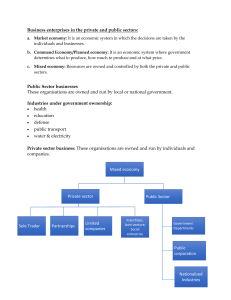
Topic 3 Political Environment of International Marketing International Marketing After studying this topic, you will be able to:: Describe the types of governments prevalent in world economics. Distinguish between the political and economic systems. Carry out the political risk analysis in an environment which is infested by a large number of political parties not in tune with each other. Find out the causes of retardation of economic growth of a country in case there is political instability due to insurgency and threat of terrorism. Get detailed information regarding the international institution affecting political environment of a country. Unit 3: Political Environment of International Marketing Contents 3.1 Scope 3.6 Summary 3.2 Types of Government 3.2.1 Political Systems 3.2.2 Economic Systems 3.7 Keywords 3.3 Political Risk Analysis 3.8 Review Questions 3.4 Management and Measurement of Political Risk 3.4.1 Privatization, Insurance, Political, Private and Government 3.9 Further Readings 3.5 Super-national Organizations and International Institutions 3.5.1 International Monetary Fund (IMF) 3.5.2 The World Bank 3.1 Scope 3.2 Types of Government There are two types of government system as follows: 3.2.1 Political Systems – Parliamentary (Open) or absolutist (closed) the citizens are supposed to be consulted from time to time for learning about their opinions and preferences. Absolutist government include monarchies and dictatorships. The ruling regime dictates government policies without considering citizens’ needs or opinions. 3.2.2 Economic Systems – the basis explains whether business is privately owned or government owned or whether there is a combination of private and government ownership. 3.2.2 Economic System • Socialist government owns and operates the basic major industries but leaves small business to private ownership. Communist theory holds that all resources should be owned and shared b all the people. • Capitalist provides for a free market system that allows business competition and freedom of choice for both consumers and companies in a market oriented system in which individuals, motivated by private gain, are allowed to produce goods or services for public consumption under competitive conditons. Case 1 Political System The biggest threat that India is facing today is the slow economic growth because of two great factors. First, terrorism from across the border in Jammu and Kashmir and other parts of the country which is dissuading the MNCs for foreign direct investment into the country. Second, poor labour legislation. Unless higher and fire system in the labour legislation is brought, foreign companies will not like to come to India for investments. The greatest risk that any foreign company faces today is the instability of a government due to terrorism in the country. Though the government is stable in the country and is running smoothly and efficiently, however, the threat of terrorism is making the MNCs to avoid investing in a big way. It is, therefore, essential that terrorism is curbed at all levels for which the government must go all out to ensure the safety and integrity of the people and the property of the country. India, after 1990, opened its economy to international institutions through modernization, privatization and globalisation. There is hope now that the economic growth of the country will touch 6.5 % of GDP as envisaged by the Reserve Bank of India Annual Report for the year 2003-04 3.3. Political Risk Analysis Risks – confiscation, expropriation, nationalization, domestication and creeping expropriation. Such actions are more likely to be levied against foreign investments though local firms are not totally immune. Nationalization involves government ownership and it is the government that operates the business being taken over. Domestication is where foreign companies relinquish control and ownership either completely or partially to the nationals. General instability risk is related to the uncertainty about the future viability of a host country’s political system. Operation risk proceeds form the uncertainty that a host government might constrain the investor’s business operations in all areas including production, marketing and finance. Expropriation is the action of the state or an authority of taking property from its owner for public use or benefit. Indicators of Political Instability • Social unrest is a social disorder that is caused by such underlying conditions as economic hardship, internal dissension and insurgency and ideological, religious, racial and cultural differences. • A liberated political climate can easily lead to a call of the long suppressed national minority group for cultural and territorial independence. Attitudes of Nationals –The nationals’ attitude towards foreign enterprises and citizens can inhospitable. Nationals are often concerned with foreigners’ intentions with regard to exploitation and colonialism, and these concerns are often linked to concerns over foreign governments’ actions that ma be seen as improper. Policies of the Host Government – Government policy formulation can affect business operations either internally or externally. The effect is internal when the policy regulates the firm’s operations within the home country. The effect is external when the policy regulates the firm’s activities in another country. 3.4 Management and Measurement of Political Risk • Avoidance – means screening out politically uncertain countries. • Understanding with a foreign government as to their rights and responsibilities. • Increase and maintain their bargaining power when their technical, operational and managerial complexity requirements are not within reach of the host country’s abilities. • Cooperation through long-term contractual agreements, alliances, interlocking directorates, inter-firm personnel flow, etc. • Product and geographic diversification to gain “flexibility”. 3.3 Description of Explanatory Variables 3.4.1 Privatization, Insurance: Political, Private and Government • Privatization – The objectives of privatization are: promotion of competition and efficiency reduction of debt and subsidies, return of flight capital and broadening of domestic equity ownership. • Political Insurance: This can be achieved through risk avoidance and risk reduction. In order to achieve these, MNCs can employ the strategy of risk shifting. • Private Insurance: Shifting political risk to a third party through the purchase of political insurance. • Government Insurance: There are non-profit, public agencies that can provide essentially the same kind of coverage. 3.5 Super-national Organization and International Institutions • A supranational union is a type of multi-national organization where negotiated power is delegated to an authority by governments of member states. • An international organization is an organization with an international membership, scope or presence. 3.5.1 International Monetary Fund (IMF) 3.5.2 The World Bank International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) International Development Assistance (IDA) International Financial Corporation (IPC) Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA) Summary • Developed countries are also quite concerned about foreign direct investments, For example, the citizens of many nations pressurize the companies of their countries not to invest in South Africa because of that country’s apartheid policy. • Companies can derive positive economic benefits when the relationship between two countries improves or when the host government adopts a new investment policy. As in the case of India, the country was highly regulated, closed economy, which discouraged foreign direct investment. • In order to appraise the political environment of a country, the knowledge of the form of government of that country is essential. The absolutist governments include monarchies and dictatorships. • Political system of many countries odes not fall neatly into these two categories. This classsifcation results in four types of governments: two party, multi-party, single party and dominated one-party. • In a two party system, there are typically two strong parties that take turns in controlling the government although other parties are also allowed. The United States and United Kingdom are classic examples of two party systems. • The two parties have generally different philosophies resulting in a change in government policy when one party succeeds the other. • The strength and the longevity of the coalition government depend largely on cooperation of government allies. Usually, various opposing parties continuously challenge the coalition government. • The countries operating with this type of system include Germany, France, Israel and India. Present government in India has 18 coalition partners. This form of government is often used by countries which are in early stages of development of a parliamentary system. • The economy of a country depends upon the political stability of that country. Italy is another politically unstable developed country. Democratic political system is a prerequisite for political stability also. Classification of government based on economic system can be another basis of its types. • In the economic systems, the basis explains whether business is privately owned or government owned or whether there is a combination of private and government ownership. 3.7 Keywords Communist Theory: This theory holds that all resources should be owned and shared by all the people (not by profit seeking enterprises) for the benefit of the society. Confiscation: It is the process of a government’s taking ownership of a property without compensation. General Instability Risk: It is related to the uncertainty about the future viability of a host country’s political system. Nationalisation: It involves government ownership and it is the government that operates the business being taken over. Political Risk: Political risk is the risk of loss that occurs as a direct result of the actions of a government or changes in the political structure in a particular country. Socialist Government: A socialist government owns and operates the basic major industries but leaves small business to private ownership.