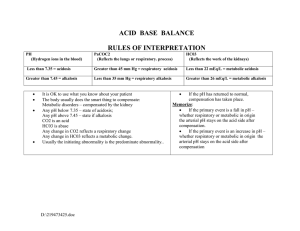
Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) Interpretation Michaela Hill, MSN-Ed, RN University of North Georgia Learning Outcomes 1 Analyze the components of ABGs with a focus on normal values and acid-base status. 2 Interpret ABG results with and without compensation occurring. 3 Determine ABG results through utilizing the Tic-Tac-Toe method. ABGs Arterial blood test Evaluates oxygenation & acid-base status Provides values for: • • • • Potential of Hydrogen (pH) Partial Pressure of Arterial Carbon Dioxide (PaCO2 ) Bicarbonate (HCO3-) Partial Pressure of Arterial Oxygen (PaO2) (Potter et al., 2016) Components & Normal Values Acid/Acidosis pH PaCO2 • • Respiratory component Carbon Dioxide is an aCid HCO3- • Metabolic Component • Bicarb is a Base PaO2 • Base/Alkalosis 7.35 45 - (too many acids) 22 35 mmHg (too few acids) - (too few bases) 7.45 26 mEq/L (too many bases) 80-100 mmHg Not always necessary for interpretation (Cleveland Clinic, 2022) Basic ABG Interpretation (1st word: Metabolicor Respiratory) Evaluate HCO3- & PaCO2 (2nd word: Acidosisor Alkalosis) Evaluate pH • If HCO3- is abnormal in the same way as pH (both acidotic/alkalotic)= Metabolic • <7.35 = Acidosis • If PaCO2 is abnormal with pH= Respiratory • >7.45 = Alkalosis Acid Normal Base Tic-Tac-Toe Method (Cresse, 2016). Example: Acid Normal Base pH= 7.31 PaCO2= 57 HCO3-= 25 pH HCO3- PaCO2 Answer: Respiratory Acidosis Example: pH= 7.25 PaCO2= 37 HCO3-= 20 Acid pH Normal Base PaCO2 HCO3Answer: Metabolic Acidosis Compensation Occurs when PaCO2 & HCO3- are inversely abnormal If pH abnormality is due to a respiratory problem, the metabolic system (kidneys) compensate If pH abnormality is due to a metabolic problem, the respiratory system (lungs) compensate (Potter et al., 2016) Image from: (Anderson, 1990) Example with Partial Compensation: Acid PaCO2 Normal Base pH pH= 7.51 PaCO2= 54 HCO3-= 31 HCO3Answer: Metabolic Alkalosis with Partial Compensation Example with Full Compensation: Acid pH ➡️ PaCO2 pH= 7.44 PaCO2= 20 Normal Base HCO3- HCO3-= 20 • pH is normal- Look to see if value is closer to acid or base side. • Here, the pH is closest to the alkolotic side. • pH must be normal to be fully compensated! Answer: Respiratory Alkalosis with Full Compensation References Anderson, S. (1990). ABGs: Six easy steps to interpreting blood gases. The American Journal of Nursing, 90(8), 42–45. https://doi.org/10.2307/3463952 Cleveland Clinic. (2022, February 18). Arterial blood gas (ABG). https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/22409-arterial-blood-gas-abg Cresse, N.J. (2016, November 28). Tic tac toe ABGs: Interpretation and patient safety. Quality and safety education for nurses (QSEN). https://qsen.org/tic-tac-toe-abgs-interpretation-and-patientsafety/ Potter, P., Perry, A., Hall, A., & Stockert, P. (2016). Fundamentals of nursing (9th ed.). Elsevier.