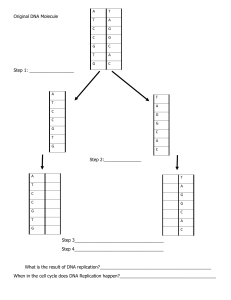
Which of the following components is not involved during the formation of the replication fork? c. DNA ligase Which of the following enzymes is the principal replication enzyme in E. coli? b. DNA polymerase III Overwinding or over tightening of DNA during replication is caused and removed by d. DNAb, gyrase Which translation factor facilitates release of peptide and ribosome? c. RF3 Which of the following is true about DNA polymerase? Select one: a. It can synthesize DNA in the 5’ to 3’ direction Human cells were infected with the virus carrying the genes for telomerase. What could be the result of such modification? c. the cells will undergo more cell divisions than normal You recognised that due to the incorrect nucleotide incorporation the in vitro transcription was interrupted due to the stalled RNA polymerase. Which factor could be used to overcome this problem? c. TFIID Which of the following proteins is able to reverse the Central dogma of molecular biology? Select one: a. Reverse transcriptase Choose the snRNP’s that form the triple complex during the splicing. c. U4, U5, U6 Which snRNP recognises 5’ splice site and facilitates in lariat formation? Select one: a. U6 What is the function of helicase? b. It separates DNA strands Which general transcription factor is capable of phosphorylating RNA pol II CTD on its serine residues? Select one: a. TFIIH Choose the termination method for prokaryotes 1. Release factor binding 2. Rho-dependent termination 3. Hairpin loop (stem loop) formation Select one: a. Only 2 and 3 Choose which of the following proteins doesn’t participate in recombination? b. DnaF Okazaki fragments occur on the __________ and are bonded together by __________ Select one: d. Lagging strand, ligase Which of the following do not belong to promoter elements? d. TATA box The study was conducted on the importance of various DNA polymerases and they were mutated one by one. Choose which out of the following will be associated with the least survival? Select one: a. DNA Pol delta Which feature best describes rho protein’s termination action? Select one: a. Recognition of A:T reach sequence b. Helicase activity Choose out of the following the mechanism which is used for repair lesions in DNA induced by chemical modification. Select one: a. Mismatch repair During the transcription there is a cleavage of pyrophosphate from incoming __________ Select one: a. Ribonucleoside triphosphate In homologous genetic recombination, RecA protein is involved in: Select one: a. involved in pairing homologous DNA and strand invasion Choose the incorrect statement about the post-transcriptional modification of tRNA. b. Polyadenylation Which one of the following proteins functions to significantly increase the processivity of DNA Polymerase III? e. The β-clamp (or sliding clamp) What is required for recognition of promoter region in prokaryotes? d. Sigma factor During the homologous recombination DNA cleavage enzyme generates ___________ on the site of double strand breaks. Select one: a. Single stranded DNA Choose the correct statement about the mammalian DNA repair systems c. They are able to repair more than 99% of the DNA lesions Choose the correct protein set that migrates the holliday junction in homologous recombination. b. RuvAB Which following protein doesn’t helicase or nuclease activity? c. RecA Which general transcription factor is capable of phosphorylating RNA pol II CTD on its serine residues? c. TFIIH What is the first event in formation of the closed complex during bacterial transcription? d. Binding sigma factor of RNA polymerase to -10 and -35 promoter regions Translocation is the process whereby the __________ moves in order to place the tRNA bound to the growing polypeptide chain in the __________ site, thereby freeing the __________ site for a new aminoacyl-tRNA. ribosome; P; A In an experiment you take a DNA in vitro and attempt to replicate it. Which combination will you add to your DNA to get the maximum replication product? b. Dna a, Dna b, Dna c, HU ,SSB polymerase I A biochemist isolated and purified molecules needed for DNA replication. When some DNA was added replication occurred, but the DNA molecules formed were defective. Each consisted of a normal DNA strand paired with segments of DNA a few hundred nucleotides long. Which of the following had been left out of the mixture? Select one: a. DNA ligase Which snRNP is able to recognise the 3’ splice site? d. U2 Which of the following factors are necessary in translation initiation in eukaryotes? Select one: a. Initiation factor 2 Which of the following is not characteristic of genetic code? d. Ambiguous Choose which best describes the function of DNA Polymerase alpha? Select one: a. Lagging strand synthesis A scientist is replicating human DNA in a test tube and has added intact DNA, the replisome complex, and the four deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates. To the surprise of the scientist, there was no DNA synthesized, as determined by the incorporation of radio-labeled precursors into acid-precipitable material. The scientist’s failure to synthesize DNA is most likely due to a lack of which of the following in his reaction mixture? c. Dideoxynucleoside triphosphates Eukaryotic and prokaryotes different with all mentioned statements except _______________ Select one: a. Ability to form replication fork Which out of the following proteins participating in homologous recombination moves along the dsDNA unwinding the strands ahead of it and degrading them: d. RecBCD enzyme Which is the first enzyme that acts in the base-excision repair? b. DNA glycosylase Which enzyme removes the RNA primer during replication? b. DNA polymerase I Human cells were infected with the virus carrying the genes for telomerase. What could be the result of such modification? b. the cells will undergo more cell divisions than normal Okazaki fragments occur on the __________ and are bonded together by __________ d. Lagging strand, ligase At which end are the new DNA bases added? c. 3’ OH end Which of the following is not characteristic of genetic code? Select one: a. Ambiguous Which out of the following isn’t necessary for rho-dependent termination? Select one: c. Stem loop structure Which translation factor binds to aminoacyl-tRNA? Select one: c. EF-Tu Choose which of the following proteins doesn’t participate in recombination? Select one: c. DnaF n which direction does the elongation of transcript is done by RNA polymerase? Select one: c. 3’->5’ direction on 5’->3’ strand If the sequence of an RNA molecule is 5’-GGCAU-3’, what is the sequence of the nontemplate strand of DNA? b. 3’-GGCTA-5’ Which out of the following proteins assemble into long, helical filaments? Select one: d. RecBCD enzyme Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases ________ link ________ to their respective tRNA molecules d. covalently; amino acids Which out of the following prokaryotic proteins or their homolog doesn’t participate in eukaryotic replication? Beta clamp Which spliceosome component does SR protein recruit? Select one: a. U6 Where does the catalytic unit of RNA polymerase be placed during the proper initiation of transcription? Select one: d. -10 site What does the Spo11 protein do during the recombination? Select one: a. Making the nick Choose the incorrect statement about mRNA. d. Introns are removed and exons are spliced together Choose the correct statement about the methyl directed repair system: When bacterial DNA replication introduces a mismatch in a double-stranded DNA, the methyl-directed repair system: d. Corrects the mismatch in the daughter strand Which is the largest class of introns found in mRNA primary transcript? b. Spliceosomal introns Choose the incorrect statement about the TBP. b. Is just associated with RNAP II