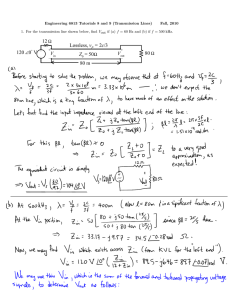
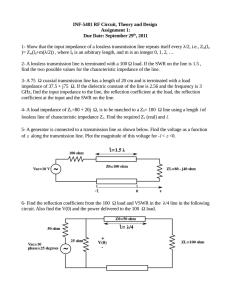
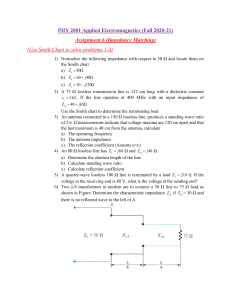
TRANSMISSION LINES LUMPED ELEMENTS TYPES OF TRANSMISSION LINES UNBALANCED– The one wire carry signal, other one for reference(GND) Ex. Co-axial cable BALANCED– Both wires carry data One carries the signal as a positive and other carries it as negative The negative signal is 180 Degree out of phase with the positive Equal noise occurs on both and can cancel each other. Ex. Unshielded Twisted Pair Cable TRANSMISSION LINES TRANSIT TIME EFFECT Signal require finite amount of time to travel along an electric circuit which is no more comparable to the time period of the signal Transmission line – Important case of EM Waves Two conductor system tr = l/v (Transit Time) Reactive drop = Finite for any Non Zero Frequency l/v <<<T (Lumped Circuit Analysis) Distributed Circuit Analysis DISTRIBUTED ELEMENTS(1) DISTRIBUTED ELEMENTS(2) EQUATION OF VOLTAGE & CURRENT INFINITESIMAL SECTION OF TRANSMISSION LINE CONDUCTORS AND DIELECTRICS ARE NON IDEAL R,L,G,C -- PRIMARY CONSTANTS OF TRANSMISSION LINE EQUATION OF VOLTAGE & CURRENT EQUATION OF VOLTAGE & CURRENT(2) PROPOGATION CONST. VOLTAGE AS A FUNCTION OF x FOR DIFF. TIME VOLTAGE AS A FUNCTION OF x FOR DIFF. TIME Voltage & Current ----- Wave type of solution PHASE & ATTENUATION CONSTANT • • PHASE SHIFT CONSTANT (β) ATTENUATION CONSTANT (α ) • β λ =2π • -20 log (e^-1) • 1 np= 8.68 dB --- Phase change per unit length of line(rad/m) --- Attenuation of the wave (np/m) EVALUATION OF ARBITARY CONSTANTS R,L, G,C ϒ , Z0 -- PRIMARY CONSTANTS OF TRANSMISSION LINE -- SECONDARY CONSTANTS OF TRANSMISSION LINE STANDING WAVES & IMPEDANCE TRANSFORMATION (Reflection Co efficient) If a line is terminated in an impedance ZL the impedance seen at a distance I from it is not ZL but is Z(l). LOSS LESS & LOW LOSS TRANSMISSION LINES Loss Less R=G=0 Low Loss R<< wL ,G << wC The Phase constant of the low loss line is same as loss less line. low loss line : α <<<< β (Take α=0 in analysis) STANDING WAVE RATIO Substitute ϒ=jβ (Lossless Line) Voltage or current is max. or min.--- Impedance is purely Resistive VSWR VSWR – Plot of |v| or |I| as a function of distance l is called the voltage or current standing wave pattern. -Easily measurable parameter , It does not require measurement of phase -Range between 1 to ∞ IMPEDANCE VARIATION ON LOSSLESS LINE Characteristics of LOSSLESS LINE Line Characteristics repeat at every λ/2 Normalized impedance inverts every λ/4 • ZL= Zo , The impedance is same at any point on the line • Characteristic impedance of a transmission line is 50Ω. Input impedance of the open circuited line is Zoc=100+j150Ω. When the transmission line is short circuited the value of the input impedance will be • • (a)50Ω (c)7.69+j11.54Ω (b)100+j150Ω (d)7.69-j11.54Ω • A lossless line in a load which reflects the part of the incident power. If VSWR=2 The % power that reflected back is • (a) 57.7 (b) 33.3 (c) 0.11 (d) 11.11 • A lossless line in a load which reflects the part of the incident power. If VSWR=2 The % power that reflected back is • (a) 57.7 (b) 33.3 (c) 0.11 (d) 11.11 • VSWR pattern in a lossless transmission line with characteristic impedance 50Ω and a resistive load is shown in figure The reflection coefficient is given by (a) -0.6 (b) -1 (e) None of these The value of the load resistance is (a) 50Ω (b) 200Ω (d) 0Ω (e) None of these (c) 0.6 (d) (c) 12.5Ω 0