Electrostatics Problems: Charge, Force, and Electric Fields
advertisement

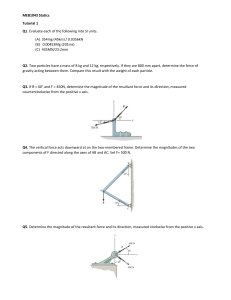
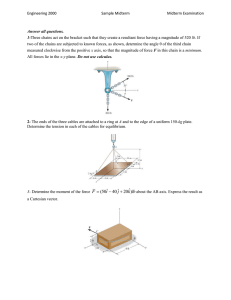
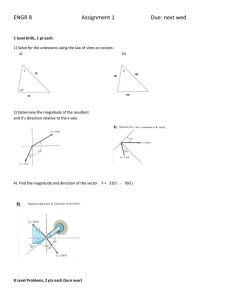
Each of two small non-conducting spheres is charged positively, the combined charge being 40 μC. When the two spheres are 50 cm apart, each sphere is repelled from the other by a force of magnitude 2.0 N. Determine the magnitude of the smaller of the two charges. A particle (charge = +40 μC) is located on the x axis at the point x = −20 cm, and a second particle (charge = −50 μC) is placed on the x axis at x = +30 cm. What is the magnitude of the total electrostatic force on a third particle (charge = −4.0 μC) placed at the origin (x = 0)? If a = 3.0 mm, b = 4.0 mm, Q1 = 60 nC, Q2 = 80 nC, and q = 24 nC in the figure, what is the magnitude of the electric force on q? If a = 60 cm, b = 80 cm, Q = −6.0 nC, and q = 4.0 nC, what is the magnitude of the electric field at point P? r^2 = a^2 + b^2 = 0.60*0.60+0.8*0.80 = 1 m r=1m Ex = E1x + E2x Ex = -E1 cos(theta) + E2 Ex = -kQ/r^2 * (b/r) + kq/b^2 Ex = -9e9*6e-9/1 * (0.80/1) + 9e9*4e-9/(0.80*0.80) Ex = 13.05 N/C Ey = E1x + E2x Ey = E1 sin(theta) + 0 Ey = kQ/r^2 * (a/r) Ey = 9e9*6e-9/1 * (0.60/1) Ey = 32.4 N/C E = (13.05*13.05+32.4 *32.4)^0.5 = 34.929 = 35 N/C A +20-nC point charge is placed on the x axis at x = 2.0 m, and a −25-nC point charge is placed on the y axis at y = −3.0 m. What is the direction of the electric field at the origin? Which one of the diagrams below is not a possible electric field configuration for a region of space which does not contain any charges?