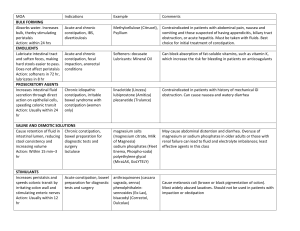
1 Bowel Disorder Drugs I. Agents for Diarrhea: Adsorbents, anti-motility drugs (anticholinergic and opiates for more severe cases)), probiotics for intestinal antibiotic induced diarrhea (AKA intestinal flora modifiers and bacterial replacement drugs, keep it neutral ) à used to tx diarrhea Adsorbents: ANTIDIARRHEAL Adsorbents MOA: Coat the walls of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract - bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol): avoid if ASA allergy - Bind to the causative bacteria or toxin causing the diarrhea o OTC which is then eliminated through the stool o Darkens stool temporarily and tongue - Activated charcoal - Anti-lipemic drugs colestipol and cholestyramine (b/c they bind and one of side effects of anti-lipid drugs is constipation) Interactions § Adsorbents decrease the absorption of many drugs, including digoxin, quinidine, and hypoglycemic drugs § Watch digoxin levels closely, monitor glucose in diabetics § Adsorbents cause increased bleeding time and bruising when given with anticoagulants (warfarin) b/c interferes with Vit K absorption § Toxic effects of methotrexate are more likely when given with adsorbents. A/E § Adsorbents § Increased bleeding time: bismuth § Constipation, dark stools & blue tongue: bismuth § Tinnitus: bismuth § Metallic taste: bismuth Anti-Motility: Opiates Examples: MOA: Primacy Action: - Paregoric, loperamide [OTC] - Decrease bowel motility and activate opioid - IMODIUM Prototype: Diphenoxylate with atropine sulfate (Lomotil): contains diphenoxylate receptors in GI tract to decrease intestinal motility (synthetic opioid agonist) and atropine - Secondary effect: reduce pain by relief of rectal spasms (anticholinergic) o Purpose of atropine is to discourage Decrease transit time through the bowel, allowing more time for recreational use of this drug b/c person water and electrolytes to be absorbed will experience unpleasant anticholinergic effect o contra: diarrhea associated with pseudomembranous colitis or toxigenic bacteria, C.Dif o SCHEDULE V Agent Use: Diarrhea 2 Contra: - Megacolon or IBD à can cause perforation - Diphenoxylate: severe e-lyte imbalance or dehydration A/E - Interaction: § Alcohol & other CNS agents: additive effect - High doses: typical opioid effects o Euphoria or CNS depression o Confusion, lethargy, hypotension, urine retention Atropine: o Anticholinergic properties: constipation, dry mouth, blurred vision, urine retention Probiotic: Dietary Supplement MOA: - Intestinal flora modifiers and bacterial replacement drugs Find this in yogurt: sometimes pt doesn’t - Bacterial cultures of Lactobacillus organisms want to take more pills so they can eat work by: yogurt instead to gain this, but yogurt has o Supplying missing bacteria to the GI tract to be separated from other meds. o Suppressing the growth of diarrhea-causing bacteria Lactobacillus acidophilus (Bacid) - Use: § § § Treat IBS ulcerative colitis C. diff-associated diarrhea & rotavirus diarrhea Interactions: § AB and antifungals: if concurrent use: ADMINISTER at least 2 HOURS apart from probiotics § Have pt eat yogurt 2 hours apart from other meds. A/E: (restoring flora and suppressing diarrhea causing bacteria) § Flatulence and gas § Bloating § Infection à ESP if severely ill or immunocompromised after Long-term AB use Contra: - Aspirin allergy - Myasthenia gravis NSG for Anti-diarrheal § Obtain thorough history of bowel patterns, general state of health, and recent history of illness or dietary changes; assess for allergies. § Do NOT give bismuth subsalicylate (pepto bismol) to children or teenagers with chickenpox or influenza because of the risk of Reye’s syndrome b/c contains aspirin § Also pepto has aspirin in it so cant take if pt has ASA allergy! § Use adsorbents carefully in older patients and those with decreased bleeding time, clotting disorders, recent bowel surgery, or confusion. § Teach patients to take medications exactly as prescribed and to be aware of their fluid intake and dietary changes. § Assess for myasthenia gravis – contra § Teach pt to take med as prescribed and monitor food intake and any changes to their diet 3 § § § Assess fluid volume status, input and output, and mucous membranes before, during, and after initiation of treatment. Teach patients to notify their prescribers immediately if symptoms persist or worsen Monitor for therapeutic effect à diarrhea go away II. Laxative to TX Constipation § Types § Bulk forming: psyllium (metomucil) § Emollient (stool softeners (docusate sodium which is what we want pt on if theyre taking an opoid) , lubricant laxatives: mineral oil) § Hyperosmotic: polyethylene glycol 3350, glycerin, lactulose § Saline: Magnesium salts § Stimulant: bisacodyl, senna - All contra-indicated in case of allergy - Cautious use in case of acute abdominal surgery o Appendectomy symptoms: abdominal pain and tenderness, N/V o Intestinal obstructions Bulk Forming Laxative (high fiber) Bulk forming [High fiber] MOA: - Psyllium (Metamucil) - Absorb water to increase bulk: temporary relief constipation Safe and available OTC, can be used long-term. § Acute & chronic constipation Also comes as wafers/crackers Use: - decrease diarrhea: IBS, diverticulosis Acute & chronic constipation A/E - Impaction or intestinal obstruction Fluid overload Electrolyte imbalances Esophageal blockage NSG - Patients should take bulk-forming laxatives as directed by the manufacturer with at least 240 mL (8 oz) of water or juice - Metamucil- 8 oz water or 1 full glass water after powder form has been stirred into it. Take fluid immediately o Has to be mixed very well!!! And drink immediately because can start to thick up - Take immediately upon stirring to avoid choking or swelling - Never take in powder formà can block airway!! Drink plenty of water!!! Prevent choking or airway obstructions!! 4 Emollients – stool softeners and lubricants Stool softeners and lubricants MOA: - Stool softeners: docusate salts: Softens - Promote more water and fat into the stools - Lubricants: mineral oil - Lubricate the fecal material and intestinal walls to help ease movement of the bowel - Surfactant: helps to lower surface tension of fluids to allow more water to be absorbed into stool (Softener- docusate) Use: - Constipation & softening fecal impaction A/E - Skin rashes With mineral oil: Decreased absorption of fatsoluble vitamins: ADEK o Need to supplement vit A,D,E,K Electrolyte imbalances Lipid pneumonia - Agents: - Polyethylene glycol (PEG) (golytle) - Sorbitol, glycerin - Lactulose (also known as liver drug b/c used to reduce elevated serum ammonia levels in pt with hepatic encephalopathy ) Use: A/E - - For pt starting on an opioid, they should also be starting on a stool softener – docusate sodium (colase) Hyperosmotic MOA: - Increase fecal water content à Results in bowel distention, increased peristalsis, and ultimately evacuation of bowel movement Chronic constipation Prevent painful elimination: episiotomy (cut woman during labor and stich her up) or hemorrhoids Evacuate bowel before diagnostic and surgical procedures- PEG used for colonoscopy Colonoscopy [High dose] Abdominal bloating Electrolyte imbalances Dehydration esp. with PEG b/c pt has to drink 4 L Rectal irritation: from constant bathroom runs Lactulose: Liver Drug - Used for Constipation - Used to Reduce Ammonia levels in hepatic encephalopathy - Contra: low-lactose diet - Form: PO (Drink) or rectal use (enema) Hyperosmotic glycerin: mild – suppository - Action: Promotes bowel movement by increasing osmotic pressure in intestines - Great use for children - Similar to sorbital - Forms: rectal solution and both adult/pediatric supp. Polyethylene glycol 3350 – PEG - Very strong/Potent laxative inducing total cleansing of bowel - Patient has to drink 4L - Powder reconstituted in large volume of fluid (1 gallon) 5 - CAUTION: Diabeticsà its VERY sweet syrup Can be taken with juice, milk or water Enema: instruct to hold 30-60 minutes Stop if experiences severe abdominal pain- d/c - Drink gradually day before test on afternoon Clear liquid diet day before procedure Starts to work à see Diarrhea: 30-60 minutes after ingestion Complete evacuation: within 4 hours Massive electrolyte imbalance can occur Pt has to have a bathroom nearby or bedside commode when drinking this A/E o o o Abdominal bloating Rectal irritation Electrolyte imbalance § Dehydration Saline Laxative: Milk of Magnesium Agents MOA: - Magnesium hydroxide (Milk of - Increase osmotic pressure within the intestinal tract, Magnesia) causing more water to enter the intestines à Results in bowel distention, increased peristalsis, and - Magnesium citrate (cherry flavor) evacuation Use: - BOWEL PREPS (laxatives) or to remove unabsorbed toxins from GI tract Contra: - RENAL DISEASE: b/c of hypermagnesemia – the kidneys cannot clear the magnesium - abdominal pain, N/V, obstruction, acute abdomen or rectal bleeding Caution: - cautious use in renal insufficiency: can result in HYPERMAGNESEMIA, toxicity A/E - Magnesium toxicity [renal insufficiency] Fluid retention Imbalances, cramping, diarrhea, increased thirst 6 Agents - Bisacodyl: PO tab and Rectal suppository o Enteric coated if PO - Senna – OTC Use: - Constipation Bowel prep before colonoscopy, surgery A/E - Rectal irritation/burning leading proctitis Nutrient malabsorption Skin rashes Gastric irritation E-lyte imbalances Discolored urine Methylnaltrexone Alvimopan Stimulant: Bisacodyl MOA: - Via intestinal stimulation à Increases peristalsis via intestinal nerve stimulation - Be careful with dependence Interactions: - Milk & antacids: destroy enteric-coating of bisacodyl o Take at least 1 hour apart from ingesting these substances NSG Need baseline Basic metabolic panel Do NOT use bisacodyl on regular basis CANT CHEW B/C ENTERIC COATED NO MILK, juice, ANTACID w/in 1 hour of taking med Peripherally Acting Opioid Antagonist MOA: - Blocks entrance of opioid into bowel Used: - Used in Treatment of constipation related to opioid use and bowel resection therapy - Allow bowel to function normally with continued opoid use Strict regulations for use Irritable Bowel Syndrome Agents - Linaclotide - Lubiprostone -Chloride channel activator [C]-removed from market - Alosetron-selective serotonin 5-HT receptor o Discontinue after 4 weeks if inadequate A/E o Constipation, GI toxicity: ischemic colitis, bowel obstruction, impaction or perforation o Pt must be enrolled in prescribing program à highly regulated BLACK BOX WARNING: ISCHEMIC COLITIS IBS is Chronic intestinal discomfort characterized by cramps, diarrhea, or constipation - pt usually cope with the symptoms by avoiding irritating foods or taking OTC laxatives and antidiarrheal drugs. 7 IBD: Sulfasalazine Sulfasalazine Others: - 5-aminosalicylates: mesalamine: decreases inflammation [inhibits prostaglandins] - Glucocorticoid: Hydrocortisone - Immunosuppressant: azathioprine - Immunomodulator: infliximab Antibiotics: Metronidazole o Use: Crohn’s disease; relief mild to moderate acute episodes of ulcerative colitis o NO ALCOHOL Contra: - Sulfa allergy, ASA allergy or thiazide diuretics; pregnancy, breastfeeding Interactions: - Sulfasalazine: Iron & antibiotics: alter absorption - Mesalamine: decrease absorption: digoxin, PO antidiabetic meds Cautious Use: liver and kidney disease A/E - Blood disorders: agranulocytosis, hemolytic & macrocytic anemia o Monitor CBC Nausea, fever, rash arthralgia à Notify provider NSG - - Can be given with food or after meals Hydration, hydration: 1200-1500 mL daily fluid intake to prevent CRYSTALLURIA and calculi formation à REMEMBER IT’S A SULFA DRUG Teach not to crush CR or enteric coated agents or do not chew 8 Antiemetics and Antinausea Drugs: Work by blocking one of the vomiting pathways thus inducing the stimulus of vomit. (combining drugs of dif. Categories increases anti-emetic effects b/c blocks more than 1 pathway Goal: to prevent and reduce N/V - Anticholinergic drugs - Antihistamines (histamine 1 [H1] receptor blockers) - Antidopaminergic drugs - Neurokinin Antagonists - Prokinetic drugs - Serotonin blockers - Tetrahydrocannabinoids Anticholinergic (Acetylcholine Blocker): Scopolamine Drug: SCOPOLAMINE [C] MOA: - Interferes w/transmission of nerve impulses going from Formulation: vestibular of inner ear to vomiting center in brain - Comes as oral, injectable, occular o Dry up GI secretions, reduce smooth muscle - Most commonly used as transdermal spasms patch à applied to hairless area behind ear every 3 days, 4h before travel Use: - Prevent and treat n/v association w/Motion sickness (car, cruise, plane) - prophylaxis & postop n/v Contra: Patch form: contra in pt with history of narrow-angle- glaucoma! Use another agent A/E r/t anticholinergic properties: - dry mouth - visual changes – blurred vision - tachycardia - constipation - urine retention - 3-D’S: dizzy, drowsy, disorientation NSG - - Can only admin this drug after careful assessment of pt health and medication history Contra in pt with history of narrow-angle- glaucoma! Use another agent Apply 1 patch to hairless area behind 1 ear every 3 days, 4 hours before travel Apply patch behind ear as directed o Area needs to be cleansed and dried before the patch is applied o If patch becomes dislodged à residual drug must be washed off and fresh patch put in place o Instruct to leave patch in place for 72 as indicated Instruct to AVOID alcohol Instruct regarding activities that require mental alertness or motor skills b/c of dizziness or drowsiness 9 Antihistamines (H-1 Receptor Blockers) Drugs: Anticholinergic antihistamine MOA: - Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) - Block H-1 receptors to prevent Ach from binding to receptors - Dimenhydrinate (Dramamine) - Possess potent Anticholinergic properties à - Meclizine antisecretory and antispasmodic - Hydroxyzine - Prevent anticholinergic event in both Vestibular and reticular systems Use: MOTION sickness, N/V Contra: SHOCK AND LACTATION (meclizine) – cat B A/E - Drowsiness, dizziness, confusion Anticholinergic effects: - dry mouth - visual changes – blurred vision - tachycardia - constipation - urine retention NSG - wont be asked about dosing just know its given before travel about 1 hr 25-50 mg 1 hours before travel & repeat daily during travel; PO: 25-100 mg/day, divided 1-4 times daily Hydroxyzine: NEVER given IV only oral or IM! Why not? à if given IV causes tissue damage, thrombosis, gangrene o also not given intraarterial or SQ so RIGHT ROUTE IS IMPT. W/ THIS MED! Anti-dopaminergics Drugs: - Phenothiazine - Prochlorperazine: PO, IM, PR (prorectum), IV [c] - - Use: - Promethazine: IM, IV, PO [c] o Preferred route: IM, PO o IV route not pref: caution for accidental intra-arterial injection causing tissue damage that needs amputation o Best dilute in 10 mL of fluid – more dilute the better à give in port furthest from pt vein, not in hand or wrist, stop if burning occurs o Sedation is beneficial A/E o Not to be given SQ Droperidol: BLACK BOX WARNING: requires continuous EKG monitoring b/c concerns of QT widening and possible ventricular dysrhythmias. Motion sickness Also used for psychotic disorders and intractable hiccups MOA: - Block dopamine receptors in the CTZ - Have antihistamine, antidopamine, and anticholinergic properties 10 Contra: - Prochlorperazine: hypersensitivity to phenothiazine, coma, those with seizures, encephalopathy or bone marrow suppression - Promethazine: contra in pt younger than 2 y/o BBW - Droperidol: requires continuous EKG monitoring b/c concerns of QT widening and possible ventricular dysrhythmias. A/E - Prochlorperazine and promethazine: sedation NSG - - Promethazine Best dilute in 10 mL of fluid – more dilute the better à give in port furthest from pt vein, not in hand or wrist, stop if burning occurs o Don’t give sub Q Droperidol: continuous EKG monitoring Neurokinin Inhibitor [Substance P] Drugs: MOA: - Aprepitant [B]: PO - inhibits Substance P/neurotkinin 1 receptors in the brain stem - Fosaprepitant: IV form of aprepitant - can be used in conjunction with serotonin blockers and - Akynzeo: New combo: 5-HT3 [palonsetron] & glucocorticosteroids substance P inhibitor [netupitant USE: - Prevents n/v associated with high emetogenic chemotherapy o chemo drugs such as high dose cisplatin – cause N/V - Postop n/v Interaction: - Warfarin, oral contraceptives: REDUCED EFFECTIVENESS o May induce metabolism of warfarin so check INR before each med cycle o Barrier contraceptive - Cytochrome P-450 enzyme inhibitor A/E PO form: Fatigue - Dizziness - possible liver damage NSG 11 Drugs: Metoclopramide [B]-Dopamine antagonist (Blocks dopamine receptors in CTZ zone) Prokinetic MOA: - CTZ zone is desensitized by impulses it receives from GI tract à - Also stimulates peristalsis in GI tract enhancing gastric emptying - Promote movement of substances via GI tract & increase GI motilityà Helpful In preventing aspiration in those receiving tube feedings. - Controls n/v by blocking dopamine& serotonin receptors in the CTZ USE: - IV: postop & chemo-induced N/V - Helps with delayed gastric emptying à stimulates peristalsis to speed it up - Gastroesophageal reflux, - Diabetic gastroparesis (can also be used for headache) Contra: - seizures, pheochromocytoma, Breast Cancer GI obstruction, allergy to procaine or procainamide A/E - TREMORS: Extrapyramidal effects tardive dyskinesia: long-term use sedation diarrhea NSG - Prescription only b/c severe A/E if not used correctly Metoclopramide given orally is best taken 30 minutes before meals and at bedtime Metoclopramide: A/E is Extrapyramidal symptoms reactions (tremors): assess pt and teach to report to provider immediately Educate pt regarding long-term use effectsà metoclopramide long term use can cause tardive dyskinesia Serotonin Blockers: [5-HT3 receptor blockers] – SETRON Drugs: MOA: Prototype: ondansetron (Zofran)-[B] - Block serotonin receptors in the GI tract, CTZ, and VC - PO, Parenteral & PO disintegrating - IV: 8 mcg can be given IVP over 2-5 minutes Others: - granisetron [patch] - palonosetron USE: - nausea and vomiting [N/V] in patients receiving chemotherapy and for postoperative nausea and vomiting Ondansetron USE: Chemo-induced n/v, postop n/v - hyperemesis gravidarum: the severe vomiting in pregnant women (become very dehydrated) 12 Concern: cleft palate development in fetus 1st trimester Contra: in pt with prolong QT syndrome – cardiac condition A/E - NSG - headache, dizziness diarrhea blurred vision prolonged QT interval - Potential for When used to prevent post-op N/V dose is given 30 min before the end of a surgical procedure If used for N/V in cancer tx: given 30-60 min before start of chemotherapy Tetrahydrocannabinoid: Dronabinol Drugs: (controlled substance) MOA: Dronabinol – synthetic derivative of THC – PO only - Tetrahydrocannabinoid is major active substance in marijuana - Is a controlled substance USE: - Nausea, Vomiting esp in cancer - Used as second line tx when use of other anti-emetics has failed - Stimulate appetite enhancer & weight gain à AIDS pt or chemo pt Contra: - Known drug allergy A/E - NSG Inhibitory effect on reticular formation, thalamus, cerebral cortex Drugs: Ginger: Zingiber officinate A/E - Herbal Products: Ginger: Zingiber officinate USE: - antioxidant & relief of nausea and vomiting, (chemotherapy, morning sickness, and motion sickness Anorexia, nausea and vomiting, skin reactions Interactions: - May increase absorption of oral medications - Increase bleeding risk with anticoagulants & anti-platelets like clopidogrel Pediatric Considerations - Syrup of Ipecac & Poisoning - NO LONGER USED as home treatment for poisoning (AAP, 2003) - Parent must call Poison control hotline @ 800-222-1222 13 NSG for anti-nausea meds - Assess complete nausea and vomiting history, including precipitating factors: what brought on the N/V? . - Assess current medications. - Assess for contraindications and potential drug interactions - Many of these drugs cause severe drowsiness; warn patients about driving or performing any hazardous tasks à tell pt about doing activities requiring mental alertness. - Taking anti-emetics with alcohol may cause severe central nervous system depression. - Teach patients to change positions slowly to avoid hypotensive effects: drowsiness, dizziness. - Chemotherapy: given 30-60 minutes before chemotherapy begins - Give med à Surgical procedures:30 before end - Caution in Peds: cautious use-paradoxical reaction à hyperactivity - Older: CNS changes, hypotension, psychotic-type reaction - Antidopaminergics: o Cautious assessment for signs and symptoms of dehydration and f/e-lyte imbalance § checking skin turgor and examining the tongue for the presence of longitudinal furrows (cracks on tongue) - Monitor vital signs, especially blood pressure and pulse rate: b.c of A/E of orthostatic hypotension and tachycardia - Monitor EKG: Seronton 5-HT à prlonged QT interval - Undiluted forms of diphenhydramine: cautious IV use at rate of 25 mg/min - Aprepitant: Monitor INR before each cycle - Promethazine: give without regard to meals if given PO - Metoclopramide given orally is best taken 30 minutes before meals and at bedtime o Metoclopramide: A/E is Extrapyramidal symptoms reactions (tremors): assess pt and teach to report to provider immediately - Educate pt regarding long-term use effectsà metoclopramide long term use can cause tardive dyskinesia - Scopolamine: apply patch behind ear as directed o Area needs to be cleansed and dried before the patch is applied o If patch becomes dislodged à residual drug must be washed off and fresh patch put in place o Instruct regarding activities that require mental alertness or motor skills b/c of dizziness or drowsiness o Instruct to leave patch in place for 72 as indicated o Instruct to AVOID alcohol - Dronabinol: give 1-3 hours before chemo; can take at home before treatment appointment OTHERS: Pancreatic Enzyme Replacements Pancrelipase, Pancreatin, Pancrease MOA: - Supplements or replaces pancreatic enzymes Pancreatic enzymes that supplement missing - Improves nutritional status pancreatic enzymes - Reduces fatty stools (steatorrhea) Use: - Cystic fibrosis and pancreatic insufficiency b/c they lack digestive enzymes 14 Interactions: - Calcium carbonate or magnesium hydroxide A/E - GI distress: abdominal cramps or pain, N/V/D Activated charcoal NSG - Take w/meals and snacks Inactivated by gastric acid 24-hour fat excretion can be done Activated Charcoal: Antidote – antagonist MOA: - Binds toxins Indications: - Ingested toxin: ASA (aspirin OD) A/E - Black stools over 3 days: tell pt GI distress NSG - Admin as directed Mix with flavorful beverage Admin NGT or PO, gastric lavage (stomach pumping) Don’t admin with antidotes