Astronomy Quiz: Solar System, Galaxies, and the Universe
advertisement

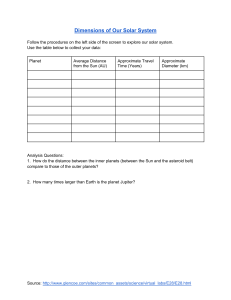
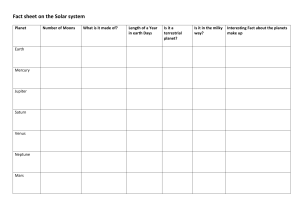
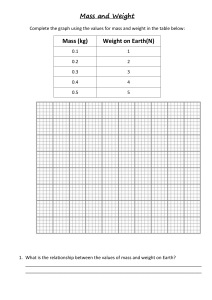
Astronomer: _____________________________________________________ UNIT III – 1st Half Quiz Matching: Match the word in Column A with the definition in Column B Column A Column B _________1) Meteoroid A) Made of Ice, rock, gases, and dust. “Dirty Snowballs” _________2) Comet B) When a small rock is burning up in Earth’s atmosphere “shooting star” _________3) K/T Event C) Point at no place before time & matter exited _________4) Meteor D) The age of the Solar System _________5) Milky Way E) Closer Galaxies move away slower while distant Galaxies are moving away quickly _________6) Hubble’s Law F) A giant asteroid hit Earth and wiped out the dinosaurs. _________7) Meteorite G) The age of the Universe H) This is spiral-shaped and contains billions of stars. Our solar system is on outer _________8) Elliptical edge _________9) 13.7 Billion I) When a small rock is in space. _________10) 4.6 Billion J) When a small rock lands on the Earth. _________11) Singularity K) Most common type of galaxy. Round to Football Shaped. Multiple Choice: Place your answer in the space provided. ________12) Compared to the Jovian planets in our solar system, Earth is (A) more dense and further from the Sun (B) less dense and further from the Sun (C) more dense and closer to the Sun (D) less dense and closer to the Sun ________13) The diagram below represents a side view of the Milky Way Galaxy At approximately which position is Earth's solar system located? (A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D ________14) Most astronomers agree that at the present time universe is (A) contracting (B) expanding (C) staying the same size (D) expanding and contracting regularly ________15) The diagram below represents the bright-line spectrum for an element. The spectrum of the same element observed in the light from a distant star is shown below. The shift in the spectral lines indicates that the star is moving (A) toward Earth (B) in an elliptical orbit around the Sun (C) away from Earth (D) in a circular orbit around the Sun _________16) In which list are celestial features correctly shown in order of increasing size? (small to large) (A) galaxy→ solar system→universe →planet (B) solar system → planet → galaxy →universe (C) planet → solar system → galaxy → universe (D) universe → galaxy →solar system → planet _________17) The diagram below represents a simple heliocentric model. Which object is represented by the letter X? (A) Polaris (B) Earth (C) the Sun (D) the Moon ________18) Compared to Jovian planets, terrestrial planets have a (A) larger size (B) lower density. (C) more rapid rotation. (D) more rocky composition. ________19) The asteroid belt can be found between (A) Earth and Mars (B) Mars and Jupiter (C) Jupiter and Uranus (D) Earth and Venus ________20) Which pair of planets best represents the sizes of Earth and Venus drawn to Scale? (A) (B) (C) (D) _________21) The diagram below represents planets A and B, of equal mass, revolving around a star Compared to planet A, planet B has a (A) stronger gravitational attraction to the star and a shorter period of revolution (B) stronger gravitational attraction to the star and a longer period of revolution (C) weaker gravitational attraction to the star and a shorter period of revolution (D) weaker gravitational attraction to the star and a longer period of revolution ________22) As viewed from Earth, most stars appear to move across the sky each night because (A) Earth revolves around the sun (B) Stars orbit around Earth (C) Earth rotates on its axis (D) Stars revolve around the center of the galaxy ________23) Which information best supports the inference that the universe began with an explosion? (A) measurements of rates of decay using carbon-14 (B) measurements of cosmic background radiation (C) calculations of the distance from the Sun to each asteroid in the asteroid belt (D) calculations of the temperature and brightness of stars Use the table below to answer the questions 24-26 ________24) Which of the Electromagnetic Radiation listed below has the shortest wavelength (A) Infrared (B) Radio Waves (C) Ultraviolet (D) X Rays ________25) Which of the Electromagnetic Radiation listed is the most dangerous? (A) Microwaves (B) Radio Waves (C) Gamma Rays (D) X Rays ________26) Which band of the visible light spectrum has the Longest wavelength? (A) Violet (B) Green (C) Yellow (D) Red Use the table below to answer the questions 27-30 ________27) How do Jupiter's density and period of rotation compare to Earth's? (A) Jupiter is more dense and has a longer period of rotation. (B) Jupiter is less dense and has a shorter period of rotation. (C) Jupiter is less dense and has a longer period of rotation. (D) Jupiter is more dense and has a shorter period of rotation. ________28) Which planet's day (period of rotation) is longer than its year (period of revolution)? (A) Saturn (C) Jupiter (B) Mercury (D) Venus ________29) Which planet has the shortest day? (A) Earth (C) Jupiter (B) Neptune (D) Saturn _________30) The diagram below represents the spectral lines from the light of an element in a laboratory on Earth. Which diagram below best represents the pattern of spectral lines from the same element when it was observed by Edwin Hubble in the light of one of the distant galaxies? (A) (B) (C) (D) EXTRA CREDIT: A) How far is 1 A.U.? (Hint: look at reference tables) _______________________________________________ B) What is the name of the only Galaxy that blue-shifting the Milky Way? ____________________________ C) Mr. Martin talked about the US Government released UFO (UAPs) footage. What were some of the details? ____________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________ D) What is located at the center of most galaxies? ______________________________