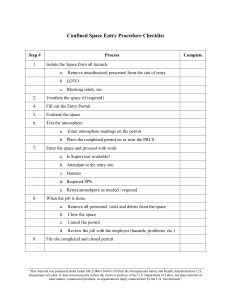
Assessment of Permit Holder Permit to Work…………………………………02 Types of Permit………………………………..03 Permit Holder…………………..……………..06 Certificates & Procedures………………..08 Definitions……………………………………….13 Locations of work…………………………….17 Emergency Procedure……………………..20 Duties………………………………………………21 Permit Cycle…………………………………….22 Permit to Work Q. What is Permit? A. Permit is a written document which authorises certain people to carry out specific job at certain time and place. It is a legal document. Q. What is PTW system? PTW system is a legal and formal documented system used to control the potentially dangerous job. (A PTW system authorises specific people to conduct specific work at a specific time and location. It ensures proper planning of the work and that risks are adequately managed by formalising the required controls. It ensures communication between site management, supervisors, operators and the work crew and is required for all work identified as being hazardous or potentially hazardous) Q. Aim of PTW system? (Objectives of PTW system) To provide a system which ensures that work activities can be carried out in a safe manner. To support clear & accurate communication. To reduce human errors and influencing the behaviour. Non routine hazards and activities can be work in a safe manner. Q. PTW Scope? A. This PTW procedure shall be used in all PDO operations and contracts, unless a contractor has opted out by using his own PDO approved system. It explains the PDO PTW system, defines when a PTW is required and the PTW approval and control process. Q. Why we use PTW system? A. To protect the peoples, environment, Assets, reputation of company and to do the job safely. Q. Why we are taking the permit? A. To make a sure that all non-routine hazardous activities can be work in a safe manner. Q. Why Permit is a legal document? A. It is a legal requirement under Omani Law. If I follow the rules and procedures and something go wrong it will save me, otherwise I can go to jail. Q. Principle of Permitry? A. It is a process use to determine whether a job needs a permit or not. Q. People involved in PTW? 1. Permit Applicant-----------------------(applies for a PTW) * 2. Responsible Supervisor--------------(authorises, verifies and assures a PTW) * 3. Area Authority-------------------------(validates, verifies and assures a PTW) * 4. Permit Holder--------------------------(accepts a PTW and supervises the work) * 5. Other Affected Custodian-----------(counter signs a PTW) * 6. Production Coordinator-------------(counter signs, verifies and assures a PTW) 7. Authorised Gas Tester---------------(conducts gas testing as part of a PTW) 8. Isolation Authority--------------------(isolates as part of a PTW) Types of Permit There are 4 types of Permit 1. 2. 3. 4. Class A Permit Class B Permit Task SOP Permit No permit Job - Red edged form - Blue edged form - White edged form – high risk work – medium risk work – Routine tasks – low risk work 1. Class A permit: (required for High Risk work) 3 copies of Class A permit 1st copy Red 2nd copy Green 3rd copy White (Original) (1st copy) (information copy) (P.H) (Area Authority) (Responsible Supervisor) Authorization period 14 days Notice period time 72 hours Validation time period daily 12hours A Job HSE plan to be attached to the PTW documentation and used to manage the work and communicate with the work crew. A site visit and examination on the first day before work starts by the Responsible Supervisor and Permit Applicant before the Responsible Supervisor initially authorises the PTW in a process facility. Work in a process facility daily examine the work site before validation by Area Authority. A site visit and examination by the Area Authority on the first day of work in hydrocarbon areas unless the Responsible Supervisor has authorised the delegation of this requirement to an Authorised Gas Tester Tracking in the Work Tracking System. Class A permit has a maximum authorisation period of 14 days only with a 7 day extension allowance. – Pre validation is not allowed for Class A permit. – 1st day gas test must be done by Area authority. 2. Class B permit: (required for Medium Risk work) 3 copies of Class B permit 1st copy Blue 2nd copy Green 3rd copy White (original) (1st copy) (information copy) (P.H) (Area Authority) (Responsible Supervisor) Authorization period 28 days Notice period time 48 hours Validation time period 12 hours (Daily validation by Area Authority) A Job HSE plan to be attached to the PTW documentation and used to manage the work and communicate with the work crew. Authorisation by the Responsible Supervisor. A site visit and examination by the Area Authority for him to authorise the PTW in a process facility on the first day before work starts in a process facility. Daily revalidation of the PTW by the Area Authority. Tracking in the Work Tracking System Note: Class B permit has a maximum authorisation period of 28 days only with a 7 day extension allowance. No Permit Job: If we want to work in non-hazardous area we use (No Permit Job) form authorised by PDO responsible Supervisor and it is valid for 28 days. Access Permit: Used for site visit only. General Survey Work: Over 95% of survey work is conducted outside of process facilities & do not require a PTW. Q. How many permit an Area authority can validate? A. Total 14 Class “B” but maximum 6 Class “A” at same time. A+B=14 But A maximum 6 Q. Where is used ‘A’ Class Permit? A. Class “A” permit is used for high risk jobs. Work in confine space entry. Hot work in Process Area. Deep excavation more than 1.5meter in process facilities using equipment. All Jobs inside station where equipment will be used in Process facilities. Q. why authorization notice period for Class A permit is 72 hours? A. Because P/A has to visit site with responsible supervisor before authorization, so it takes time, that’s why it needs 72 hours. Q. How many people sign the permit? / Who sign the permit? 1. Permit Applicant 2. Responsible Supervisor 3. Area Authority 4. Permit Holder 5. Authorized Gas Tester 6. Production Coordinator (for A Class) 7. Other Affected Custodian (if required) 8. Isolation Authority (if required) But normally 4 people sign the permit: 1. 2. 3. 4. Permit Applicant Responsible Supervisor Area Authority Permit Holder Q. How many documents (minimum) attached with the permit? 1. Permit 2. PTW check list 3. Job HSE plan 4. TRIC 5. HRA 6. Job content agreed 7. Approved Location Drawing 8. Certificates (if required) Q. Does just having a permit make a job safe? A. Just having a permit is not enough to make a job safe, we must comply with requirements of the permit and job HSE plan. Q. Fill up Permit method? Permit Applies By permit applicant Box No 1, 2, 3, 4 & 8 with Headers Permit Agreement By other affected custodian Box No 5 If we are going work near Sub-Station then Electrical Supervisor will be an affected custodian. If we are going work near Drilling Rig then Rig Supervisor will be affected custodian. Q. When we Suspend a Permit? 1. Any unsafe situation develops. 2. On emergency evacuation. 3. Reportable incident occur at site. 4. Oil or gas leak at site. 5. Work is delayed or interrupted more than 4 hours. 6. Work with higher priority than this permit work. 7. Validation period is expired. 8. Permit holder changes. Q. When we Cancel a Permit? 1. Work completed. 2. Work situation is different from description. 3. Authorised period has expired. 4. All available validation spaces have been used. 5. Work uncompleted but permit Box No. 10a have no space. Q. Your actions when permit is suspended? Check that the work site and equipment affected by work site have been left in a safe condition. Sign Box 10c of the pink/blue copy of the permit to confirm that work has been suspended. Take the permit to the issue point, sign the green copy and give it to the area authority who will keep it there until ready to re start the work if the work is in a process facility this must be done. Q. What is validation & pre validation? A. After the permit is authorized by responsible supervisor, the permit holder takes permit to the area authority where area authority signs in permit box 10a, this is called validation. Pre validation means to get validation in the evening for next day if it is allowed by the responsible supervisor. Pre-validation cannot be done at the beginning of the first day of the work. For Class A permit pre validation is not allowed. Q. PDO HSE policy? To protect the health and safety of workers. To protect the environment. Save the interest of local community. Empower the employ to stop the unsafe work. Permit Holder Q. Who is permit holder? A. A person has a valid and authorised PTW license. Q. How many Permit a permit holder can hold at a time? A. Class ‘A’ Type only 1 permit. Class ‘B’ Type only 4 but at same Location (Visible by Visual Contact) Note: If he is holding an A class permit he cannot hold any other permit. Q. What will a Permit Holder do when you take permit from Applicant? A. I will take briefing from Applicant about job, location and requirements of job HSE plan then I will check the description, activities, type of permit and attached documents. If everything is complete and correct, I accept the permit and go for validation. Q. Responsibilities of Permit Holder? Before starting the job on a permit: 1. Understand the work and requirement of Job HSE plan. 2. Take the permit, check all the documents complete and correct. 3. Take the validation from authority and accept the permit. 4. 1 copy for site and 2 copies keep in rack. 5. Conduct the tool box talk about hazards and control at site. 6. Get daily validation by area authority. During work: 1. Permit will be display at site in plastic wallet. 2. Follow the requirement of Job HSE plan and TRIC. 3. All the time stay at work site and supervise the work party. 4. Ensure that the worksite and equipment are safe whenever work is suspended. Before suspending Permit: 1. Ensure that work site and equipment are safe. 2. Stop all the work and move all the crew to a safe place. 3. Return the Permit to area authority after suspension. Q. What we will you check in permit? 1. Permit type 2. Permit No. 3. Work description 4. Location 5. Dates 6. Signs 7. Attached certificates 8. Job HSE plan 9. TRIC card 10. Procedures 11. Lifting plan 12. Drawings Q. Explain changeover of permit holder? A. Within process facility Both permit holder must be obtain the area authorities approval to change and the outgoing permit holder will sing 10C and will suspend, new permit holder will sing box 10B of both copies of the permit for acceptances. At remote location where he is unable to reaches to area authority so they will contact with area authority by phone and will take approval the outgoing holder will sing 10C and will suspend, after new permit holder accept and will sing in 10B of the permit. The outgoing permit holder cannot leave the site whenever he has fully briefed the new permit holder and the permit holder will singed to accept the permit in his presence. Q. Who is other Affected Custodian? (General question to all Permit Holders) A. When a Permit will affect, or be affected by, another Supervisor’s area, this Supervisor will sign as Other Affected Custodian, for example working near 100 meter of drilling rig. He is responsible for: Identifying any additional hazards due to his assets. Agreeing that the work affecting, or affected by, his area can be done. Deciding on any additional precautions required due to potential hazards relating to his assets. Worksite Examinations PTW Type Examination by Permit Applicant & Responsible Supervisor Examination by Area Authority Process Facility Before Authorisation 1st Day Hydrocarbon Area Every Day 1st Day Every Day CLASS A YES* YES YES ** YES NO*** CLASS B NO YES NO NO**** NO Certificates and Procedures Q. What is Certificate? A. It is written permission to provide additional authorisation for specific job. Q. Does just having a permit make a job safe? A. Just having a permit is not enough to make a job safe, we must comply with requirements of the permit and job HSE plan. Q. Write down name of secondary certificate? Mechanical isolation Electrical isolation / De-isolation Confined Space entry Excavation Radiography Over Headline clearness Additional Gas Test record Electrical Safety Document Safeguarding Isolation Q. Certificates related to Civil? 1) Excavation certificate. 2) Confined space certificate. 3) OHL certificate. Q. How much copy of excavation certificate with colours? Yellow (at site) Green (Permit issue Point) Q. When we use Excavation certificate? A. When we do excavation more than 30 cm. Q. Why we use Excavation certificate? A. To find out underground services. Q. How much deep cable detector can detect? A. It depend upon the model and company but mostly 500mm deep can be measure. Q. How you will check underground facilities? A. I will check from drawing, root markers, with the help of trial pit, and with cable detector. If I found anything I will do manual excavation. Q. Who will signed the excavation certificate? 1. Permit Applicant 2. Responsible Sup 3. Permit Holder 4. Pipeline department 5. Telecom department 6. Electrical department 7. Instrument department 8. Geomatics department Excavation Procedure: Get an authorized permit and excavation certificate. Check all the documents are complete and correct. Understand the work and job content. Take the validation from area authority & accept the permit. 1 copy for site, 2 copies keep in rack. Reached at site & examine the site. Conduct tool box talk. Arrange the TBT about the hazard and control at site. Check the drawings. Layout of area. Identify underground facilities. Check the sign boards and route markers. Use cable and material detectors. If have any doubt dig trail pit 1x1x1 meter (maximum distance 3 meters) If there is no underground facilities I will start mechanical excavation. Precaution: Heavy machinery excavation may only carry out up to 1 meter from flow lines and shall apply banks man. On no account shall permission be given such excavation less than 1 metre from live lines. Excavation is essential at a distance less than 1m from live lines to ensure the line is isolated and depressurised. Breaking of hard rock’s held pneumatic (jack hammer) tools may proceed within 1 meter of live lines and depressurised lines provided that tool bit is visible all the time. Q. What is Confined Space? A. Any enclosed area having depth of 1.5 meter or more and minimum way of access. E.g. tanks, vessels and deep excavation. Oxygen required in confined space 20 – 21% Q. Why we need (use) confined space certificate? A. In confined space there may be presence of poisonous gases, oxygen deficient environment or presence of flammable gasses. So whenever we are going to work in a confined space we require this certificate. Q. Which work will required confined space entry certificate? A. If entry in to Vassals, Tanks, Cellars, & Deep pit more than 1.5 meter.its authorisation period is 12 hrs. Q. Who and how many persons sign confined space certificate? 1). Applicant 2). Responsible Sup or Area Authority 3). P.H 4). Authorization Gas Tester Note: 1st certificate will be authorizing by responsible supervisor Next certificate, area authority can authorize. Q. How many copy of confined space entry certificate with colours? 1. First Copy Yellow Work site 2. Second Copy Green Permit issue Point Confined Space Entry Procedure: After reached the site. Conduct tool box talk. Conduct gas test and continuously monitoring and mentioned on gas testing sheet. Check the area with long stick for reptiles before entrance. All members should have H2s monitor. Use buddy system. Record in and out time of each person. Q. What is buddy system? A. This system is used to work in confined space; one person outside the confined space is provided all the time, that person communicates continuously with person who is working inside. These people will work turn by turn after 30 minutes. Q. Who is AGT? I. A persons have a valid Gas testing card and permit to work licensed. II. An “Authorized Gas Tester” is person who has passed the gas testing course and hold a valid gas tester card and has also passed permit holder or permit applicant course. Q. How do you will do Gas Test? A. If it is a confined space like tank, deep excavation then I will 1st switch on gas tester check oxygen level in normal air if it is 20.8% that mean gas detector is working properly, then I will tie gas detector with rope and check at all levels of space bottom, middle and top, because toxic and flammable gases may be present anywhere. Some gases are lighter some are heavier. Q. What is OverHead Line? (OHL) A. Between live lines and boom should be distance maximum of 35 meters. Fixed goal post maximum distance both side is 15 meters. Q. When we use OHL certificate? A. Whenever we work within 15 meters of OHL. Q. How many copies of OHL Clearness certificate with colours? 1. Pink Area electrical supervisor 2. Green Permit issue point 3. White on site Q. Who will sign the OHL Clearness certificate? 1. Applicant 2. Permit holder 3. Area Electrical Supervisor Q. Why we required the OHL Clearness certificate? A. To safe the people from any electric shock. OHL Procedure: After reached the site. Conduct tool box talk. Erect the goal posts (Maximum height 5.5 meter) 15 meter both side of OHL. Must have CEP (Competent Electric Persons) at site before start work under OHL. Must lock the boom of Excavator or JCB with chain. Maintain min distance from OHL is 3 meter. Passage below OHL If working within 15meter of OHL or Both sides We need OHL Clearance certificate; we will erect goal post on both sides of OHL. Width and height of poles will be as written in OHL certificate. I will use height lock or chain lock for excavator or JCB. While crane is passing under OHL make sure that boom of crane is in fully lowered condition. Q. What is the procedure for carrying out cold cutting (for mechanical) or excavation (for civil) A. Cold cutting must cover identifying the line, marking the line, draining out of line, and key hole pressure testing. Excavation must cover excavation certificate, cable detection, trial pit & physical identification of route markers. Q. What action permit holder for Cellar cleaning? A. The procedure for cellar cleaning is given below. First I need validated Permit by area authority Confined space entry certificate Ensure that all supplies isolated Additional Gas testing Record Entry and Exit Paper Arrange Proper Tool box talk meeting Explain Job to crew and discuss hazards associated with job. Provide Ventilation from confined space by using fan or any other source if required. Start Gas test in case found any gases then we use breathing apparatus. Apply Buddy System One banks man will be on top Continuously site supervision by Permit Holder Start the Job of cellar cleaning Check for Snake and Scorpion before entering visually and with stick etc. During cellar cleaning will maintain Job rotations plane. Q. What is procedure for working in Harweel/Birba/Alnoor station? A. Get authorized permit, check permit, understand work and job requirement from P/A, Go to station, get validation, enter name of all crew including me in log register, put h2s cards of all crew in h2s rack, keep mobile phones in rack, make sure that nobody have any source of ignition i-e lighter, match box with him, I need also 2 SCBA holders with me because Harweel/Birba/Alnoor station is high h2s facility. I will hold TBT explain emergency procedure, assembly point, explain work and related hazards and there controls and start the work. Q. What are the controls of heavy plants movement? Provide trained operator and Proper Banks man with Jackets. Check plant conditions. Keep safe distance from each other and from existing facilities. Do not over speed, do not use mobile, and never stand behind or in front of the plant. Q. What are the civil activities? Excavation. Back filling, installation of foundation, Anchor and sleeper. New well pad with cellar, beam pump base. Cellar cleaning. Grading and levelling. Construction of Roads. Construction of Ramp. Installation of Fence. Septic tank, Soakage pit, Shuttering and Rebar, Block work. Concrete Poring. Precast in Yard work. Q. What are the Hazards in civil work? A. H2S Gas. Crossing and working under suspension load. Over Loading, using Mobile while Driving, Over speeding, working near live line, working under OHL, working inside Confine Space, work at height without fall prevention equipment, underground facility, lack of knowledge or experience, Dust, Notice, Pollution, Temperature, Crude Cleaning, Defective equipment, improper tools or equipment, moving machinery, Open Trench. Heavy plant movement, poor plant condition, untrained operator and banksman, Run over the workers, manual handling. Poor condition of tools, Poor housekeeping. Loose Soil. Falling Object. Uneven ground etc Q. What are the daily Routine Hazards? A. H2S, High Pressure Lines, Underground Services, working at height, plant movement, Deep excavation, uneven slippery, Heat, Dust, Noise, Falling, Bad communication, Untrained persons, Open trench, Trench collapse, Concrete, Snake, Scorpions, Crude oil, Vehicle movements, MORN and Sharp edges. Q. What are main hazards and control in your jobs? A. Heavy plant movement ,poor plant condition, untrained operator and banks man, over speed, roll over plant, strike with objects, run over the workers, working near existing facilities, pipelines, manual handling, poor condition of tolls, sharp edge tools, poor housekeeping, poor condition of lifting equipments i.e. slings, belts etc. working near OHL H2S Controls: Provide trained operators and banks man, check plant conditions, do not over speed, do not use mobile while driving, use seat belts, keep safe distance from other plants at least 10 meter. Do not stand behind or in front of plant; keep at least 1.5 meter distance from pipe line. Plan before lifting, estimate weight, make good posture, do not use improper tools, maintain proper housekeeping, and check lifting equipment and colour code provide goal post on both sides of OHL. Follow emergency procedure. Hazard Control Underground Services Check the drawing, Check the route marker, Use cable detector, Material detector, Make trial pit. Heavy Machinery Provide competent operators and flag man to do the right signal. H2S Conduct Gas testing. Trench Collapse Excavation step by step and V shape cutting. Heat Drink more water and take rest in shade. Dust Use dust mask, cover body. Noise Use ear plug. Q. What is H2S? Hydrogen Sulphide is a highly toxic, flammable and invisible killer. Found in confined space, pipelines, process facilities and hydrocarbon areas. Classification of H2S Sweet 0-49 PPM PTW, H2S card. Low 50-499 PPM PTW, H2S monitor. High 500-699 PPM PTW, H2S monitor and escape set, Buddy System. Sour 700 above PTW, H2S monitor and SCBA, Buddy System, stand by vehicle and Communication system. High Sour areas are Alnoor, Bibra and Harweel. Q. How do you do H2S Classification of area? RED FLAG --------- High H2S Area YELLOW FLAG--------- Medium H2S Area GREEN FLAG--------- Non-H2S Area Q. Is H2S flame able? A. Yes, it is flame able and highly toxic invisible killer gas, which is heavier than air, quickly moved and mix with air. Dissolve in water. Q. If your best friend falls what will you do? Will you help him? A. If it is H2S Emergency, I will not go to pick him up, if I have SCBA holder I will send him for help, otherwise I will inform Area Authority. I will not go to help because if I will go instead of helping him I will also die. Definitions Q. HEMP? A. Hazards & Effects Management Process. This is a process which is used to explain the hazards and there control and recovery measures. It has 4 elements. Identify: First of all we have to identify the risk related to job. Access: Then we will recognize the risk, is it as low as reasonably practicable? Control: Necessary measures to manage the risk. Recover: Events if controls and barriers fail. Recovery measure is actions taken to bring the condition in normal situation after the failing of controls. HRA and Job HSE Plan are the part of HEMP. HRA Defines hazards, controls and recovery measure related to the health, while Job HSE Plan describes hazards, controls and recovery measure related to job. Q. What is Control & Recovery? Control: Any measure taken to ensure that work can be done safely. Recovery: Any measure taken to bring situation to normal after any unexpected consequences. Q. What is TRIC? A. Tool Box Risk Identification Card: It is a site risk assessment in which we will focus on the hazards at the worksite when we carry out the job. Q. What is Job HSE Plan? A. Document which must be attached to every permit describing the hazards associated with work and the controls required insuring that the work can be done with minimum risk to Persons, environment, assets and repute of company. (Job HSE Plan is also a part of HEMP) Q. What is difference between TRIC & Job HSE Plan? A. In Job HSE Plan we assess the Hazards when we are planning the job. & In TRIC we assess the hazards at the time of implementing the job at work site. Q. Difference between TRIC & Job HSE Plan? Job HSE Plan = Common hazard. TRIC = Daily specific location hazards. Q. What is HRA? A. Health Risk Assessment It is part of HEMP which explains hazards, controls and recovery measures related to the health at work site. Q. What is the difference between Job HSE Plan & HRA? A. Job HSE plan identify the hazards due to work & its location and define the safety precautions required where as HRA identifies the health hazards to the individual who are carrying out the activity. Q. What are the uses of Job HSE Plan? Identify the Hazards Risk assessment Identify any other activities that may conflict with work Personal protective equipment Control of applied Recovery Q. Write down the sections of the Job HSE Plan? Activity no and Work description by permit applicant Hazard assessment Risk assessment Action by area authority Action by permit holder Agreement on content of job HSE plan Acceptance by Permit Holder Q. What is Dynamic Risk Review? (Pause & Check) When work is in progress at site, other party come at site or conditions changes (e.g. work or weather) we stop the work, then hazard, risks and controls must be reassessed. It is used where the hazards may change or new hazards may be identified during the work, or at intervals throughout the work to assess if any changes warrant a re-group of the work party for a revised TRIC discussion. Q. HAZARD? A. Anything with the potential (Ability) to Cause damage. Q. What is Risk? Risk is combination of effects. Anything with the potential likely to cause damage, or chances or probability something will be damage. Q. What are the Consequences? A. The amount of damage. Q. ALARP? A. As Low As Reasonably Practicable It is a process in which we try to minimise the risk involve in the work. Q. ABBI? A. Above Below Behind Inside. Q. What is LOA? A. Limitation of Access. Q. STOP? A. Safety Training Observation Program: The basic principle of STOP is that all injuries and occupation illness can be prevented. Q. PEAR? A. People, Environment, Assets & Reputation of the company. Q. LTI? A. Lost Time Injuries (must know the latest LTI of PDO) Q. RTA? A. Road Traffic Accidents: (More than 60% of all Life-Saving rule violations are related to road transport.) Q. Hot Work? A. Work which may result/involve an open flame, Production of spark and any other source of ignition. e.g. Grinding, Cutting, Welding. Q. CCR? A. Central Control Room Q. SHOC? A. Safe Handling Of Chemicals. It is a written document from manufactures, in which they informed us the properties of the chemical and control masseur if miss used. Q. What is FOC? A. Fibre Optic Cables. (Depth up to 70 cm) Q. What is LV? A. Low Voltage. (Depth up to 70 cm) Q. What is HV? A. High Voltage (Depth up to 1meter) Q. What is ESR? A. Electrical Safety Rule. Q. What is ESOP? A. Electrical Safety Operation Procedure. Q. Isolation Boundary? A. The set of Valves, electrical switchgear. OR Similar Devices used to establish an area safe from hazardous fluid. Q. What is WINDROW? A. Materials placed in longitude Axis of pipeline in tri angular shape. (Minimum height 1 meter and base width 1.5 meter) Q. SCBA? A. Self-Contain Breathing Apparatus: It is used in high H2S areas for breathing. Q. Tips of affected tool box talk? Simple language. Positive behaviour. Two way communication. Q. Conduct tool box talk with your crew. A. AsSalam-o-Alikum...&...Good Morning. Discuss golden Rules and lifesaving rules. Tell them about today’s job. For Example: we are going to do excavation. In excavation there are some hazards ,like underground services heavy machinery, poisonous reptiles ,slip trip ,sun light ,dehydration and there controls. Inform about latest LTI and PDO emergency number. Q. What is tool box talk? A. It is two way communication between the TBT leader and other crew members. In TBT job and activities are explained, hazards, there control and recovery measures and JOB HSE plan requirements are discussed, emergency no, emergency plan and assembly point is discussed. Make sure that all members understand the work and related hazards. TBT must be held on work site just before starting work each time. Q. What are the main Rules of PDO? A. There are 2 main rules of PDO. 1).Golden Rules 2). Life Saving Rules Q. What is the PDO Golden & Life Saving Rules? Golden Rules: You & I 1) Comply with the law, standards and Procedures. 2) Intervene on unsafe or non-compliant action. 3) Respect our neighbour. Life Saving Rules: 1. Obtain a valid work permit whenever requires. 2. Do gas test whenever required. 3. Verify isolation. 4. A valid permit before entering confine space. 5. Obtain a valid permit to work before overriding. 6. Work at Height with fall Prevention equipment. 7. Don’t walk under suspended load. 8. Don’t Smoking. 9. Follow the safe journey plan. 10. Fasten seat belt. 11. Don’t use mobile and do not exceed speed. 12. Do not use Drug and Alcohol within the site. Q. What is Mercury & its effects? A. It is a silver colour liquid. When it comes in open air evaporates very rapidly and directly affect the nervous system, headache, stomach pain. Q. What is NORM? A. Naturally Occurring Radioactive Materials. NORM are materials deposited in the form of uranium (238), Thorium (232). It’s found in safety valves, well heads, Manifold, Separators, Oil cooler, Pig wax and storage cells. NORM Restricted Areas: 1) Saih Rawal 2) Ramlatul Rawal 3) Zuliah 4) Huwaisah Q. What are the precautions of NORM? Limited number of persons. Wear disposable coverall and PVC gloves. No eating, no drinking, no smoking Wash with water before leaving the site. Monitoring with dose meter. All the tools cover with the polythene. All the garbage should properly disposed off. Locations of Work Q. How many Types of Fields? A. Green field & Brown field. Q. How many types of areas are there in PDO? A. There are three types of areas, Process Facilities, Hydrocarbon & non-Hydrocarbon Q. What is Process Facility? A. “Area within the boundary fence” of any hydrocarbon processing facilities. Including: Gathering and pumping stations. Storage and processing areas. Terminals MSV Level area around the live well head. Q. What are Hydrocarbon areas? A. “Area outside the boundary fence” of process facility where hydrocarbon are present. Area within 10 meters of gas pipeline. Area within 25 meters of main Oil line. Area within 50 meters around flowline which has flanged joint. 50 meters area outside the boundary fence of process facility 50 meters around well pad. Area within 100 meters around drilling Rig. Q. Non-Hydrocarbon areas? Areas where hydrocarbons have never been present. All green field areas. Electric switching station and power distribution systems. Administration, recreation and accommodation. Labourites and medical facilities. Construction sites for new facilities. Q. Critical Sour areas? A. An area anywhere within the Emergency Planning Zone (EPZ) of a Critical Sour area. Q. Restricted areas? All process facilities are classified as ‘Restricted Areas’, however some non-process facilities such as telecoms facilities are also classified as ‘Restricted Areas’. Q. Write down the Procedure of working in a Process Facility? I need an authorized Permit from applicant, get it validated from area authority after I will accept the permit put Copy of Permit Rack Keep Tag marker on Location Board I will write name of worker, permit no and job in entry register I will place H2S card in H2S Rack Place mobile phones of all in rack Then I will ensure that there is no source of ignition with anybody If I am going to work in high H2S /areas then I will take 2 SCBA holders with me also. Enter with H2S Monitor on condition Identify Assembly Point and Emergency exit gate Arrange toll box meeting and Brief Job to crew. And start the work. Q. What is Zone? A. We classified the area according to hazards. Zone0, Zone01, Zone02 & Non-Hazard Zone Zone 0: Where flammable/explosive atmosphere always present in normal operations. E.g. Flair area, Tanks & Vessels. (Area where explosive/flammable gases are continuously present.) Zone 1: Where flammable/explosive atmosphere is likely to occur in normal operation. E.g. Heater area, compressor nearby, valves, rotating seals. Zone 2: Where explosive atmosphere is unlikely to occur in normal operation. E.g. outside the fence, Leakage of pipelines in faraway areas Non hazard Zone: Areas where flammable/explosive gases could not be found. E.g. accommodations and hospitals. Note: (Hot Work is not allowed in areas classified as Hazardous Zone 0 or Hazardous Zone 1, unless absolutely essential. Hot Work includes all open flame work and other work that may cause sparks, such as grinding, electrical work or vehicle entry.) Q. Can we execute or work in “Zone 0”? A. NO. We can only work in zone 0 by converting it into zone 2. Q. What is EPZ? EMERGENCY PLAINING ZONE: Geographical area around a well head, flow line or station containing high H2S that requires specific emergency response planning. Minimum H2S Concentration of 100PPM at edges of this area could be found at the time of major leakage. (Geographical area around a well head, flow line or station containing high H2S at the end of this area. Minimum H2S Concentration of 100 PPM could be found at a time of major leakage) Birba, Harweel and Alnoor comes in EPZ. Q. What are the requirements to work in EPZ? There are the requirements for working in EPZ. 1. High risk H2S entry card 2. Personal H2S monitor 3. SCBA holder. 4. Source of communication 5. Standby vehicles within 400 m area of working crew 6. Valid Permit 7. Cam lock Rig Walker or chemical escape hood filter. Q. What is RED ZONE & YELLOW ZONE? A. Red Zone: An area where a high Toxic gas present for long Time. Working in the red zone the work party is not only wear the cam lock rig walker but to also wear the appropriate co-welled or fast mask in conjunction with connection to the fix breathing air system for the duration of working in the red zone 50000 ppm. Yellow Zone: An area where a Toxic gas are likely occur. Only rig walker can be used. 20000 ppm. Q. If you need vehicle in process facility what is the procedure? A. Vehicles are not allowed to enter or to drive within 50m of a process facility so if we required vehicle entry in process facility we need a permit, vehicle type and registration no should be mentioned on the permit, inform area authority, write on log register, make free vehicle from source of ignition and mobile phones, do gas test before entering vehicle, gate will be closed after each entry and exit. Continuous gas testing is required if engine is running. Q. What is OSBL? A. OSBL - Outside battery limit (EPZ Area) that means outside off the fence in a process plant or facilities. Requirements of OSBL: i. Valid permit ii. High risk H2S Valid Card iii. Personal H2S Monitor iv. Stand by Vehicle v. Source of Communication vi. SCBA Holder vii. Came lock chemical escape hood filter Q. What is ISBL? A. ISBL - Inside battery limit (EPZ Area) that means inside station/inside fence ex: HMPS Well Pads. Requirements of ISBL: i. Valid permit ii. High risk H2S Valid Card iii. Personal H2S Monitor iv. Stand by Vehicle v. Source of Communication vi. SCBA Holder vii. Rig Walker / ELSA Q. How much area is HARWEEL, BIRBA, and ALNOOR? HARWEEL 13 KM BIRBA 7 KM ALNOOR 5 KM Q. Is EPZ sizing? A. The clouded area which may have levels of H2S at 100 ppm or greater. Q. What does 100ppm H2S Mean? – 50-150ppm H2S loss of sense of smell – so that you cannot rely on your sense of smell to let you know that you are in trouble. – 100ppm H2S is the level considered “Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health” (IDLH). Q. 0.01% H2S is =? 100 ppm Q. 10% H2S =? 100 000 ppm Q. What do you need to aware of EPZ? Consider changes in conditions Training rescue personnel Risk assessment Muster area or assembly point Immediate action plan/emergency evacuation planning Q. What is the approximate walking distance of an escape evacuation point (Assembly)? A. 400 m approximately. Emergency Procedure Q. In case of emergency what are your responsibilities? A. What kind of emergency sir? H2S or Fire 1) Due to H2S leak: (My Responsibilities are..... 1. Stop the job and equipment. 2. Hold breath. 3. Wear escape hood. 4. Check the wind direction & move across the wind direction. 5. Also inform crew to go to assembly point against wind direction. 6. Head counting and check log book. 7. Inform to area authority and call the PDO emergency Number 2438-5555, 2467-5555. 2) Fir emergency: (My Responsibilities are..... 1. Stop the job and equipment. 2. Remove the workers from site. 3. Head counting and check log book. 4. Inform the area authority. 5. Check the fire and try to extinguish the fire. 6. If not possible then we will go to assembly point through nearest escape route. Q: What is the emergency number? A: From PDO Number 5555 From Mobile/GSM 24385555, 24675555 Q. What I will tell at emergency number? A. My name and number, my location, type of emergency, what kind of help we need and will not disconnect the call until he tells me. Q. What is empowerment to stop the work? A. If any unsafe work is being carried out any one can stop the work and can safe someone from unwanted, unexpected consequences. Everyone is empowered by PDO to stop any unsafe work or condition. Q. If someone fall in the station then what we will do? A. We consider it H2S emergency and will follow H2S emergency procedure. Q. If anyone fall in trench what will you do? A. I will stop the job and equipment if trench deep more than 1.5 meter I conduct gas test if there is no gas, we will bring him out and take him on a safe place open his cloth and shoes and give him 1 st aid. If area authority is not nearby I will call the PDO emergency. Q. How many types of emergencies are there in PDO Areas? 1. H2S Leak 2. Road Accident 3. Fire Emergency 4. Electrical Shock Q. How you will check wind direction? A. I will kick on the ground and check direction of dust, or I can check from wind sock, or from smoke of flare, or by waving tissue or paper I can check wind direction. Duties Permit Applicant Fill up the application Prepare Job Safety Plan Prepare Certificates Appoint the Permit Holder Visit the site in case of Class A permit Brief the permit holder Get the signature from other effected custodian Ensure the permit is cancel after completion Get the signature of Responsible Supervisor Forward the list of permit required validation for the next day by 16Hrs to Responsible Supervisor Responsible Supervisor Review the Permit HSE Plan & certificates. Visit the site in case of Class “A” Permit along with Area Authority & Permit Applicant. Check and agree with scope. Authorize the permit Forward the list of the permit required for the next day to Area Authority. Authorize the isolation if required Approve pre validation if required Track all permit for conflicting activities Archive the completion Permit. Area Authority Validate Class A and Class “B” permits before work starts. Get the approval from Responsible Supervisor for daily validation. Before validation visit & inspect the site. Review all HSE Plan attached to the permit Conduct the first gas test each day for a Class “A” Permit. Prepare of site isolation. Monitor all the equipment and machine as per HSE Plan. Cancel the permit for safety reason or incompletion work. Check for conflicting of activity. Permit Holder Get validation from the area authority Understand the content of the permit and Job HSE Plan. Brief the content of Permit & Job HSE Plan to the crew. Display the Permit Check and inspect all the tools & equipment as per HSE Plan. Conduct gas test (if required) Suspend the permit for any emergency Suspend the permit if the period expired. Cancel the Permit on completion of the Job. PTW Life Cycle Permit Applicant – Apply the permit. Permit Coordinator – Check the quality. Responsible supervisor – Authorized the permit. Permit Applicant – Brief the Permit Holder. Area Authority – Validate the permit. Permit Holder – Accept the permit. Permit Holder – Tool box discussion. Permit Holder – Carryout the work. Permit Holder – Suspend the permit. Permit Holder, Area Authority – Cancel the permit.