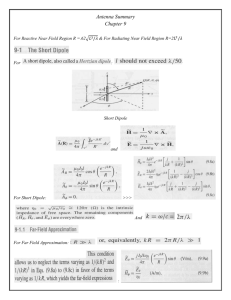
Lecture 4 Hertzian dipole (The elemental electrical dipole) HERTZ ANTENNA The Hertzian dipole (Fig.4-1) is a theoretical short dipole (short length of straight wire smaller than the wavelength L<<λ) with a uniform current along its length driven by an AC current of frequency ω. Infinite small length of wire (Fig.4-1) A Hertzian dipole is a thin, linear conductor whose length L is very short compared with the wavelength λ; L should not exceed λ/50. Hertzian dipole consists a short conducting wire of length ℓ terminated in two small conductive spheres or disks (capacitive loading). Fig.(4-2) Fig.(4-2) Hertzian dipole antenna We assume the current in the wire to be uniform and to vary sinusoidally with time i(t ) I . cos t Re[ Ie jt ] Since the current vanishes at the ends of the wire, charge must be deposited there .The relation between the charge and the current is dq (t ) i (t ) dt In phasor notation q(t ) Re[ Qe jt ] Or We have I jQ I Q j The positive sing is for the charge on the upper end and the negative sign for the charge on the lower end Radiation pattern of a Hertzian dipole The magnitude of the normalized field strength (with respect to the peak value) versus θ for a constant ϕ (an E-plane pattern) and the magnitude of the normalized field strength versus ϕ for 2 (the H-plane pattern) is shown in Fig.(4-3) H-plane pattern E-plane pattern Fig.(4-3 B) Radiation pattern of a Hertzian dipole Where F(θ) and F(ϕ) is the maximum radiation (4-4) Radiated Electric Field Radiation Resistance and Radiated Power for Hertzian dipole The radiation resistance (Rrad), defined as the value of resistor driven by the current in the dipole antenna which would lead to the some average power dissipation as the average radiated 2 2 power Rrad 3 ( ) The term 0 0 120 377 is called the impedance of free space and has standard value 12 F 7 H 8 , 85 10 Permeability of air 0 0 4 10 m Permittivity m of air I 02 2 2 [ ( ) ] Radiated power is Prad 2 3 Where I 0 -current in the dipole -length of the dipole -wave length I 2 ( I ) 2 0 Or radiated power Prad ( ) Rrad 12 2 2 ( ) And Rrad 0 6 0 377 and 2 ,we get 2 2 2 80 ( ) 790( ) Substituting for Rrad 2 -phase constant rad m The directivity D of the antenna is defined as the ratio of the maximum power density to the average power density ( Prad ) max D 3 1,5 2 ( Prad )average Radiation characteristics of a Hertzian Dipole Normalized radiation field pattern E ( , ) sin E ( , ) max S ( , ) Pn( , ) sin 2 S ( , ) max En( , ) Normalized radiation power pattern Average radiation intensity Directivity Gain D( ) Prad ( I ) 2 Uaverage 0 ....( w ) 2 sr 4 48 P U ( ) rad 1,5 sin 2 Uaverage 4 G Dmax 1,5 (assuming loss less) Effective length e Iaverage ...(m) I max e 2 0 2 0 2 0 Ae 0,1192 ....m 2 4 Rrad 3160 4 790( ) 2 Effective aperture Beam Area A Poynting vector 4 41000 2 2 sr...or... A 27333..(deg rees ) 2 3 D D S ( , ) E2 ( , ) E2 ( , ) Z0 .... w m 2