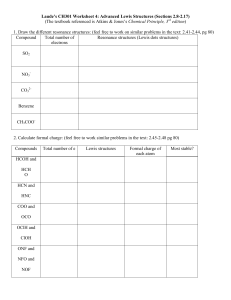
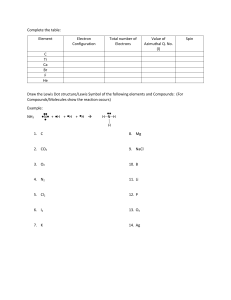
Name: _____________________________ Date: __________________ Grade _______ Work Session 5: Lewis Dot Structures and Resonance 1A) What is the ground-state electron configuration of carbon? 1B) Draw the Lewis electron-dot symbol for an uncharged atom of carbon. 2A) What is the ground-state electron configuration of phosphorus? 2B) Draw the Lewis electron-dot symbol for an uncharged atom of phosphorus. 3A) What is the electron configuration of oxide? 3B) Draw the Lewis electron-dot symbol for an oxide ion. 4A) What is the electron configuration of the sodium ion? 4B) Draw the Lewis electron-dot symbol for the sodium ion. Chem1A – Work Session 5: Lewis Structures and Resonance 1 5) Sum the valence electrons, and draw Lewis dot structures for the following: (a) Water, H2O (b) BeCl2 (c) PF3 (d) HCl (e) AsCl3 6) The ‘octet rule’ applies only to period 2 elements – C, N, O, and F. In terms of atomic orbitals, explain why. 7) On the following molecules, expand the condensed structures and fill in the missing electrons. (Condensed structures are in CH-21.3.) Chem1A – Work Session 5: Lewis Structures and Resonance 2 8) Draw the Lewis dot structures for the following condensed structures. Note that none of the atoms have a formal charge. CH3OH (methanol) CH3CH2CHO (propanal) 9) Draw the Lewis dot structures for the following molecules. Note that none of the atoms have a formal charge. HCN (hydrogen cyanide) CO2 (carbon dioxide) 10A) For each structure of periodate (IO4-), calculate the formal charge on the iodine atom. 10B) For the periodate structure with zero (0) charge on the central atom, draw a resonance structure. Chem1A – Work Session 5: Lewis Structures and Resonance 3 11) Draw Lewis dot structures for the following conjugate acid-base pairs. *The atoms in nitrate follow the ‘octet rule’, which inevitably results in adjacent (+) and (-) charges. (a) bromide (b) hydrobromic acid (c)* nitrate (d) nitric acid 12) Draw Lewis dot structures for the following: (a) carbonate, CO32- (b) bicarbonate, HCO3- (c) carbonic acid, H2CO3 13) Draw the Lewis dot structures for acetate and acetic acid. Chem1A – Work Session 5: Lewis Structures and Resonance 4 14) Draw a Lewis dot structure for the polyatomic ion sulfite such that the central atom has zero (0) formal charge. Next to your diagram, draw a plausible resonance structure. 15) Draw a Lewis dot structure for the polyatomic ion sulfate such that the central atom has zero (0) formal charge. Next to your diagram, draw a plausible resonance structure. Chem1A – Work Session 5: Lewis Structures and Resonance 5 Polarity 16) Define ‘electronegativity’. 17) When the difference in electronegativity is less than 0.5, the bond is . 18) Label the following bonds as polar, non-polar, or ionic. Above the atoms, indicate the direction of the bond dipole and the partial (d) (or full charges) if applicable. partial (d) or full charges Non-polar/Polar/Ionic Na¾I C¾H C¾Si O¾H 19) What is a dipole moment? Does bond length influence the dipole moment? 20) What is the difference in electronegativity of potassium iodide (KI)? Why should this be characterized by percent ionic character rather than electronegativity? Chem1A – Work Session 5: Lewis Structures and Resonance 6 Periodic Trends 21) For the following molecules: (A) H H | | H—C—N— H | " H (B) (C) H—C≡N: H—C=N— H | " H a) Arrange the molecules in increasing carbon-nitrogen bond length. b) Arrange the molecules in order of decreasing carbon-nitrogen bond energy. 22) Using only the periodic table, arrange the members of each of the following sets in order of increasing bond strength. Briefly justify your answers. a) Br―Br, Cl―Cl, I―I b) S―H, S―Br, S―Cl c) C=N, C―N, C≡N 23) Using the only periodic table, arrange the members of each of the following sets in order of increasing bond length. Briefly justify your answers. a) H―F, H―I, H―Cl b) C―S, C=O, C―O c) N―H, N―S, N―O Chem1A – Work Session 5: Lewis Structures and Resonance 7