIOLOGY GRAM POSITIVE BACILLI 15. Which statement correctly describes Lactobacillus acidophilus? a. b. c. d. Prefers alkaline pH range Strict pathogen Produce large quantities of lactic acid Characteristic tumbling motility 6