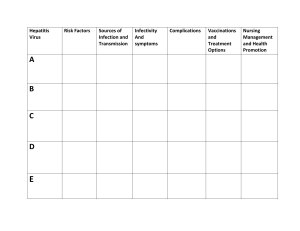
HSS1100 MICROBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY STUDY GROUP #10 Fri, Apr 2, 2021 🐣 Virus Work Sheet Part 2 Fill-in-the-Blank Summary Sheet Viruses require LIVING cells for growth and replication. They have DNA or RNA NEVER both. Basic Components 1. Nucleic acid = infectious genetic material 2. Protein coat = protection 3. Surface antigen = protein or carbohydrate and highly variable Five Steps of Replication 1. Adsorption 2. Penetration and uncoating 3. Protein and nucleic acid synthesis 4. Maturation and assembly 5. Release How do we detect viral infections? 1. Detect the virus itself 2. Detect for immune response I. Glandular Viruses 1. Mumps Prevention: MMR vaccine (live attenuated) Spread by salivary and respiratory secretions 2. Infectious Mononucleosis (Epstein-Barr Virus) A blood picture detects for increase in atypical lymphocytes A monospot test detects RBC agglutination and for the presence of EBV antigens 3. Cytomegalovirus (CMV) - Pregnant women - Transplant patients - Immunocompromised (ex. AIDS) pts II. Hepatitis Viruses 1. Hepatitis Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver HSS1100 MICROBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY STUDY GROUP #10 Fri, Apr 2, 2021 🐣 a) Hepatitis A - Is found mainly in children and young adults - Detection of suspected clinical cases: detection of IgM, immunity: detection of IgG (before travel) b) Hepatitis B - Incubation: 90 days - Infective serum 30-60 days before onset of symptoms ^^ Tells us serum/blood is infected BEFORE symptoms c) Hepatitis C - Blood and sexual transmission d) Hepatitis Delta Agent - Viroid relies on Hep B presence for replication in cells e) Hepatitis E - Fecal - oral transmission - Symptoms similar to Hep A, but 20% mortality in pregnant women f) Hepatitis G - Blood and sexual transmission - Vaccine – NO 2. Yellow Fever Virus Causes haemorrhagic fever with hepatitis Transmitted by mosquitos III. CNS viruses For diagnosis always first exclude possibility of bacterial or fungal infection CNS Viruses with a HUMAN Reservoir 1. Mumps aseptic meningitis in children 2. Enteroviruses aseptic meningitis in infants and children 3. HSV1 RARE cause of herpetic encephalitis in young adults 4. HSV1 or 2 RARE cause of meningo-encephalaitis in neonate or young adults HSS1100 MICROBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY STUDY GROUP #10 Fri, Apr 2, 2021 🐣 CNS Viruses with an ANIMAL Reservoir 1. Arbovirus Over 200 different types Found in tropical rainforest areas 2. Rabies virus Long incubation Prevention by vaccination of wildlife and pets IV. Viruses of the Immune System 1. HIV Virus is cytocidal to helper T4 cells AIDS develops from decreasing immune status Vaccine – NO Most effective treatment is cocktail of treatments called HAART HSS1100 MICROBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY STUDY GROUP #10 Fri, Apr 2, 2021 🐣 Multiple-choice questions 1. Which of the following statements is false? a) Hepatitis A and hepatitis E are transmitted primarily via the fecal-oral route. b) A killed vaccine is available for hepatitis C. c) Hepatitis A virus produces acute but not chronic hepatitis. d) Hepatitis delta agent can only affect persons infected with hepatitis B. e) All of the above are true. There are vaccines available only for hepatitis A and B. Hepatitis A causes acute infection, but there is no carrier state and no chronic hepatitis. Hepatitis B can lead to chronic hepatitis and the chronic-carrier state. 2. Yellow fever virus is transmitted by: a) Aerosols. b) Ticks. c) Cattle. d) Mosquitos. e) Direct contact. 3. In a patient with hepatitis B, co-infection with hepatitis delta agent results in: a) Decreased severity of disease. b) Increased risk of fulminant hepatitis. c) Decreased progression to a chronic carrier state. d) No change in the severity or chronicity of the disease. Fulminant hepatitis: “A rare syndrome of massive necrosis of liver parenchyma and a decrease in liver size (acute yellow atrophy) that usually occurs after infection with certain hepatitis viruses” 4. Rabies virus is transmitted by: a) Saliva b) Urine c) Blood d) Feces Rabies virus is transmitted via saliva (CNS virus with animal reservoir) HSS1100 MICROBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY STUDY GROUP #10 Fri, Apr 2, 2021 🐣 5. Arbovirus causes: a) Meningitis b) Fungal infection c) Acute encephalitis (rabies) d) Encephalitis 6. ___ can cause pneumonia in young children. a) Arbovirus b) Mumps virus c) Adenovirus d) Cytomegalovirus 7. __ causes bilateral inflammation of __ glands. a) Mumps; thymus b) Mumps; parotid c) Epstein-Barr; thymus d) Epstein-Barr; parotid 8. __ is a rare cause of herpetic encephalitis in young adults. a) Mumps b) Enterovirus c) HSV1 d) HSV1 or 2 1. Arbovirus is associated with deserts (F) – associated with tropical rainforest areas. 2. Hepatitis G causes jaundice (F) – no jaundice 3. Hepatitis B is transferred by blood/blood products (T) 4. Hepatitis E is transferred fecal-oral (T) 5. Yellow Fever Virus has a mortality rate of 50% (T)