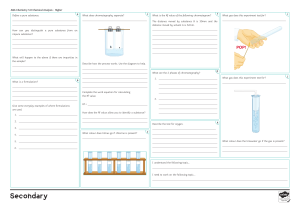
David Pascall 3 West Chemistry 30% Assessment Title: Separation Techniques, Paper Chromatography Aim: To separate the components in screened methyl orange using paper chromatography Discussion 1. What is paper chromatography? Identify mobile and stationary phases of this experiment ● Paper chromatography is used to separate a mixture of dissolved substances which are coloured or can be coloured and which will travel through a material e.g filter paper. The mobile phase is the solvent that moves through the paper, carrying different substances with it, the stationary phase is contained on the paper and does not move through it. 2. Why is it necessary to draw the base in pencil ● It is necessary to draw the base line in pencil because the pencil lead does not dissolve in solvent, thus it will not affect the separation. 3. Why is it necessary to ensure that the spot is not immersed in the solvent ● It is necessary to ensure that the spot is not immersed in the solvent because the samples will dissolve in the solvent right at the beginning, contaminating the whole solvent, causing the chromatogram to be inaccurate. 4. Explain what happens and why using chemical terms ● First, in the stationary phase, a spot of the mixture is placed near the bottom of a piece of chromatography paper. The paper is then placed upright in a suitable solvent , such as water. During the mobile phase, as the solvent soaks up the paper, it carries the mixtures with it. Different components of the mixture will move at different rates. 5. Which of the dyes in screened methyl orange is more soluble in the mobile phase? ● Blue dye is more soluble in the screened methyl orange in the mobile phase because the blue dye is further up the chromatography indicating its higher solubility. 6. Calculate the Rf values of each component and explain the relevance of calculating Rf values ● Rf of Blue dye = 5.7cm - Distance travelled 6cm - Solvent front = 0.95 ● Rf of Yellow dye = 2.4cm 6cm = 0.4 Rf values are used as identification as well as it can be used to predict where a particular substance would be located on the chromatogram. ● Precautions 1. When applying the screened methyl orange onto the chromatogram, persons involved must be careful in placing the drop in the middle of the baseline 2. Ensure that the amount of water in the beaker would be enough so that the spot is not immersed in the solvent. 3. Ensure that while the solvent is travelling up the chromatogram that it doesn't touch the others in the beaker which would cause them to stick to each other. ● Limitations More water could have been added so the chromatogram could have properly absorbed the solvent giving better results. ● Conclusion Overall, the experiment was a success as the aim was completed the screened methyl orange was separated into two coloured dye blue and yellow using the method of paper chromatography. ● Reflection Chromatography allows food companies to identify the components in the food. Companies analyse their products for nutrients such as proteins, vitamins, preservatives etc. The experiment itself proved that this skill could be used many other different fields.