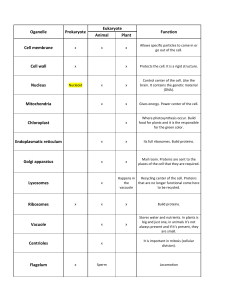
International Medical School General Biology Exam 1. The receptor for IP3 is also ❏ a potassium channel ❏ a sodium channel ❏ the sodium-potassium pump ❏ a calcium channel ❏ a calcium pump 2. What kind of enzyme is the product of the Ras gene, i.e. the Ras protein? ❏ GTPase ❏ phosphodiesterase ❏ ATPase ❏ phosphatase ❏ kinase 3. Intracellular compartmentalization is a characteristic of: ❏ multicellular organisms ❏ all prokaryotic cells ❏ animal cells ❏ all eukaryotic cells 4. Eukaryotic pre-mRNAs undergo a number of modi ications such as capping at the 5' end. A 5' cap: ❏ contains a triphosphate bridge between the terminal base and the 5' end of the premRNA ❏ consists of a modi ied terminal adenine nucleotide ❏ has a 3'-to-5' linkage between the terminal nucleotide and the 5' end of the pre-mRNA ❏ carries a negative charge in the terminal base due to methylation ❏ is identical for all mRNAs that are transcribed by RNA polymerase II 5. The chromatin remodeling complexes play an important role in chromatin regulation in the nucleus. They: ❏ can slide nucleosomes on DNA ❏ have ATPase activity ❏ interact with histone chaperones ❏ can remove or exchange core histone subunits ❏ All of the above 6. The transcription factors that bind DNA and stimulate transcription are: ❏ repressors ❏ small effector molecules ❏ activators ❏ promoters ❏ operators f f f 7. Which of the following events occurs in mitotic metaphase? ❏ Nuclear envelope breakdown ❏ Nuclear envelope reassembly ❏ Chromosome attachment to spindle microtubules for the irst time ❏ Chromosome alignment at the spindle equator ❏ Mitotic spindle assembly International Medical School ❏ Centrosome duplication 8. Which of the following statements is false? ❏ The α-helix and the β-sheet are the most common tertiary protein structures ❏ A single chain polypeptide can contain both α-helix and β-sheet regions ❏ The α-helix is determined and maintained by hydrogen bonds ❏ A β-sheet is formed when a polypeptide chain folds back on itself ❏ The α-helix is the structural basic unit of ibrous proteins 9. Why do cells not have membrane transport proteins for O2? ❏ Because they need to keep the oxygen concentration low inside the reducing environment of the cell ❏ Because oxygen can dissolve in water and leak in via water channels ❏ Because oxygen can dissolve in the lipid bilayer and diffuse in and out rapidly without the need for a transporter ❏ Because oxygen is transported in and out of the cell in special oxygen-carrying proteins such as hemoglobin ❏ Because oxygen transport across a membrane is energetically unfavorable 10. Chloroplasts and mitochondria have many common features because they both: ❏ have the function of oxidizing glucose ❏ are the site of photophosphorylation ❏ have the function of producing glucose ❏ are present in plant cells ❏ are derived by endosymbiosis 11. What is the maximum number of tRNA that a cell can have? ❏ 64 ❏ 61 ❏ 3 ❏ 21 ❏ 20 12. Which of the following reactions is NOT catalyzed by an RNA? ❏ the phosphodiesteric bond cleavage required for the splicing process ❏ the ligation of phosphodiesteric bonds required in the splicing process ❏ the formation of peptide bonds during protein synthesis ❏ the cleavage of phosphodiesteric bonds in the DNA 13. Which of the following statements regarding protein synthesis is CORRECT? ❏ The information for the amino acid sequence of a protein is contained in the nucleotide sequence of messenger RNA ❏ Lysosomes are the site of protein synthesis ❏ Protein synthesis is a process that leads to the formation of ATP ❏ Protein synthesis occurs exclusively during embryogenesis ❏ In eukaryotes, protein synthesis occurs in the nucleus f 14. Indicate which of the following transport processes occurs via the mechanisms described as 'Vesicular Transport' ❏ Import into nucleus ❏ Export from nucleus ❏ Import into mitochondria International Medical School ❏ Return from Golgi to ER ❏ Return from ER to cytosol 15. Apoptotic cells are ef iciently phagocytosed by neighboring cells or macrophages. Which of the following DOES NOT normally happen in this process? ❏ The apoptotic cell releases some of its cytoplasmic content to induce a local in lammatory response ❏ The apoptotic cell exposes phosphatidylserine at its surface, which interacts with receptor proteins on the surface of phagocytes via “bridging” proteins ❏ The apoptotic cell loses or inactivates “don’t eat me” signals ❏ The apoptotic cell rounds up and detaches from its neighbors, which facilitates phagocytosis ❏ Ras 16. Which of the following is NOT a correct monomer/polymer pairing? ❏ Amino Acid/Protein ❏ Nucleotide/Nucleic acid ❏ Monosaccharide/Polysaccharide ❏ Monosaccharide/Oligosaccharide ❏ Cellulose/Triglyceride 17. Which of the following enzymes is NOT involved in DNA replication ❏ DNA Polymerase III ❏ DNA Polymerase I ❏ RNA Polymerase ❏ Primase ❏ Helicase 18. Which of the following statements regarding prokaryotes and eukaryotes is CORRECT? ❏ The process of oxidative respiration does not occur in prokaryotes ❏ Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes possess ribosomes ❏ Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes possess mitochondria ❏ Prokaryotes are not provided with a cell membrane ❏ Prokaryotes have single-helix DNA 19. In contrast to transporters, the channel proteins in cellular membranes ❏ undergo a conformational change every time they transport a solute ❏ interact strongly with the solute(s) that they transport ❏ form pores that are always open ❏ can only mediate passive transport 20. Compared to the cytosol, which of the following is generally true about the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum in our cells? ❏ It has a higher pH ❏ It has a more reducing environment ❏ It has a much higher calcium ion concentration ❏ It has a higher density of ribosomes ❏ All of the above f f 21. Which of the following statements about phospholipids is FALSE? ❏ They can form bilayers or micelles ❏ They are completely apolar International Medical School ❏ They make up biological membranes ❏ They have polar parts and nonpolar hydrophobic tails 22. Nucleosomes that are positioned like beads on a string over a region of DNA can interact to form higher orders of chromatin structure. Which of the following factors can contribute to the formation of the 30-nm chromatin iber from these nucleosomes? ❏ Interactions that involve the histone tails of neighboring nucleosomes ❏ Interaction of the linker histone H1 with each nucleosome ❏ Binding of proteins to DNA or the histones ❏ ATP-dependent function of chromatin remodeling complexes ❏ All of the above 23. The primary structure of a protein is determined only: ❏ by the number of disul ide bonds 2 ❏ by the sequence of amino acids ❏ by the number of amino acids ❏ by the isoelectric point ❏ by the molecular weight 24. Which of the following are NOT G-protein-coupled receptor ligands? ❏ neurotransmitters ❏ photons ❏ Opiates ❏ Peptide hormones ❏ Steroid hormones 25. Which of the following events occurs in mitotic metaphase? ❏ Nuclear envelope breakdown ❏ Nuclear envelope reassembly ❏ Chromosome attachment to spindle microtubules for the irst time ❏ Chromosome alignment at the spindle equator ❏ Mitotic spindle assembly ❏ Centrosome duplication 26. Which of the following molecules is NOT involved in protein synthesis? ❏ Anions ❏ GTP ❏ ribosomes ❏ all tRNAs with their incorporated amino acids ❏ mRNAs 27. Given the 5'-AGGTAT-3' sequence, ind the complementary sequence ❏ 5'- AGGTAT- 3' ❏ 5'- ATACCT- 3' ❏ 5' - TCCATA- 3' ❏ 5'- CCTATA- 3' ❏ 5'-TATGGA- 3' f f f f 28. What can be induced by the acetylation of the N-terminal tail of an histone? ❏ binding of other histone proteins ❏ gene silencing ❏ DNA replication International Medical School ❏ gene expression ❏ formation of heterochromatin 29. The process of differentiation at the cellular level always involves: ❏ the activation of speci ic genes and the continuous demolition of proteins synthesized by other genes ❏ the block of the transcription process and the enhancement of the transformation process ❏ the blocking of ribosomes that synthesize unhelpful proteins ❏ the destruction and subsequent elimination of DNA fractions that do not serve the differentiated cell ❏ the activation of some genes and the repression of other genes 30. In the RER occurs: ❏ The glycosylation of proteins ❏ Glycogen hydrolysis ❏ The synthesis of integral membrane and secretion proteins ❏ The synthesis of lipids and steroid hormones ❏ The synthesis of cytoplasmic proteins 31. Protein subunits that interact speci ically with DNA sequences ... ❏ typically recognize sequences of two to three nucleotide pairs in length ❏ do so via hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, and hydrophobic interactions ❏ typically form about ive weak interactions at the protein–DNA interface ❏ often bind loosely to DNA ❏ All of the above 32. The molecule of immediate use from cellular energy reactions is: ❏ ATP ❏ Oxygen ❏ Glycogen ❏ Glycine ❏ Cytochrome C 33. Which of the following cytoskeletal ilaments are abundant in an animal cell nucleus? ❏ Micro ilaments ❏ Microtubules ❏ Septins ❏ Intermediate ilaments ❏ Spectrin ilaments 34. The Nucleolus is: ❏ a cytoplasmic organelle closely adherent to the nucleus, in which the synthesis of ribosomes takes place ❏ a nuclear structure, with a simple membrane, externally lined by ribosomes ❏ an old term by which, in the past, the nucleus was referred to ❏ a nuclear structure, not enclosed by a membrane, site of ribosomal RNA synthesis ❏ a simple structure of the nucleus found in bacteria f f f f f f f 35. The plasma membrane consists of: ❏ triglycerides and proteins ❏ proteoglycans International Medical School ❏ steroids ❏ acetylcholine and ATP ❏ phospholipids and proteins 36. In which cellular compartment are mitochondrial proteins synthesized? ❏ Cytoplasm ❏ RER ❏ Nucleus ❏ REL ❏ Golgi apparatus 37. Which of the following is a major consequence of activation of phospholipase C- β (PLCβ) by the Gq trimeric GTPase? ❏ Elevation of intracellular cAMP levels, leading to the activation of protein kinase ❏ Elevation of PIP3 levels in the plasma membrane, leading to the activation of protein kinase ❏ Elevation of IP3 in the plasma membrane, leading to the activation of protein kinase ❏ Elevation of intracellular cGMP levels, leading to the activation of protein kinase ❏ Elevation of intracellular Ca2+ levels, leading to the activation of protein kinase 38. Indicate which of the following structures is based on actin ilaments ❏ The cell cortex ❏ The mitotic spindle ❏ The nuclear lamina ❏ Cilia ❏ Flagelli 39. Which of the following events normally activates a GTP-binding protein? ❏ Activation of an upstream guanine nucleotide exchange factor ❏ Activation of an upstream GTPase-activating protein ❏ GTP hydrolysis by the protein ❏ Phosphorylation of a bound GDP molecule by an upstream phosphorylase ❏ Pi release after GTP hydrolysis 40. Why might a base substitution in a gene, in position 3 of the codon, not alter the corresponding amino acid sequence? ❏ Ribosomes correct the changes. ❏ The genetic code is universal ❏ There is a post-transcriptional correction of the messenger RNA sequence ❏ There is a post-transcriptional correction of the protein ❏ The genetic code is degenerate f 41. Which division in meiosis is more similar to mitosis? In which division do sister chromatids separate from each other? ❏ Meiosis II; meiosis II ❏ Meiosis I; meiosis I ❏ Meiosis I; meiosis I ❏ Meiosis I; meiosis II ❏ Meiosis II; meiosis I International Medical School 42. Which of the following is NOT the role of molecular chaperones in the folding of cellular proteins? ❏ They assist proteins in folding into their correct conformations ❏ They help prevent formation of protein aggregates ❏ They specify the inal three-dimensional shape of proteins ❏ They catalyze the folding of proteins in the crowded environment of the cell ❏ They make the protein-folding process in the cell more reliable 43. Which are the major biological macromolecules? ❏ DNA, RNA and carbohydrates ❏ Nucleic acids, carbohydrates and proteins ❏ Nucleic acids, carbohydrates, proteins, and fats ❏ DNA, water, carbohydrates and fats 44. Which amino acids are phosphorylated by kinase proteins? ❏ Tyrosine, threonine, glycine ❏ Phenylalanine, serine, tyrosine ❏ Threonine, serine, tryptophan ❏ Serine, leucine, tyrosine ❏ Serine, threonine, tyrosine f f 45. The proteins that are transported in the Golgi apparatus: ❏ are nonfunctional proteins that will later be destroyed by lysosomes ❏ are synthesized by free ribosomes ❏ are synthesized by ribosomes bound to the endoplasmic reticulum ❏ are histone proteins that are modi ied here before being transferred to the nucleus ❏ are proteins used in mitochondrial catabolism