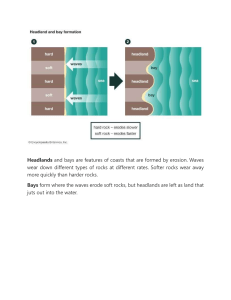
Arches are formed when destructive waves (waves which Teacher form erosional features along Student the coast) strike against the base of headlands to form caves. The erosional processes of corrasion (the physical action of sand and rock fragments carried by waves being hurled against the base of cliffs leading to their breakdown) and hydraulic Measuring action (the force of waves as they repeatedly break against a Sand cliff, causing fragments of rock to become dislodged) lead to the Plate 4: Measuring the width of an Arch formation of caves in the area between high and low tide. As these processes continue on either side of a headland the caves formed become deep enough to meet each other, creating a tunnel through the headland known as an Arch. Students observed several arches which were not quite large which indicated small amounts of erosion. (See Plate..) Arc Due to constant wave erosion of Arches, Stacks are formed S when arches are widened, eventually, the roof of the Arch cannot be supported anymore and breaks off and falls into the sea. The seaward part of the Sta headland becomes detached from the rest of the headland and is called a Stack. When Stacks are repeatedly eroded they are Sa known as Stumps. In the study area a stack was Plate : Stack Found In Middle found which was quite eroded and some distance away from the headland indicating frequent strong erosional processes leading to its deterioration. ( See Plate..)