Common Excel Functions: SUM, AVERAGE, MIN, MAX, MEDIAN, ROUND, MEAN
advertisement
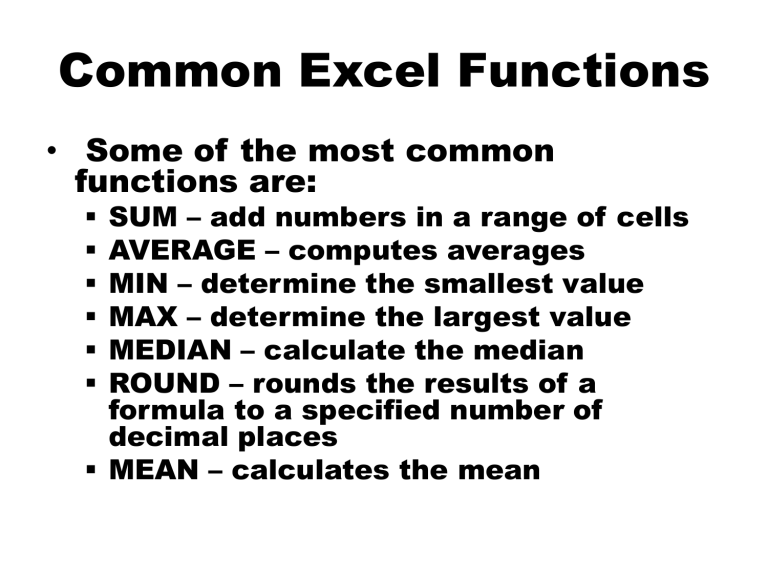
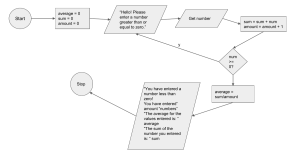
Common Excel Functions • Some of the most common functions are: SUM – add numbers in a range of cells AVERAGE – computes averages MIN – determine the smallest value MAX – determine the largest value MEDIAN – calculate the median ROUND – rounds the results of a formula to a specified number of decimal places MEAN – calculates the mean Common Excel Functions • =round(cell, n) Allows to round a number to the decimal (n) place of your choice. If (n > 0) rounds to the n decimal places If (n == 0) rounds to the nearest integer If (n < 0) rounds to n decimal places to the left of the decimal point H/w roundup, rounddown, int, mround Common Excel Functions = mod(n, d) Gives the remainder on dividing the number n by d • The V in VLOOKUP means "vertical". • HLOOKUP works similarly, but finds data going across columns, instead of down rows. • VLOOKUP(lookup_value,table_array,c ol_index_num,range_lookup) Vlookup • Lookup_value The value to search in the first column of the table array. • Table_array Two or more columns of data. Use a reference to a range or a range name. • Col_index_num The column number in table_array from which the matching value must be returned. Vlookup • Range_lookup A logical value that specifies whether you want VLOOKUP to find an exact match or an approximate match H/w • Distinguish between the vlookup, hlookup and lookup functions • Make use of these in the 247 expenditure problem Vlookup Date and time functions • Dates stored as integers and all times as decimal fractions. Can then add, subtract, compare, … dates and times just like any other numbers • date() returns the number that represents a particular date H/w • What does each of these functions do:• now, today and weekday • How get difference b/w times or dates Logical functions • Based on the boolean types whose values are True and False . • not(exp) returns the boolean value that is not the value of the evaluation of the expression exp which will be:• False if exp evaluates to True • True if exp evaluates to False • and(exp1,exp2,…) returns the boolean value True if all of the expressions evaluate to True otherwise False • or(exp1,exp2,…) returns the boolean value True if one of the expressions evaluate to True otherwise False Logical functions • Based on the boolean types whose values are True and False . • What does the xor()operation do? • IF(exp,trueV [,falseV]) returns boolean value based on the results of the evaluation of the expression exp which will be:• trueV if evaluates exp to True • falseV if evaluates exp to False (optional) Logical functions Example • A cell say a3 contains some number. • For each write a simple test that:– Gives “same” if a3 is 5, else “not same” – Gives “higher” if a3 is above 5, otherwise “lower” – Gives “lower” if a3 is above 5, otherwise “higher” H/w • What does each of these functions do:• sumif, countif, … Logical functions • The if function can be nested that is used within another if function. • A student may be in the Business faculty. Business students may take the BS101, BS201 or BS203 programmes • For each write a simple test that determines :– if a student is in the faculty of Business – If a programme is in the Business faculty – Whether a student is taking a Business faculty programme Text functions • A string (or Text) is a sequence of characters. Characters derived from some character code such as ASCII code (xor Unicode) Some examples of functions on strings:• char(intv) returns character whose ASCII code is intv • len(txt) returns the length or number of characters in the text string txt • lenb(txt) returns the number of bytes used to represent the text string txt Text functions Some examples of functions on strings:• lower(txt) converts uppercase letters in the text string txt to lowercase letters • upper(txt) converts lowercase letters in the text string txt to uppercase letters • MID(txt,st,num) returns a specific number num of characters from a text string txt, starting at the position st Text functions Some examples of functions on strings:• left(txt[,num]) returns the first character (or first num characters) from a text string txt • right(txt[,num]) returns the last character (or last num characters) from a text string txt • concatenate(txt1[,txt2,…]) returns the string formed by concatenating the given strings txt1, txt2,…, txtn • proper(txt) returns ….. • exact(txt, txt2) returns ….. Text functions Some examples of functions on strings:• search(txt1, txt2[,num]) locates text string txt1 within a second text string txt2, and returns the number of the starting position of the first text string txt1 from the first character of the second text stringtxt2. (not casesensitive) • find returns … • Substitute returns … • text returns ….. Other functions • Other useful functions in specialised fields such as Engineering, Finance, Mathematics and Statistics. Some examples of functions :• rand() returns a random number in the open interval (0-1) • pmt(rate, nper, pv, [fv], [type]) returns the periodic payment for an annuity