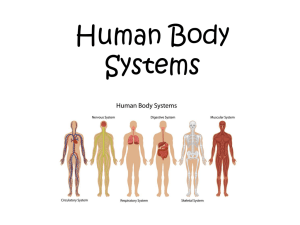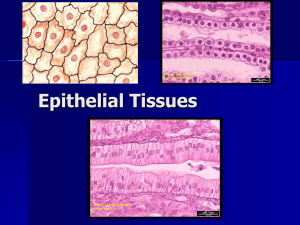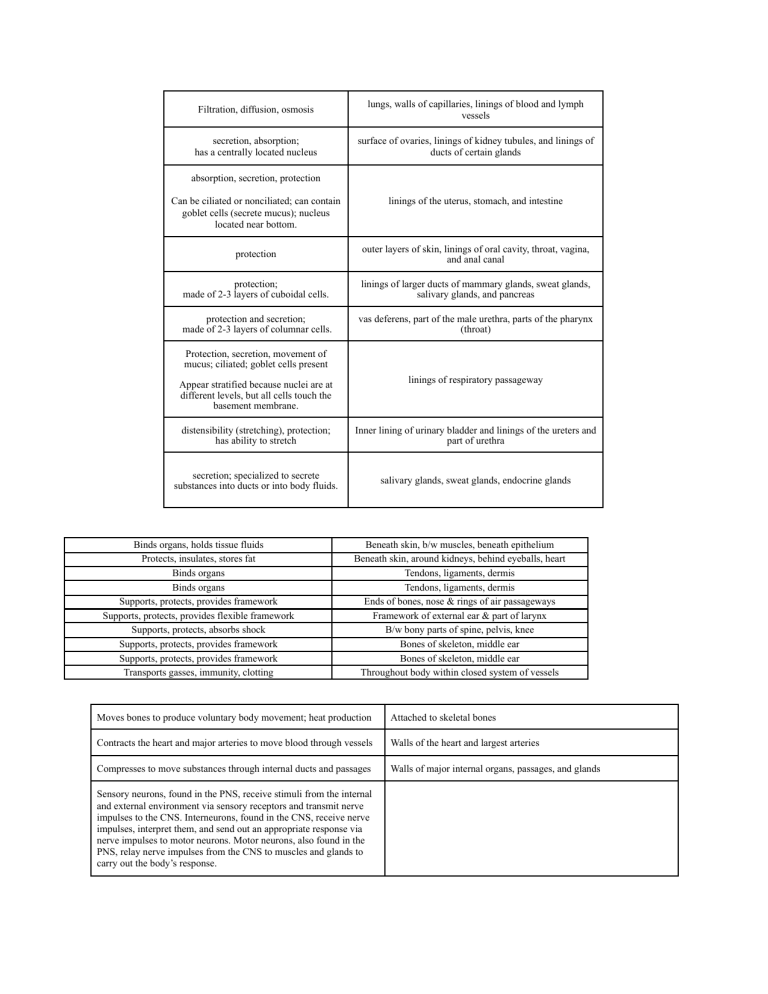
Filtration, diffusion, osmosis lungs, walls of capillaries, linings of blood and lymph vessels secretion, absorption; has a centrally located nucleus surface of ovaries, linings of kidney tubules, and linings of ducts of certain glands absorption, secretion, protection Can be ciliated or nonciliated; can contain goblet cells (secrete mucus); nucleus located near bottom. linings of the uterus, stomach, and intestine protection outer layers of skin, linings of oral cavity, throat, vagina, and anal canal protection; made of 2-3 layers of cuboidal cells. linings of larger ducts of mammary glands, sweat glands, salivary glands, and pancreas protection and secretion; made of 2-3 layers of columnar cells. vas deferens, part of the male urethra, parts of the pharynx (throat) Protection, secretion, movement of mucus; ciliated; goblet cells present linings of respiratory passageway Appear stratified because nuclei are at different levels, but all cells touch the basement membrane. distensibility (stretching), protection; has ability to stretch Inner lining of urinary bladder and linings of the ureters and part of urethra secretion; specialized to secrete substances into ducts or into body fluids. salivary glands, sweat glands, endocrine glands Binds organs, holds tissue fluids Protects, insulates, stores fat Binds organs Binds organs Supports, protects, provides framework Supports, protects, provides flexible framework Supports, protects, absorbs shock Supports, protects, provides framework Supports, protects, provides framework Transports gasses, immunity, clotting Beneath skin, b/w muscles, beneath epithelium Beneath skin, around kidneys, behind eyeballs, heart Tendons, ligaments, dermis Tendons, ligaments, dermis Ends of bones, nose & rings of air passageways Framework of external ear & part of larynx B/w bony parts of spine, pelvis, knee Bones of skeleton, middle ear Bones of skeleton, middle ear Throughout body within closed system of vessels Moves bones to produce voluntary body movement; heat production Attached to skeletal bones Contracts the heart and major arteries to move blood through vessels Walls of the heart and largest arteries Compresses to move substances through internal ducts and passages Walls of major internal organs, passages, and glands Sensory neurons, found in the PNS, receive stimuli from the internal and external environment via sensory receptors and transmit nerve impulses to the CNS. Interneurons, found in the CNS, receive nerve impulses, interpret them, and send out an appropriate response via nerve impulses to motor neurons. Motor neurons, also found in the PNS, relay nerve impulses from the CNS to muscles and glands to carry out the body’s response.