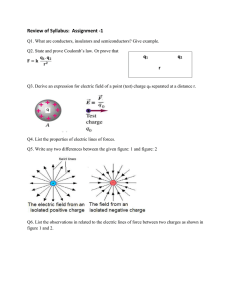
FINAL ACTIVITY What’s in Your Name? Deadline: Friday, 2 hours before Final Examination Direction: Answer the following questions that corresponds the 1st 15 letters your name. Example, if your name is Charles-Augustin De Coulomb, then you need to answer questions letter C, H, A, R, L, E, S … and so on, up to its 15th letter. However, if the same letter appears, then you need to answer the sub-question. For example: Since there is a second letter “A” in A-ugustin (the 1st letter “A” is in ch-A-rles), you will answer question A1. If there will be more than two same letter within the 15-letter that is needed to be answered then, the succeeding same letters will be a bonus point. For example is the letter “L” and “I”, in the name Galileo Galilei, since there are three L and I, you only need to answer G, A, L, I, L1, E, O, G1, A1, I1, E1. If your name is less than 15 letters then, you are lucky for this activity. Only the First Name and Surname will be used. No Middle Name. A. What is an electric force? A1. What is the difference between a capacitor and a battery? B. What is an electric charge? B1. What is the difference between an electric field and gravitational field? C. What is a proton? C1. Give one example computation for electric field. D. What is an electron? D1.Who developed Coulomb’s Law? E. What is a neutron? E1. What are the three laws of motion? F. What is potential energy? F1. Send a video recording of you via FB messenger reciting the Coulomb’s Law G. What is electric potential energy? G1. What is the value for Coulomb’s constant? H. What is a capacitor? H1. Send a video recording of you via FB messenger reciting the Newton’s First Law of Motion I. What is a battery? I1. What is the difference between alternating current and direct current? J. What is an electric insulator? J1. Which is better between alternating current and direct current? K. What is an electric conductor? K1. What is the difference between positive charge and negative charge? L. What is an electric circuit? L1. Send a video recording of you via FB messenger reciting the Newton’s Second Law of Motion M. What is Coulomb’s Law? M1. What is your main challenge or problem in doing PETA 1? N. What is the formula for Coulomb’s Law? N1. What is your main challenge or problem in doing PETA 2? O. What is a static electricity? O1. What is your main challenge or problem in doing PETA 3? P. What are the parts of an atom? P1. Give another example computation on Coulomb’s Law Q. What are the parts of an electric circuit? Q1. Give another example computation on electric force R. What are the basic parts of a capacitor? R1. What does the following instruments measure: 1) ammeter; 2) ohmmeter; 3) voltmeter; 4) galvanometer; 5) wattmeter; 6) multimeter S. What is an electrostatic force? S1. Define nucleus in an atom T. Give one example computation for Coulomb’s Law. T1. Send a video recording of you via FB messenger reciting the Newton’s Third Law of Motion U. What is the contribution of Thales of Miletus in electricity? U1. Solve for the electric charge if q1 = 15.0C, q2 = 3.50C; r = 5 m V. Give one important contribution of the Greeks in electricity? V1. Solve for the electric charge if q1 = 2.00C, q2 = 9.50C; r = 100 cm W. What is the formula for electric force? W. Solve for the electric charge if q1 = 2.20C, q2 = 1.10C; r = 65 cm X. Give one example computation for electric force? X1. Solve for the electric charge if q1 = 14.05C, q2 = 60.5C; r = 1 m Y. What is the unit for electric charge? Y1. Solve for the electric charge if q1 = 10C, q2 = 10C; r = 1000 cm Z. What is an electric field? Z1. Solve for the electric charge if q1 = 22.11C, q2 = 27.04C; r = 10m Ñ. What causes static electricity? Ñ1. Give an example of static electricity