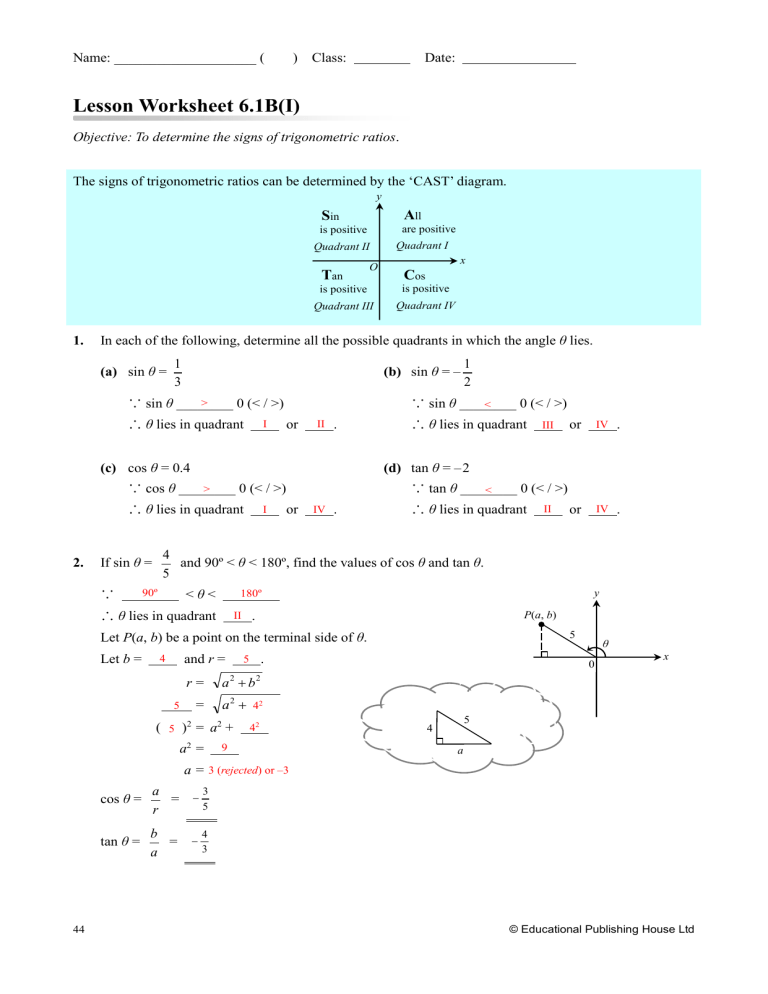
Name: ____________________ ( ) Class: Date: Lesson Worksheet 6.1B(I) Objective: To determine the signs of trigonometric ratios. The signs of trigonometric ratios can be determined by the ‘CAST’ diagram. y All are positive Sin is positive Quadrant II Tan is positive O Quadrant III 1. x Cos is positive Quadrant IV In each of the following, determine all the possible quadrants in which the angle θ lies. (a) sin θ = 1 3 (b) sin θ = – > ∵ sin θ ________ 0 (< / >) ∴ θ lies in quadrant I or II . ∴ θ lies in quadrant ∴ θ lies in quadrant or IV . I or IV . ∵ tan θ ________ 0 (< / >) < or IV . ∴ θ lies in quadrant II 4 and 90º < θ < 180º, find the values of cos θ and tan θ. 5 If sin θ = <θ< 90º y 180º ∴ θ lies in quadrant P(a, b) . II Let P(a, b) be a point on the terminal side of θ. Let b = III (d) tan θ = –2 ∵ cos θ ________ 0 (< / >) > ∵ 1 2 ∵ sin θ ________ 0 (< / >) < (c) cos θ = 0.4 2. Quadrant I and r = 4 5 . 5 r= a 2 b2 = a 2 42 ( 5 )2 = a2 + a2 = 5 42 9 θ 0 x 5 4 a a = 3 (rejected) or –3 44 cos θ = 3 a = 5 r tan θ = 4 b = 3 a © Educational Publishing House Ltd Chapter 6 3. 1 and 270º < θ < 360º, find the values of sin θ and tan θ. 4 (Leave the answers in surd form.) If cos θ = ∵ <θ< 270º y 360º ∴ θ lies in quadrant . IV θ Let P(a, b) be a point on the terminal side of θ. Let a = 1 and r = a b = 4 . 4 2 r= 4 2 1 P(a, b) b2 12 ( 4 )2 = ( 1 )2 + b2 b2 = x 0 4 b 15 b = 15 (rejected) or – 15 b 15 15 sin θ = = = r 4 4 tan θ = 4. b 15 = = 15 a 1 If tan θ = 3 and 180º < θ < 270º, find the values of sin θ and cos θ. Exercise 6.1: 10, 11 (Leave the answers in surd form.) ∵ <θ< 180º 270º ∴ θ lies in quadrant III y . Let P(a, b) be a point on the terminal side of θ. Let a = –1 and b = r = a b 2 –3 θ . 0 2 x = (1) 2 (3) 2 P(a, b) = 10 3 3 b sin θ = = = r 10 10 cos θ = a 1 1 = = r 10 10 Try More 5. If cos θ = 2 13 and 90º < θ < 180º, find the values of sin θ and tan θ. (Leave the answers in surd form if necessary.) ∵ 90º < θ < 180º ∴ θ lies in quadrant II. Let P(a, b) be a point on the terminal side of θ. Let a = –2 and r = 13 . sin θ = 3 b = r 13 tan θ = 3 b 3 = = a 2 2 r = a 2 b2 13 = ( 2) 2 b 2 ( 13 ) 2 = (–2)2 + b2 b2 = 9 b = 3 or –3(rejected) © Educational Publishing House Ltd 45




