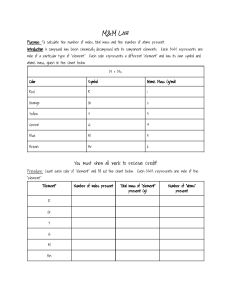
Lecture 2 General Chemistry Review LEARNING OBJECTIVES = “topics covered on the exam” •The structure of the atom, the main features of the subatomic particles, and the importance of isotopes in determining atomic mass. •The format of the periodic table and general location and characteristics of metals, metalloids, and nonmetals. •The essential features of ionic and covalent compounds and the distinction between them. •The definition of a mole unit. •The relationship between amount of substance (mol), mass (g), and number of chemical entities. •Mole-mass-number information in a chemical formula. 1 With many slides from Suzanne Bart…. General Chemistry Review 2 What is the stuff things are made of? Page 57, your book https://www.moneycontrol.com/news/trends/travel-trends...... Gold is made of atoms with p⁺, n⁰, e⁻. Cotton towels are also made of atoms with p⁺, n⁰, e⁻. Can you turn cotton towels into gold? Atoms cannot be created or destroyed. Law of Conservation of Mass Know how to use the Periodic Table Also know how to use this one ! Do not get confused by different names for the same thing! Page 57, your book Might be on exams… Inside cover, your book The atomic number is the smaller one, the atomic mass number is the larger one. Ionic vs. Covalent Compounds Ionic Compounds Often metal + non-metal Crystalline solids (made of ions) High melting and boiling points Conduct electricity when melted Many soluble in water but not in nonpolar liquid Covalent Compounds Often non-metal + non-metal Gases, liquids, or solids (made of molecules) Low melting and boiling points Poor electrical conductors in all phases Many soluble in nonpolar liquids but not in water Need more help! Look for my handwritten notes posted on blackboard. Practice – Ionic vs. Covalent Compounds 1. NaBr 2. BF3 3. CO 4. Li2S 5. P2Br4 6. MgBr2 7. Be(OH)2 8. SF6 9. NH3 10. SO3 11. N2S 12. CaO 13. PH3 14. SiO2 15. NO2 sodium bromide boron trifluoride carbon monoxide lithium sulfide diphosphorus tetrabromide magnesium bromide beryllium hydroxide sulfur hexafluoride ammonia sulfur trioxide dinitrogen sulfide calcium oxide phosphorus trihydride silicon dioxide nitrogen dioxide Covalent Compounds: Molecules Ionic Compounds and Polyatomic Ions Isotopes and how to determine atomic mass Page 57, your book Sample Problem Calculate the atomic mass of silicon given the following data: Isotope Abundance Mass Silicon - 28 92.2297% 27.9769 amu Silicon - 29 4.6832% 28.9765 amu Silicon - 30 3.0872% 29.9738 amu Ans. 28.085 amu What do you with this question? The mass of 3He is: a) the same as 3H b) slightly less than that of 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 neutron c) slightly more than that of 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 neutron d) equal to that of 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 neutron What do you with this question? The mass of 3He is: a) the same as 3H Correct! b) slightly less than that of 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 neutron 42% of students chose this answer c) slightly more than that of 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 neutron 24% of students chose this answer d) equal to that of 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 neutron 24% of students chose this answer What were you thinking? Is this question about mass and isotopes? Yes, but also about nuclear chemistry… Terminology • Atomic mass number refers to the number of p⁺ and n⁰ in an atom • Molecular mass refers to the average mass of a molecule. • Molar mass refers to the mass per mole of substance. Sample Problem #1 Your text lists the following atomic masses: Al 26.982 Br 79.904 Calculate the molecular mass of aluminum tribromide (AlBr3). Ionic or covalent? Sample Problem #1 AlBr3: 1 Al = 26.982 x 1 = 26.982 3 Br = 79.904 x 3 = 239.71 Total = 266.69 Molecular Mass • Answer to Sample #1: 266.69 • What does this number refer to? Units! • Unit of molecular mass: “amu” = atomic mass units • 1 amu = 1.661 x 10-24 g • 1 molecule of AlBr3 = 266.69 amu Molecular Mass and Molar Mass Amu’s aren’t really a convenient unit to talk about… That is Avogadro’s number 1 mole of things = 6.022 x 1023 of those things (“things” can be atoms, molecules, or eggs…) Relating amu, g, and moles for AlBr3 1 H atom weighs 1.008 amu = 1.677 x 10-24 g 1 mol of H atoms weighs 1.008 g (1.677 x 10-24 g) x (6.022 x 1023/mol) = 1.008 g/mol 1 mol of AlBr3 weighs 266.69 g *Remember: 1 molecule of AlBr3 = 266.69 amu* Still don’t get it? Look for my handwritten notes posted on blackboard. More on Moles and Atoms • How many moles of sodium (Na) atoms correspond to 1.56 x 1021 atoms of sodium? Answer: 1.56 x 1021 atoms (1 mole / 6.02 x 1023 atoms) = 2.59 x 10-3 moles Na • How many grams of sodium is that? Answer: 2.59 x 10-3 moles (23.0 g /1 mole) = 0.0595 g Na Sample Problem #2 How many pounds does 1 mole of coffee beans weigh? (Assume each bean weighs 2 grams) Answer to Sample Problem #2 1. 1 mol coffee beans x (6.022 x 1023 / mol) = 6.022 x 1023 coffee beans 2. 6.022 x 1023 coffee beans x (2 g / 1 coffee bean) = 1.024 x 1024 g coffee beans 3. 1.024 x 1024 g coffee beans x (1 lb / 454 g) = 2.653 x 1021 lb coffee beans Wake Up! Practice – Calculating Molecular Weight Paclitaxel or Taxol (from the Pacific Yew tree) Chemotherapy medication and anti-cancer drug Chemical Formula: C47H51NO14 Calculate the molecular weight of Paclitaxel. Ans. = Pacific Yew tree If you got this right, skip the next slide, if you got this wrong, practice more. Practice – Calculating Molecular Weight Catechol (argan oil, fruit) C6H6O2 3,4-Dihydroxy-Benzoic Acid (acai oil, hibiscus) C7H6O4 Vanillin (Vanilla plant) C8H8O3 Gallic Acid (oak, algae, fruit) C7H6O5 (+) Catechin Hydrate (apple, tea) C15H14O6 · H2O Caffeic Acid (coffee, spearmint) C9H8O4 3,4-Dihydroxy Benzaldehyde (mushrooms, cork oak) C7H6O3 Juglone (walnut) C10H6O3 Quercetin (fruit, vegetables) C15H10O7 Mass Conservation Again… • Law of Conservation of Mass – Atoms cannot be created or destroyed – In chemical reactions, atoms of one element cannot be converted in atoms of another element 4 H atoms, 4 O atoms and 1 C atom are present before and after the reaction. The total mass before and after the reaction remains the same. The total mass before and after the reaction remains the same! When the following equation is balanced, what will be the Al(NO3)3 : Al2S3 mole ratio? Al(NO3)3 + Na2S → Al2S3 + NaNO3 A.1:1 B.3:2 C.1:2 D.2:3 E.2:1 If you get this wrong, go to the next slide. TEST DRIVE Mock Exam • Sponsored by Academic Success Center • https://www.purdue.edu/asc/about.html • 60-minute, timed practice exam • Mon. Sept. 9 at 8:00 PM • Elliott Hall of Music • Doors open for check-in at 7:00pm • Registration is REQUIRED & Spots are limited! https://tinyurl.com/TestDriveF19