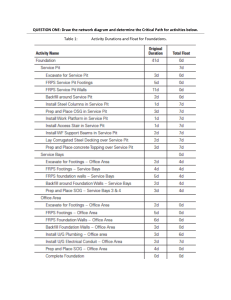
Project Management Critical Path Analysis • A project is a specific and temporary activity with a start and end date, with clear goals set, defined objectives needed to be completed in a given budget. Project • Elements of a project – 1. Resources (FOP) 2. Money 3. Scope 4. Time Project Planning and Management • A project must be planned, managed, cost efficient to be successful • Key elements of project management • Defining the project, setting goals • Dividing it into smaller activities • Controlling and managing it at every stage • Assigning clear roles • Quality standards issue Impact of Project Failure • Bad publicity • Loss of future contracts • Penalty payments Reasons for failure • Not enough information • Lack of finance, legal issues • Lack of coordination • Community against the product • Errors, wastage • Bad management, customers could not buy the product • Workers aren't motivated, not skilled enough, incompetent • Economic situations (neg) • Outdated project, quickly changing market • Bad planning- resources aren't sufficient • Or because the student didn’t do their homework Critical Path Analysis CPA is a planning technique that identifies all tasks in a project, puts them in the correct sequence and allows for the identification of the critical path. Activities that must be completed to achieve this shortest time make the critical path 1.Identify the objective Process of identifying critical path – 2.Put the tasks in a sequence and draw a network diagram 3.Add durations 4.Identify the critical path Network Diagrams • It is a diagram used in critical path analysis that shows the logical sequence of activities and the logical dependence between them – so the critical path can be identified • EST (Earliest Start Time) = EST of previous activity + duration of current activity • LFT (Latest Finish Time) = LFT in the previous node- duration of current activity • Free float shows the length of time an activity can be delayed without delaying the start of next activity • Free float = EST (next activity)-duration- EST (Current activity) • Total float = LFT- Duration- EST • Total float is the amount of time an activity can be delayed by without delaying the whole project • Total float = 0 the activity is on the critical path and cannot be delayed Dummy Activities • Indicated by a dotted line • Does not consume time or resources • Used when – • A & B start a project, C follows only A but D follows A + B Advantages of Critical Path Analysis Used to assist planning and management of complex projects Helps calculate accurate delivery dates Calculation of EST allows special orders to be managed Calculation of LFT helps act as a checklist of measuring the success and efficiency Knowing the critical path helps understand which activities to focus on, which can’t be delayed Additional resources needed for speeding an activity could be used from non-critical activities Reduces total time taken as it encourages simultaneous development rather than sequential. Critical Path Analysis - Evaluation Doesn’t guarantee project success Skilled labour, motivated workers also needed Good management Experienced senior managers