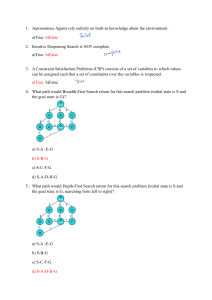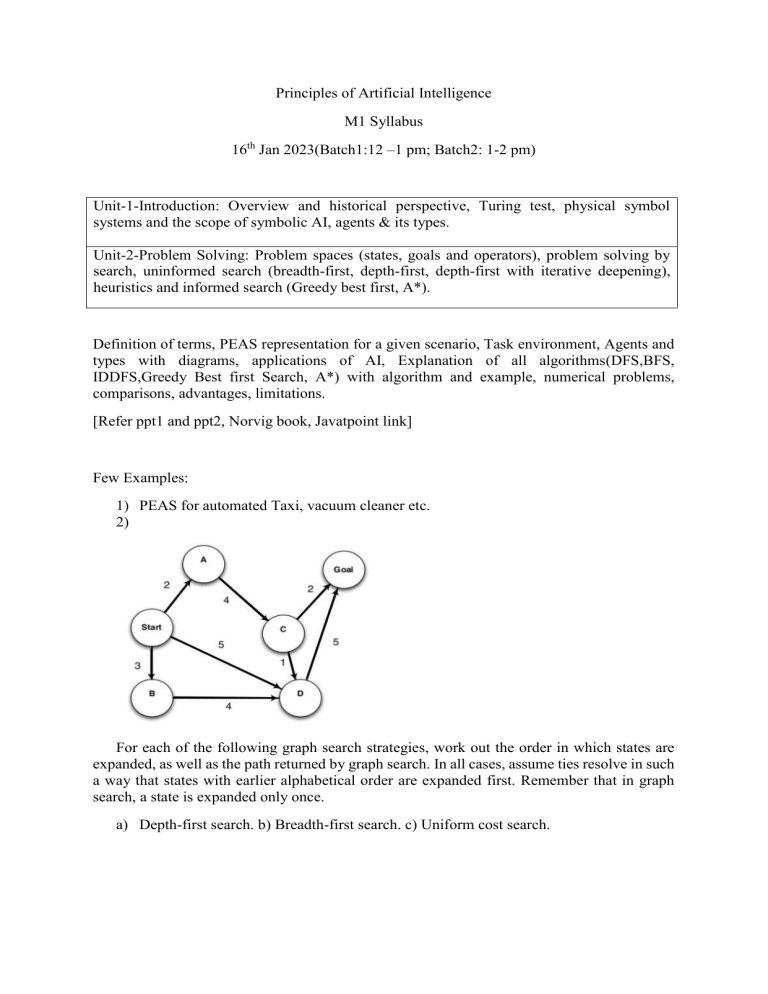
Principles of Artificial Intelligence M1 Syllabus 16th Jan 2023(Batch1:12 –1 pm; Batch2: 1-2 pm) Unit-1-Introduction: Overview and historical perspective, Turing test, physical symbol systems and the scope of symbolic AI, agents & its types. Unit-2-Problem Solving: Problem spaces (states, goals and operators), problem solving by search, uninformed search (breadth-first, depth-first, depth-first with iterative deepening), heuristics and informed search (Greedy best first, A*). Definition of terms, PEAS representation for a given scenario, Task environment, Agents and types with diagrams, applications of AI, Explanation of all algorithms(DFS,BFS, IDDFS,Greedy Best first Search, A*) with algorithm and example, numerical problems, comparisons, advantages, limitations. [Refer ppt1 and ppt2, Norvig book, Javatpoint link] Few Examples: 1) PEAS for automated Taxi, vacuum cleaner etc. 2) For each of the following graph search strategies, work out the order in which states are expanded, as well as the path returned by graph search. In all cases, assume ties resolve in such a way that states with earlier alphabetical order are expanded first. Remember that in graph search, a state is expanded only once. a) Depth-first search. b) Breadth-first search. c) Uniform cost search. 3) Consider the following graph. The numbers written on edges represent the distance between the nodes. The numbers written on nodes represent the heuristic value. Find the most cost-effective path to reach from start state A to final state J using A* Algorithm.