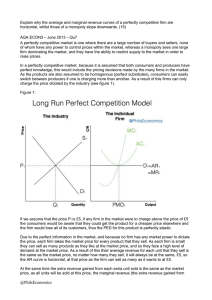
UNIT III 1.What is the shut-down point for a perfectly competitive firm?2 2.What do you mean by monopoly power? 2 3. Define oligopoly market. 2 4. Mention two features of monopolistic competition. 2 5. What do you mean by price discrimination? What do you mean by first degree, Second degree and third degree price discrimination? Or Explain different types of price discrimination with example. 5 6. When price discrimination is possible and profitable (conditions of price discrimination) 7. Mention the important assumptions of perfectly competitive market. 5 8. Explain how equilibrium price and quantity are determined under monopoly. 10 9. State the relation among price, marginal revenue and price elasticity of demand. 10. What is called a price-taker firm? Is a monopoly firm price taker? 11. What do you mean by normal profit and super normal profit? 12. Define Lerner's Index. Ans: Lerner index, in economics, a measure of the market power of a firm. Formalized by the RussianBritish economist Abba P. Lerner in 1934, the Lerner index is expressed in the following formula: Lerner index = (P – MC)/P where P represents the price of the good set by the firm and MC represents the firm's marginal cost. It is used as a measure of a firm's market power. The Lerner index always has a value between zero and one. 13. Distinguish between firm and industry. 14. Define a monopolistically competitive market and explain its features. 15. Is selling cost relevant in a perfectly competitive market? Justify your answer. 16. Distinguish between perfectly competitive market and monopoly market. 17. How long will a perfectly competitive firm continue production in the short-run even if it incurs losses? 18. What is oligopoly market? 2 19. Distinguish between perfect competition and pure competition market. 2 20. What is MR? Demonstrate shapes of AR and MR curves when (i) price is fixed, (ii) price is variable. l+(2+2)=5 21. Explain graphically how price and output are determined in a monopolistically competitive market. 22. What is market? State the main features of perfectly competitive market. Explain the supply curve of a perfectly competitive firm in short run 23.Explain the method of price and output determination under monopoly in the short run. 10 24. Why there is no supply curve of a monopolist? 25. Can a perfectly competitive firm earn supernormal profit in long run?- justify Unit IV 1.Give an outline of marginal productivity theory of distribution. 2. Explain the concept of economic rent. 3. What is quasi rent. 4. Discuss about functional distribution of income. 5. Discuss modern theory of factor pricing. 6. What is collective bargaining? UNIT V 1. What do you mean by circular flow of income? 2. Discuss circular flow in a modern economy. Also mention the leakages and injections in the model. 3. Distinguish between real and nominal GDP. 4. What is GDP at constant price? 5. What is GDP Deflator? 6. Discuss the concept of Demand-Supply and saving- investment approach of determining equilibrium level of income. 7. Discuss different types of unemployment. 8. Explain Phillips curve. 9. What is natural rate of unemployment? 10. Discuss different types of inflation. What are the major causes of inflation? 11. Distinguish between cost- push and demand pull inflation. (with diagram) 12. Briefly discuss the economic effects of inflation. 13. Discuss different measures to control inflation.