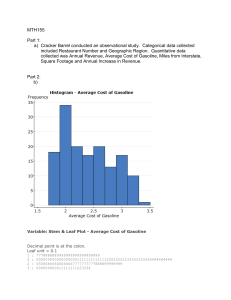
Republic of the Philippines Zamboanga Peninsula Region PROVINCE OF ZAMBOANGA DEL SUR ZAMBOANGA DEL SUR PROVINCIAL GOVERNMENT COLLEGE Pagadian City Name:_______________________________________________ Course Program :_____________________________________ Date:_________________ Year:_________________ GENERAL BOTANY MIDTERM LONG QUIZ 2022 TEST I. IDENTIFICATION (2pts Each). 1. __________________ It is the arrangement of leaves on the stem and branches. 2. __________________ a type of leaf arrangement where all the pairs of leaves on the stem are arranged one above the other. 3. __________________ a type of leaf arrangement where one the pair of leaf is placed at right angle to next or lower pair of leaf. 4. ____________________ It represents the midrib of a pinnately compound leaves that is present laterally on a common axis. 5. ____________________ each of the leaflike structures that together make up a compound leaf. 6. ____________________ A type of venation that is found commonly in monocotyledonous plants. 7. _____________________ A type of venation that is found commonly in dicotyledonous plants. 8. _____________________ it is in fact the conducting strands of water, mineral salts and food and form the structural framework of the lamina. 9. _____________________ It is the largest, most important green and flattened part of the leaf. 10. ____________________ Parts of a typical leaf that plays a vital role in photosynthesis, gaseous exchange and transpiration. 11. ____________________ Is the part of leaf connecting the lamina with the branch or stem. 12. ____________________ Is a branch of biology which deals with the study of plants. 13. ____________________ is a type of flower that lacks a functioning pistil or stamen. 14. ____________________ a phenomenon where a female archegonium produces chemicals that attract/direct the sperm movement for fertilization. 15. ____________________ it is the gametophyte of ferns and other primitive plants. 16. ____________________ a plant produces two kinds of spores that develop into male and female cones are called. 17. ____________________ Is a slender lateral branch that arises from the base of the main axis of the plant. 18. ____________________ is a salt-tolerant plant that grows in soil or waters of high salinity, coming into contact with saline water. 19. ____________________ A type of trees that enters a dormant period by falling off or shedding their leaves during the difficult times as a means of survival. 20. ____________________ Small, green leaf-like structures at the base of the flower that protect the flower bud. 21. ____________________ They are plants that have a male reproductive organs in one individual and female in another. 22. ____________________ A plant that has flowers and produces seeds enclosed within a carpel. 23. ____________________ A type of flowers that contains both function of pistils and stamens. 24. ____________________ A part of Stamen where the pollen grains grow. 25. ____________________ They are so called the runners of aquatic plants, an sub-aerial modification of stem. 26. ____________________ They are the undeveloped shoots from which leaf or flower parts arise. 27. ____________________ a plant that has seeds unprotected by an ovary or fruit. 28. ____________________ The Discoid stem with compactly arranged fleshy leaves above and fibrous roots below is commonly called. 29. ____________________ Leaf blade in some leguminous plants become swollen and it is called. 30. ____________________ it is a pair of lateral outgrowths at the leaf base on the either sides of axillary bud called. 31. ____________________ it is the expansion of leaf base that covers the stem partially or completely in monocots plants. 32. ____________________ it is a thin, expanded, green structure that has limited growth. 33. ____________________ An aerial modification of stem where the axillary bud becomes fleshy and rounded due to storage of food. 34. ____________________ An aerial modification where a stem gets their shape transformed into leaf like structure. 35. ____________________ A part of a seed structure where the stem is developed 36. _____________________ what is the type of seed dispersal is dandelion plants possess. 37. _____________________ A kind of fruit where flowers fuse to form one fruit. 38. _____________________ what kind of fruit are the blackberries, strawberries and rasberies. 39. _____________________ it holds the structure that grows pollen grains. 40. _____________________ is it’s a ripened ovary. 41. _____________________ it produces spores underneath the frond of a fern. 42. _____________________ it is the process by which plants loose water vapour. 43. _____________________ A common leaf margins with a smooth edge with no teeth or notches. 44. _____________________ A common leaf margins with a margin cut into sharp, deep, irregular teeth or incisions. 45. _____________________ A common leaf Shapes with a Tapering long, narrow point. 46. _____________________ is the largest and most diverse division of gymnosperm. 47. _____________________ it has a terminal rosette of leaves and bear seeds in cones. 48. _____________________ They are seeds not enclosed in a fruit. 49. _____________________ Habit of appearance of plants with soft or succulent stems. 50. _____________________ refers to any plant adapted to life in a dry or physiologically dry habitat. TEST II. ENUMERATION (2pts Each). A. Enumerate the five types of palmately compound leaves. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. B. Enumerate the four kinds of pinnately compound leaves. 6. 7. 8. 9. C. Enumerate the morphology of flowering plants. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 16. D. Enumerate all the modifications of Roots under Tap and adventitious type of roots. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. E. Enumerate the 3 food storage modification of roots. 22. 23. 24. F. Enumerate the four vegetative types of buds. 25. 26. 27. 28. G. Enumerate the 3 types of modifications of stem. 29. 30. 31. H. Enumerate the examples of underground modification of stem. 32. 33. 34. I. Enumerate the examples of Sub-aerial modification of stem. 35. 36. 37. J. Enumerate the examples of aerial modification of stem. 38. 39. 40. K. Enumerate the modifications of Leaves 41. 42. 43. 44. L. Enumerate the three types of Seed Dispersal. 45. 46. 47. M. Enumerate atleast 3 types of Plant Photoperiodicity. 48. 49. 50. TEST III – MATCHING “U” TYPE (2pts Each). ______ 1. Starfruit/Balimbing A. Cucurbita pepo ______ 2. Banana B. Zea mays ______ 3. Kalabasa C. Ipomoea batatas ______ 4. Sayote D. Oryza sativa ______ 5. Mango E. Psophocarpus tetragonolobus ______ 6. Mais/Corn F. Vitis rotundifolia ______ 7. Rice/Palay G. Averrhoa carambola ______ 8. Avocado H. Brassica oleracea ______ 9. Sweet Potato I. Mangifera indica ______ 10. Santol J. Artocarpus heterophyllus ______ 11. Tomato K. Solanum lycopersicum ______ 12. Jackfruit L. Ipomoea aquatic ______ 13. Pickle Tree/ Kamias M. Cocos nucifera ______ 14. Broccoli N. Sandoricum koetjape ______ 15. Singkamas O. Chrysophyllum cainito ______ 16. Kamoteng kahoy P. Lansium domesticum ______ 17. Swamp cabbage/Kangkong Q. Sechium edule ______ 18. Pipino R. Pyrus malus ______ 19. Sunflower S. Allium cepa ______ 20. Upo T. Curcuma longa ______ 21. Strawberry U. Saccharum officinarum ______ 22. Grape/Ubas V. Fragaria ananassa ______ 23. Sigarilyas W. Pachyrrhizus erosus ______ 24. Pandan X. Manihot esculenta ______ 25. Turmeric Y. Raphanus sativus ______ 26. StarApple Z. Cucumis sativus ______ 27. Makopa AA. Citrullus lanatus ______ 28. Sugarcane BB. Lagenaria siceraria ______ 29. Atis CC. Zingiber officinale ______ 30. Apple DD. Nephelium lappaceum ______ 31. Sitaw EE. Annona squamosal ______ 32. Talong FF. Musa paradisicum ______ 33. Papaya GG. Carica papaya ______ 34. Cashew HH. Anacardium occidentale ______ 35. Luya II. Helianthus annuus ______ 36. Potato JJ. Persea Americana ______ 37. Black Pepper KK. Solanum tubersum ______ 38. Watermelon LL. Syzygium malaccense ______ 39. Onion MM. Pisum sativam ______ 40. Lanzones NN. Phaseolus vulgaris ______ 41. Pea OO. Citrus Limonium ______ 42. Lemon PP. Piper nigrum ______ 43. Peanut QQ. Arachis hypogaea ______ 44. Patola RR. Pyrus malus ______ 45. Okra SS. Averrhoa bilimbi ______ 46. Repolyo TT. Solanum melongena ______ 47. Coconut UU. Tamarindus indica ______ 48. Sampalok VV. Abelmoschus esculentus ______ 49. Radish/Labanos WW. Pandanus dubius ______ 50. Rambutan XX. Brassica oleracea