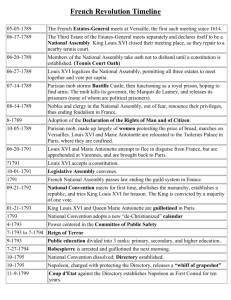
FRENCH REVOLUTION 97% vs 3% Third Estate (extreme hunger and poverty) vs. the Aristocracy, King’s Court and the Clergy Bottom line: Hope and a fair society. End of absolutism (Monarchy) and feudal system. Inspiration: The American Revolution. The embodiment of the enlightenment political dreams. Upheaval: Poor economic policies of Louis XVI. American Revolution debt. Extravagant spending Queen Marie Antoinette (“Madam Deficit”) Changes of Reform based on democracy, citizenship and undeniable rights Liberté, Egalité, Fraternité Effect: Will gradually tore down the ancient structures of society and governments of Europe. The end of medieval times. The French Revolution will be the embodiment of the enlightenment political reality. The embodiment of the enlightenment political ideas of the French philosophes TIMELINE May 5 - June 17,1789: Call of the Estates-General meeting at Versailles.The first such meeting since 1614. The Third Estate of the Estates-General meets separately and declares itself to be the National Assembly. King Louis XVI closed the meeting place, so they repair to the tennis court. June 20,1789: Tennis Court Oath: After being locked out of the Estates-General meeting room, deputies of the Third Estate assembled on a tennis court and swore not to separate until a constitutional regime is established. June 27, 1789: Formal creation of the National Assembly July 2,1789: Louis XVI legalizes the National Assembly. July 7 – 13, 1789: The National Assembly appoints a committee of thirty members to draft a constitution. The National Assembly proclaims itself the Constituent National Assembly, with full authority and power to decree laws; their primary task is to draw up and adopt a constitution. Jacques Necker, the King’ finance minister is dismissed. Demonstrations and speeches take place at the Palais–Royal in Paris. The electors of Paris form a standing committee and a citizens ’militia. July 14,1789: The French Revolution begins with the storming and fall of the Bastille Castle. “No,Sir, it's not a revolt; it's a revolution.” August 4,1789: The end of feudalism and serfdom in France was announced by the National Assembly. Nobles and the clergy accepts to renounce their royal privileges and starts paying taxes. August 26,1789: The Declaration of the Rights of Man and The Citizen was issued and adopted by The National Assembly. Universal suffrage is adopted. Inspiration: The Declaration of Independence and the United States Constitution Base: Equal opportunity, freedom of speech, popular sovereignty and representative government. Introduction: Men are born and remain free and equal in rights. Second article. Rights of liberty, property, security, and resistance to oppression. Total of 17 articles of rights. October 5,1789: The women of Paris invaded Versailles. Parisians, led by a large number of women, march upon Versailles to demand lower bread prices and force the royal family back to Paris, where they will take up residence at the Tuileries. Louis XVI is considered by many a “prisoner” in Paris. The Assembly, still in Versailles, declares, in the spirit of constitutional monarchy, its inseparability from the king. November 1790: The National Assembly confiscates all church lands. July 1790: The Civil Constitution of the Clergy. Reorganize the Catholic Church and strips all their political and social configuration since the Middle Ages. Louis XVI accepts reluctantly a constitutional monarchy. All Catholic Church properties are seized by the French government. June 20,1791: Flight to Varennes. King Louis XVI and Queen Marie Antoinette are arrested while trying to flee from France and are return to Paris. September 3, 1791: Adoption of the constitution. September 14,1791: King Louis XVI formally signs the new constitution. October 1,1791 - The Legislative Assembly is formed. Ends the guild system in France. March 20,1792 - The guillotine becomes the official method of execution. April 20,1792 - France declares war against Austria. August 10, 1792: Louis XVI separated from his family and jailed alone. September 21,1792: The National Convention meets for first time. Abolishes the monarchy, establishes a republic, and tries Louis XVI for treason. December 1792: Commencement of the trial of King Louis XVI. January 21,1793 - Louis XVI sentenced and executed by the guillotine. Nine months after Marie Antoinette will be guillotined. Starts Civil War. Austria, Great Britain, Prussia, Holland, Sweden and Spain form a coalition against the revolutionaries. March 1793: Bitter struggle in the National Convention. April 6,1793: The Committee of Public Safety is formed with broad power all French society. It will rule France during the Reign of Terror. August 1793 : A National Draft was issued calling for all able-bodied men to enlist in the army. September 1793 to July 1794 : The Reign of Terror begins as Robespierre, the leader of the Committee of Public Safety, declares that terror will be the "order of the day" for the revolutionary government. The Law of Suspects is decreed. Anyone suspected of opposing the revolutionary government is arrested. Thousands of people will be executed over the next year. The Reign of Terror court sentenced 20,000 to 40,000 people to death. Also, starts the wave of dechristianization of France. Robespierre forms The Cult of the Supreme Being June 8,1794: Robespierre celebrates the Festival of Liberty, Reason, and the Supreme Being in Paris. July 27,1794: The Reign of Terror comes to an end as Robespierre is arrested by the National Convention. The day after Robespierre was beheaded by guillotine. July 14,1795: "La Marseillaise" is adopted as the national anthem of France. November 2,1795: The Directory is formed and takes control of the government and all military of France. Control all executive responsibilities and appointments. November 9,1799: Coup d’ état. Napoleon takes over France. Overthrows the Directory. Establishes the French Consulate. End of the French Revolution. Begins the Napoleonic Age up to 1815. THE AGE OF NAPOLEON TIMELINE 1769: Napoleon is born in the Mediterranean Island of Corsica. 1798-1799: Napoleon forces invades Egypt. “From the heights of the Pyramids, forty centuries look down on us”. France takes a short control of Egypt as less than a year, British navy beats French forces in the Battle of the Nile. Napoleon returns to France. 1799 - 1804: First Consul. Dictatorship. 1803: Napoleon sold France’s Louisiana Territory to the United States for $15 million. 1804: Napoleon crowns himself Emperor. Names himself Napoleon I. Establishes an authoritarian state. -Restore relations with the Catholic Church -Creation of Napoleonic Code of Law Equality under the law; Protection of private property -Creation of the National Bank of France -Centralized the government. Streamline the military -Centralized education -Sponsored of the arts and sciences 1805: France is defeated in the Battle of Trafalgar by the British. A year later Napoleon in reprisal against the British created an economic warfare with his so-called Continental system. 1808: France occupies Spain. Name Jose Bonaparte, king of Spain. 1804-1814: The French Empire period. 1804-1808: Great victories against Austria, Prussia, Portugal and Spain. -French Empire (France) -Dependent States: Spain, Holland, Kingdom of Italy, Switzerland, Duchy of Warsaw, Confederation of the Rhine -Allied States: Austria, Prussia, Russia, Sweden -Major enemy: great Britain 1812-1813: Napoleon disastrous invasion of Russia. At the same time, Great Britain and Spain joined and beat Napoleon forces. In his return from Russia, ‘The Battle of Nations’ a coalition of Austrian, British, Prussian, Russian and Swedish troops defeats Napoleon forces. Also France loses battles in Spain and Portugal. As he retreats and arrives in France he abdicates as Emperor and goes into exile in Elba. 1814: The Congress of Vienna. European nations convenes and agrees on an Europe with a balance of power. Monarchy re-established with Louis XVIII (younger brother of Louis XVI). March 20,1815: Napoleon returns to Paris and its welcome with cheers. Re establishes the French Republic and starts The Hundred Days Period. European countries ally against Napoleon. June 18,1815: Battle of Waterloo (today Belgium). Commanded by the British’ Duke of Wellington made true in battle Napoleon last decisive and final defeat. Marked the end of Napoleon military career. June 22,1815: Great Britain and European allies obliged Napoleon to abdicate his head state position. In October his exiled to the remote British Island of Saint Helena in the South Atlantic Ocean. May 5,1821: Napoleon dies in St. Helena. In 1840 his body his transferred to France and entombed at Les Invalides in Paris.