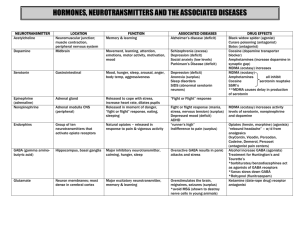
St ep by st ep ef f ect on syn apt ic t r an sm ission When a neuron receives enough stimulus an electrical impulse reaches the axon terminal and becomes chemical due to the neurotransmitters. Regularly, when releasing serotonin, the vesicles holding the neurotransmitter merge with the membrane and release serotonin into the synaptic gap. The neurotransmitters then attach themselves to the postsynaptic neurons protein receptors and relay the stimuli. Eventually, the serotonin neurotransmitter ether dissolves or get reabsorbed. When ecstasy is ingested, ecstasy gets taken up by the serotonin transporters in the pre-synaptic neuron because Ecstasy acts like Serotonin. This causes the transporter to work in reverse by transporting serotonin out of the pre-synaptic neuron because it became confused. As a result, more serotonin gets trapped in the synaptic gap and rebinds to the protein receptors causing the neuron to be over stimulated. This process also happens with dopamine where ecstasy becomes an inhibitor to the dopamine transporters, which prevents dopamine from being reabsorb resulting in constant stimulus down the postsynaptic neuron. Wh at par t s of t h e br ain does Ecst asy ef f ect ? Body text Ecstasy affects a nerve pathway called the serotonin pathway. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter regulates mood, emotions, and perceptions. Meaning Ecstasy also affects places such as the neocortex which is important in perceptions, the limbic system which includes the amygdala, hippocampus, basal ganglia and hypothalamus, which is involved in mood and fear. An experiment was performed on monkeys to determine if ecstasy can damage neurons. They were given ecstasy for four days and another group of monkeys for seven years. Two weeks after a monkey received ecstasy, most of the serotonin was gone meaning that the serotonin terminals damaged long-term because seven years later there was minimal recovery. Changes in limbic areas of the brain were also found. Where to get more information/help: https://drugabuse.com/ecstasy/how-to-help-an-addict/ In t er est in g f act s Sometimes Ecstasy contains rat poison as a filler It was first invented in 1912 by the Merck pharmaceutical laboratories to suppress appetite and it was also used for military purposes Wh at is ecst asy/ Ef f ect s on t h e body Love Dr u g Side ef f ect s Ecst asy - Impaired judgment False sense of affection Confusion/ confused episodes Blurred vision Nausea Long?term Con sequ en ces - - Liver failure Dehydration Exhaustion Risk of a heart attack Kidney, liver and brain damage Long?lasting lesions on brain tissue Irreparable damage to the nervous system Sleep problems Severe anxiety/paranoia Muscle tension Long?lasting brain damage affecting thought and memory Degenerated nerve endings Memory loss Hemorrhaging - Death - Ecstasy is a drug that affects the release of serotonin in the brain and it is often called ?the love pill? or MDMA in powder form. Its chemical name is methylenedioxymethamphetamine It can come in any color or shape but it is produced white. Ecstasy can regulate mood, appetite and increase the perceptions of the 5 senses, especially sight, sound and touch. This causes people on this drug to become sexually active when being touched. Taking Ecstasy often can cause a build up of tolerance meaning more of the drug is needed to get high, moreover, your body begins to become dependent. This means that people are not addicted to Ecstasy but addicted to the feeling it gives. Often the drugs sold under the name Ecstasy contains many other street drugs such as cocaine and other hallucinogens. This causes people to see or feel things that are not really there. Often the bodies natural alarm signal when is in danger is turned off. As a result, people on this drug take risks and push themselves past what their body can take. For example, ecstasy increase the body temperature and in warm crowded places like a club that can cause overheating and dehydration.