5th Grade Math & Science Lesson Plan: Percentages & Ecosystems
advertisement

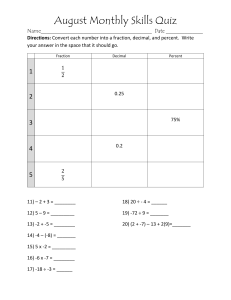
Lesson Plan for week of January 30 – Feb 3, 2023 AREA OF STUDY TOPIC/SUBTOPIC TIME MA 5.53 Determine the percent represented by a shaded region on a grid and record it in decimal, fractional, or percent form. PREVIOUS KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES (I.E. CONCEPTS, SKILLS, ATTITUDES) LEARNING OUTCOMES/ OBJECTIVES Students will be able to: 1. convert to and from fraction to percent to decimal, and vice versa Percent to fraction to decimal Decimal to fraction to decimal Fraction to decimal to percent test MA 5.54 Solve real-world Students will be able to: 1. Differentiate between fraction, decimal, and percent 2. Covert to and fro Students will be able to: TEACHING/ LEARNING STRATEGIES/ACTIVITIES CONTENT (EXAMPLE AND KEY POINTS) Day 1 1. Introduction: Have groups match strategy with matching terms (converting fraction to decimal; decimal to percent; vice versa). 2. Development: Groups will be given a table to complete by converting between fraction to decimal to percent. 3. Group members will be timed to attempt converting a problem. When time is up, student will rotate their worksheet to another group member to solve given the same time frame. 4. Members rotate over and over using their time to solve. 5. After five rotations, class discussion and checking. 6. Repeat with other problems to convert. 7. Conclusion: Complete individual seat work to convert fraction to decimal to perfect and vice versa. Day 2 1. Review, using examples, converting fraction, decimals and percent back and forth. 2. Review rules to follow when taking a test. 3. Issue test and discuss test items. 4. Have students complete test. 1. Percent is a fraction out of 100. 2. Base ten blocks can be used to model percent. 3. A percent can be expressed as a decimal or a fraction. 4. A decimal in the hundredth place can be expressed as a percent as a fraction. 5. A fraction out of 100 can be expressed as a decimal and as a percent. 6. Any fraction can be modelled using fractions strips and can be expressed as a decimal and percent. 7. Any fraction can be expressed as a decimal and as a percent using a standard algorithm. Day 3-4 1. Introduction: Have groups match the 1. Percentages can be applied to real-life situations. 2. Applying percentages to real-life 1 SKILLS ATTITUDES Observing Interpreting Decimals Representing Decimals Application of Percent Noticing Pattern Analytical thinking Speaking Display leadership skills Logical thinking Creative thinking Critical thinking Problem Solving Teamwork OpenMindedness Tolerance Active Listening Metacognition Reasoning Written Communication COMPETENCY BASED ASSESSMENT STRATEGIES COMPETENCY BASED EDUCATION LINKAGES Competency # 2 Emotional Intelligence Competency # 3: Critical and Innovative/ Inventive Thinking #4: Collaboration #6: Digital Literacy Competency # 2 Emotional Intelligence Competency # 3: Critical and Innovative/ Inventive Thinking #4: Collaboration #6: Digital Literacy Competency # 2 Emotional Intelligence RESOURCE REFERENCE MATERIAL/ INSTRUCTIO NAL AIDS Mathematics :A Complete Course Volume 1, pgs. 252 MacMillan Mathematics 6 Teacher’s Book pgs. 45-47 Mathematics :A Complete Course Volume 1, pgs. 252 MacMillan Mathematics 6 Teacher’s Book pgs. 45-47 Mathematics :A EVALUATION problems involving percentages such as tax and interest calculations. 1. 2. Percentage Rate Base 3. distinguish between percentage, base, and rate in word problems use percentage, base, and rate to understand a daily life experience solve for percentage, base, and rate 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. terms PERCENTAGE, BASE and RATE with its appropriate meaning. Have groups share their results. Development: Gary had 30 apples. He gave 20% of the apples to his best friend Camron. How much apples did he give away? Groups discuss and solve. Reflect on definitions of percentage, base, and rate. Discuss to create formulas to calculate percentage, base, and rate. 7. 8. Using formula, groups will recheck their solutions to Gary sharing his apples. 9. Groups share new found results. 10. Conclusion: Solve three problems; using the different formulas. tax Students will be able to: 1. define GST 2. identify GST rate in Belize 3. demonstrate and explain how to solve for tax and interest in real-life Day 4 1. Review formulas using examples. 2. Individually complete worksheet solving word problems finding percentage, base, and rate. Day 5 1. Introduction: Pass out copies of store receipts to groups. Have groups identify and discuss what type of information is included on the sales receipts. 2. Create list on the board. 3. Development: Briefly discuss the information bringing focus on GST section. 4. Further discussion on the basic points situations requires an understanding of base, rate, and percentage. 16 3. Base is the original amount or the number that represents the whole amount. It is the amount you are taking a percentage of. 4. Percentage is the number or the amount that represents a part or portion of the whole or the base. It is the result obtained when the rate is applied to the base. 5. Before calculating for percentages it is important to identify the numbers within a problem as a base, rate, or percentage. 6. Rate –a percent that tells how the base is related to the percentage. The rate has the percent sign. It is the ratio of an amount to the base. When applying the rate to the percentage or base, it must be first converted to a decimal or fraction. 7. Percentage and rate can be calculated using tables and a number line. 8. To calculate for percentage, multiply the base by the rate. Before multiplying the base by the rate, remember to first change the rate to a decimal or fraction. 9. To calculate for rate divide the percentage by the base. Then multiply the answer by 100 and add the percent sign Competency Some possible responses may include the following: Name of the store Address of the store Phone number of the store Store number Date and time of transaction A list of items purchased Price of each item Subtotal Competency # 2 Emotional Intelligence Competency 2 # 3: Critical and Innovative/ Inventive Thinking #4: Collaboration #6: Digital Literacy # 3: Critical and Innovative/ Inventive Thinking #4: Collaboration Complete Course Volume 1, pgs. 252 MacMillan Mathematics 6 Teacher’s Book pgs. 45-47 Mathematics :A Complete Course Volume 1, pgs. 252 MacMillan Mathematics 6 Teacher’s Book pgs. scenarios using standard algorithms 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. General Science 30 minutes Changes in Ecosystem SC 3.17 Differentiate between and list the components of a Terrestrial and an Aquatic ecosystem such as the Barrier reef and Tropical rain forest. Ecosystems Food Chain Food Web Defining the terms: terrestrial, aquatic, barrier reef and rain forest. Students will be able to: 1. Investigate how different organisms obtain energy 2. Identify producers, consumers, and decomposer s concerning taxes, specifically sales tax (GST). Given a scenario, discuss and demonstrate how to calculate GST in their groups. Groups share their strategies. Demonstrate and discuss how to calculate GST. Groups refer back to their solutions and make corrections applying correct strategy. Conclusion: Define GST and solve one problem as Exit Ticket. Day 1 1. Introduction: Play game to review food chain and food web. 2. Development: Complete worksheet interpreting and answering questions from a food web. 3. Conclusion: Whole class discussion and checking of the answers to the worksheet activity. Day 2-3 1. Introduction: Review definition of food web and the different roles through game. 2. Development: Groups work together to create a food web using pictures, yarns, and labels. 3. Conclusion: Groups presentation of their food web. Sales tax Total (including sales tax) Cash given Change received A tally of the number of items purchased Tax is the amount of money that a government requires people to pay based on income, sales, and other activities. E.g., income tax, property tax, and sales tax such as GST. A tax rate is a percentage at which an individual or a business company is taxed by the government. In Belize, GST is a rate of 12.5%. Tax can be calculated the same way as calculating percentage or rate. All organisms need energy in order to survive, grow, and reproduce. They obtain this energy in a variety of ways. Ultimately, the energy in an ecosystem comes from the sun, and flows through an ecosystem from one organism to another through complex ecological relationships. #6: Digital Literacy think-Pair-Share activity • Classifying organisms (table) • Table differentiating terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems Area #3 Critical and Innovative/Inventive Thinking Area #4 Collaboration Some organisms can use the sun’s energy to produce their own food; while others like humans need to eat food (consume) in order to gain energy; still others break down (decompose) dead material for energy. We call these organisms producers, consumers, and decomposers, respectively. Carnivore: An animal that eats meat Consumer: An organism that obtains energy by consuming another organism; includes carnivores, herbivores, and omnivores Decomposer: An organism that obtains energy by breaking down dead organic material Energy flow: The transfer of energy through a food chain from one organism to another Food Chain: The flow of energy in an ecosystem beginning from the sun to a primary producer (plant) to a consumer to decomposers. 3 45-47 Herbivore: An animal that eats plant materials Omnivore: An animal that eats both plant materials and meat Predator: An organism that hunts another organism Prey: An organism that is hunted by a predator Producer: An organism that obtains energy through photosynthesis: sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water A food web is a group of food chains within an ecosystem. Most living things eat more than one type of animal or plant. So, their food chains overlaps and connect. Apex predators are animals that hunt other animals but have no predators hunting them. Apex predators are at the top of the food chain. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 4 5