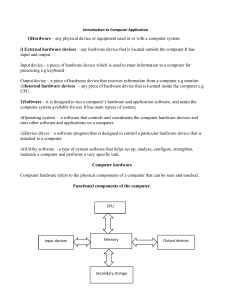
CO_LAB_3 D.Shanmukh Cs21b018 1)perf: perf is a performance analysis tool for Linux systems that provides a variety of sub-commands for measuring various performance metrics, including CPU performance, memory performance, and more. perf is designed to be used by system administrators and developers to diagnose performance issues and improve system performance. How to use: The perf command can be used in a variety of ways, depending on the desired performance metric and the sub-command used. For example, to measure CPU performance, the following command can be used: $ perf stat -e cycles -a This will measure the number of CPU cycles used by all tasks on the system. To measure memory performance, the following command can be used: $ perf mem -v This will display a detailed breakdown of memory usage by tasks on the system. Example: In this example, we use the perf command to measure CPU performance. The following command will measure the number of CPU cycles used by all tasks on the system. $ perf stat -e cycles -a [The output of this command will display the number of CPU cycles used by all tasks on the system.] 2) cat /proc/cpuinfo: The "cat /proc/cpuinfo" command is used to display information about the CPU(s) on a Linux system. This information includes details about the architecture, clock speed, cache size, and other information about the CPU(s) that can be useful for performance analysis and optimization. How to use: Simply run the command "cat /proc/cpuinfo" in the terminal. The output of this command will provide detailed information about the CPU(s) on the system. Example: In this example, we use the "cat /proc/cpuinfo" command to display information about the CPU(s) on a Linux system. $ cat /proc/cpuinfo [The output of this command will provide detailed information about the CPU(s) on the system, including details about the architecture, clock speed, cache size, and more.] 3) lscpu: lscpu is a command line tool that displays information about the CPU architecture and hardware on a Linux system. It provides a detailed view of the CPU, including information about the number of processors, cores, and threads, clock speed, architecture, and cache size. How to use: Simply run the command "lscpu" in the terminal. The output of this command will provide detailed information about the CPU architecture and hardware. Example: In this example, we use the lscpu command to display information about the CPU architecture and hardware on a Linux system. $ lscpu [The output of this command will provide detailed information about the CPU, including information about the number of processors, cores, and threads, clock speed, architecture, and cache size.] 4) time <executable>: The time command is used to measure the amount of time it takes for an executable to run. This can be useful for performance analysis, as it provides a way to measure the execution time of an application or command. How to use: To measure the execution time of an executable, simply run the time command followed by the name of the executable, like this: $ time <executable> Example: In this example, we use the time command to measure the execution time of the "ls" command. $ time ls [The output of this command will display the amount of time it took for the "ls" command to run, along with other information such as memory usage.] 5) cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/cpuinfo_cur_freq: The "cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/cpuinfo_cur_freq" command is used to display the current frequency of the CPU. This information can be useful for performance analysis and optimization. How to use: Simply run the command "cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/cpuinfo_cur_freq" in the terminal. The output of this command will provide the current frequency of the CPU in kilohertz. Example: In this example, we use the "cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/cpuinfo_cur_freq" command to display the current frequency of the CPU. $ cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/cpuinfo_cur_freq [The output of this command will provide the current frequency of the CPU in kilohertz.]