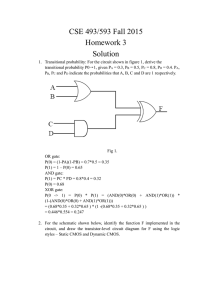
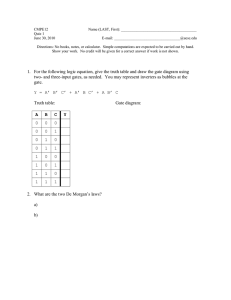
1.1.6 Component Identification Digital Answer Sheet 1) NOT Logic gate: Complete the Truth Table? From analysis of the truth table, why do you think this is called an “INVERTER” gate? X 0 1 The power is inverted from the gate switrch, it flips the x inputs for the z output Z 1 0 3) NAND Logic gate: Complete the Truth Table? From analysis of the truth table, why do you think this is called a “NAND” gate? (NOT AND) 2) AND Logic gate: Complete the Truth Table? From analysis of the truth table, why do you think this is called an “AND” gate? X 0 0 1 1 X 0 0 1 1 Y Z 0 1 0 1 Y 0 1 0 1 Z 1 1 1 0 4) OR Logic gate: Complete the Truth Table? 5) NOR Logic gate: Complete the Truth Table? From analysis of the truth table, why do you think this is called an “OR” gate? From analysis of the truth table, why do you think this is called a “NOR” gate? (NOT OR) X 0 0 1 1 Y Z 0 1 0 1 X 0 0 1 1 6) XOR Logic gate: From analysis of the truth table, why do you think this is called an “XOR” gate? (EXCLUSIVE OR) X 0 0 1 1 Y 0 1 0 1 Z Y Z 0 1 0 1 Clock Signals (The 555 Timer) 1) Using the Circuit Design Software (CDS), create the three LM555CN test circuits shown below on the same sheet. The 555 Timer Oscillator is one of the most common circuits used in introductory electronics. We will use this design to generate a clock signal in the Random Number Generator (our first full circuit design). We will look more closely at this circuit in the next lesson. In each of the three circuits, the only value that is changed is capacitor C2. Circuit A Circuit B Circuit C When C2 is changed from 12μF to 6μF. What happens? The frequency of the clock signal _______________. (increases/Decreases) When C2 is changed from 12μF to 24μF. What happens? The frequency of the clock signal _______________. (increases/Decreases)