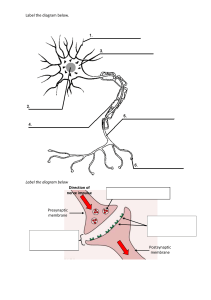
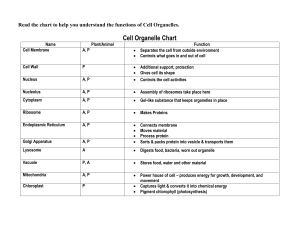
Feb 3, 2023 Animal Cell Cell- Microscopic unit made up of bubbly fat material filled with a water-based mixture of molecules and tiny particles. Organelles 1. Plasma membrane/cell membrane- outer boundary/layer of the cell. 2. Cytoplasm- material encoded by the cell membrane that includes the organelles and liquid inside the cell. 3. Nucleus- the genetic code (DNA) 4. Nucleolus- “tiny nucleus” small area in the nucleus where it is in the involved synthesis of ribosomal RNA. 5. Endoplasmic reticulum- ribosomes and other molecules that synthesize within its membrane, also manufacture that make up cellular membrane. a. Smooth ER- synthesizes lipids and steroid hormones, detoxifies harmful by-products, not surrounded by ribosomes. b. Rough ER- involved with the production, folding, quality control and dispatch of some proteins and is specked with ribosomes 6. Ribosomes- site of protein synthesis 7. Golgi Apparatus- stack of flattened sacs, receives materials from the ER, processes and then packages it in tiny vesicles for possible export from the cell. 8. Mitochondria- site for ATP synthesis and energy conversion. 9. Lysosome- “suicide bags” contain digestive enzyme 10. Microtubules- tiny hollow beams that form part of the supporting cells skeleton. 11. Cytoskeleton- gives shape to the cell, provides mechanisms for movement,, and provides attachment points for organelles. 12. Microvilli- increase the membranes surface area for more efficient absorption. (hairlike sa kilid) 13. Cilia- numerous short, hairlike organelles that propel material along the cell's surface. 14. Flagelle- single long, hairlike organelles found in sperm cells to propel them through the female reproductive tract toward the egg. 15. Vesicles- membranous bubbles formed by the golgi apparatus or by pinching inward of the cell membrane to engulf external substances. 16. Centrosomes- microtubule organizing center, is a dense area of cell fluid near the nucleus. a. Centrioles- formed by the parallel microtubule 17. Spindle fibers- a network of microtubules, extending from centrosomes during cell division, distributes DNA equally to the resulting daughter cells. Epithelial Cell 4 Basic Types Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissues 2. Connective Tissues 3. Muscular Tissues 4. Nervous Tissues These function together and cannot function without each other. Epithelial Tissue/ Epithelium- consist of sheets of cells that cover the external surface of the body and line the internal cavities, form various organs and glands and line their ducts. It is either single layer or multilayer. External and internal are different from each other. Epithelial Cells are polarized: 1. Apical surface- faces the lumen or the external environment. (ara sa pinakababaw) a. Microvilli,cilia, stereocilia 2. Lateral surface- faces the adjacent cells (center) a. Tight junction (zonula occludens), adherens junction (zonula adherens), desmosomes (macula adherens), gap junctions 3. Basal surface- attaches to the basement membrane a. Basement membranes, hemidesmosomes 4 types of Epithelium Based on Idealized Shapes of Epithelial Cells 1. Squamous Cells are flat or scalelike. 2. Cuboidal (cubelike) are cube-shapedabout as wide as they are tall. 3. Columnar (tall and thin, similar to a column) cells tend to be taller than they are wide. They can be ciliated or nonciliated. 4. Transitional cells change shape as the need arises, being stretched or composed into ant of the three shapes above. Stratified- made up of one or more layer (ga tangkas2) Inner lining of the urinary systems (ureters,urinary bladders, urethra, inner lining of the allantoic duct) Lining from the uterine tubes, lining of bronchioles of the larger respiratory tracks Follicle of the thyroid glands, kidney tubules, ducts in many glands, surface of the ovary. Absorption and secretion. Types of Epithelium Based on the number of the cell layers: 1. Simple epithelium- of a single layer of cells, each cell extending from the basement membrane to the free surface. 2. Stratified epithelium- (keratinized/non keratinized) consists of more than one layer of cells, but not only the basal layer attaches the deepest layer to the basement membrane. Lining of lung, alveoli, endothelium, lumen of blood, lymphatic vessels, heart chambers. Also found in mesothelium, the serous membrane of our body. Epiglotties, Oral cavities, pharynx, esophagus, vagina, uterine cervix, female urethra, anus Pseudostratified columnar epithelium (ciliated/nonciliated)- Special type of simple epithelium - Consists of one layer of cell, with all the cells attached to the basement membrane. There appear to be two or more layers of cells of because some of the cells are tall and extend to the free surface, whereas others are shorter and do not extend to the free surface. Larynx, Respiratory tract, lining of epididymis, lining of urinary tract, lining of female urethra,membranous spongy urethra in male, lining of large respiratory ducts of glands,