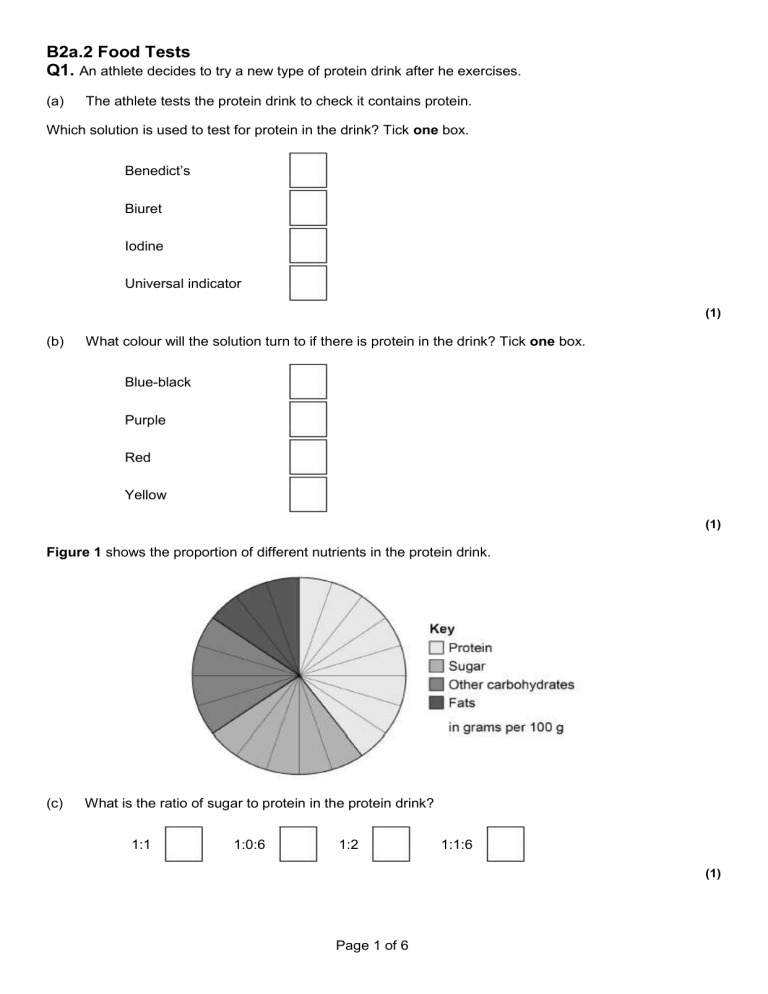
B2a.2 Food Tests Q1. An athlete decides to try a new type of protein drink after he exercises. (a) The athlete tests the protein drink to check it contains protein. Which solution is used to test for protein in the drink? Tick one box. Benedict’s Biuret Iodine Universal indicator (1) (b) What colour will the solution turn to if there is protein in the drink? Tick one box. Blue-black Purple Red Yellow (1) Figure 1 shows the proportion of different nutrients in the protein drink. (c) What is the ratio of sugar to protein in the protein drink? 1:1 1:0:6 1:2 1:1:6 (1) Page 1 of 6 (d) Why is a high protein diet useful to an athlete? Tick one box. Provides amino acids to make new muscle. Provides fatty acids to produce urea. Provides glucose for energy. Provides lactic acid for anaerobic respiration. (1) When the athlete drinks the protein drink the substances are digested. The products of digestion are absorbed into the bloodstream. Absorption happens in the small intestine. Figure 2 shows a section of the small intestine. (e) How is the small intestine in Figure 2 adapted to absorb the products of digestion quickly? Tick two boxes. It has a large surface area. It has a long diffusion pathway. It has a thin surface. The concentration inside the small intestine is low. It has a poor blood supply. (2) (f) Figure 3 shows the proportion of different nutrients in four protein drinks. Figure 3 Page 2 of 6 Which protein drink should an athlete with diabetes use? Give a reason for your answer. Drink ____________________ Reason ____________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (2) Q2. Four foods were tested for starch, sugar and protein. The table shows the results. Food (a) Test for starch: colour after iodine test Test for sugar: Test for protein: colour after colour after Benedict’s test Biuret test A Blue-Black Brick red Blue B Orange Blue Lilac C Blue-Black Yellow Blue D Orange Orange Lilac Give three conclusions about food D. 1 _________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 2 _________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 3 _________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (3) (b) Starch is broken down into glucose. Which type of enzyme breaks down starch? Tick (✓) one box. Carbohydrase Lipase Protease (1) Page 3 of 6 (c) Which part of a cell releases energy from glucose? Tick (✓) one box. (1) Mitochondria Nucleus Ribosomes Vacuole (d) Which food in the table above would be the most suitable for a person with Type 2 diabetes to eat? Give two reasons for your answer. Food ______________________________________________ Reason 1 ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Reason 2 ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (3) Q3. Describe how to test a sample of food for protein, starch and sugar. Give the colours that would be seen if the food sample contained protein, starch and sugar. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________(6) Page 4 of 6 Mark schemes Q1. (a) biuret 1 (b) purple 1 (c) 1:1.6 1 (d) provides amino acids to make new muscle 1 (e) it has a large surface area 1 it has a thin surface 1 (f) C 1 lowest sugar (content) 1 [8] Q2. (a) it does not contain starch 1 it contains sugar ignore high / low amount 1 it contains protein 1 (b) carbohydrase 1 (c) mitochondria 1 (d) B no marks if incorrect or no food given if no food written on answer line check the table 1 does not contain sugar 1 does not contain starch (that can be converted to sugar) ignore references to protein 1 Page 5 of 6 [8] Q3. Level 3: The method would lead to the production of a valid outcome. All key steps are identified and logically sequenced. 5−6 Level 2: The method would not necessarily lead to a valid outcome. Most steps are identified, but the method is not fully logically sequenced. 3−4 Level 1: The method would not lead to a valid outcome. Some relevant steps are identified, but links are not made clear. 1−2 No relevant content 0 Indicative content Protein • grind up food • add Biuret (reagent / solution) or add copper sulfate (solution) and sodium hydroxide (solution) or add Biuret 1 and Biuret 2 • turns purple / lilac Starch • add iodine (solution) • turns black / blue-black / dark blue - ignore blue / purple Sugar • grind up food • mix with water • add Benedict’s (reagent / solution) • heat mixture (≥ 65 °C) • in a water bath • turns (brick) red / orange / brown / green / yellow For Level 3 correct references to all three tests are needed. [6] Page 6 of 6