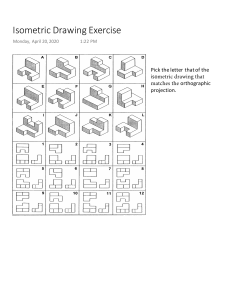
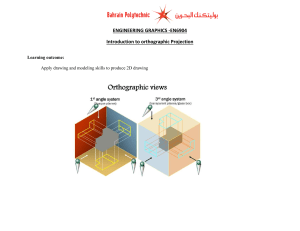
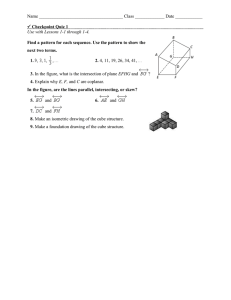
1-2 Drawings, Nets, and Other Models 1-2 1. Plan 1 What You’ll Learn 2 1 2 3 4 5 • To draw nets for three- 1. dimensional figures Isometric Drawing Orthographic Drawing Foundation Drawing Identifying Solids From Nets Drawing a Net To make a foundation drawing, as in Example 3 Math Background Geometric principles are the basis of drawing techniques. For example, isometric dot paper is a pattern of the vertices of equilateral triangles and can easily be used to draw equilateral triangles and hexagons that tesselate a plane. A B C . . . And Why 1 Lesson 1-1 Draw the next figure in each sequence. See margin. orthographic drawings Examples GO for Help Check Skills You’ll Need • To make isometric and A To make isometric and orthographic drawings To draw nets for threedimensional figures A Objectives C D D E 2. O X H ■ O X New Vocabulary • isometric drawing • orthographic drawing • foundation drawing • net Drawing Isometric and Orthographic Views You will study both two-dimensional and three-dimensional figures in geometry. A drawing on a piece of paper is a two-dimensional object. It has length and width. Your textbook is a three-dimensional object. It has length, width, and height. Representing a three-dimensional object on a twodimensional surface requires special techniques. Vocabulary Tip In Greek, isos means “equal” and metron means “measure.” In an isometric drawing, all 3-D measurements are scaled equally. You can make an isometric drawing on isometric dot paper to show three sides of a figure from a corner view. The simple drawing of a refrigerator at the right is an isometric drawing. More Math Background: p. 2C Lesson Planning and Resources 1 1. Answers may vary. Sample: EXAMPLE Isometric Drawing Make an isometric drawing of the cube structure at the left. See p. 2E for a list of the resources that support this lesson. Isometric drawing: PowerPoint Bell Ringer Practice Fro nt Check Skills You’ll Need Step 1 For intervention, direct students to: Finding and Using a Pattern Quick Check Lesson 1-1 Extra Skills, Word Problems, Proof Practice, Ch. 1 E B 1 On isometric dot paper, make an isometric drawing of the cube structure. See back of book. H 10 10 cm 10 cm Chapter 1 Tools of Geometry 10 cm 4 7 cm Special Needs 10 cm 10 Step 3 ■ A 1, 2. Step 2 ht Rig Below Level L1 Have students reproduce the net in Example 4 using scissors and graph paper. learning style: tactile L2 Provide cubes for students to examine as they work through Examples 1–3. learning style: tactile 2. Teach An orthographic drawing is another way to show a three-dimensional figure. It shows a top view, front view, and right-side view. 2 EXAMPLE Guided Instruction Orthographic Drawing Make an orthographic drawing from the isometric drawing at the left. Isometric drawing: 2 Orthographic drawing: nt ht Rig 3 Top Dashed lines show hidden edges. Front Quick Check Careers Architects use orthographic drawings for floor plans. Ask: A floor plan of your school building would show which view? top Solid lines show visible edges. Fro EXAMPLE EXAMPLE Error Prevention Because a foundation drawing shows the base, students may think there is a bottom view. Remind them that the top view shows the base. Right PowerPoint 2 Make an orthographic drawing from this isometric drawing. See back of book. Additional Examples 1 Make an isometric drawing of the cube structure below. Fro nt A foundation drawing shows the base of a structure and the height of each part. A foundation drawing of the Sears Tower is shown at the right. EXAMPLE 49 89 65 109 109 89 65 49 89 The Sears Tower is made up of nine sections. The numbers tell how many stories tall each section is. Foundation Drawing Fro Isometric drawing: 2 Make an orthographic drawing from the isometric drawing in Additional Example 1. Connection 3 The foundation drawing shows four heights in the nine sections of the Sears Tower in Chicago, Illinois. 2 2 1 Fro nt Quick Check ht Rig 1 Front Front 3 a. How many cubes would you use to make the structure in Example 3? 9 cubes b. Critical Thinking Which drawing did you use to answer part (a), the foundation drawing or the isometric drawing? Explain. Answers may vary. Sample: The foundation drawing; you can just add the five numbers. Lesson 1-2 Drawings, Nets, and Other Models Advanced Learners Have students research the Platonic Solids or Archimedean Solids and draw their nets. Students can then make models of these solids. learning style: verbal Have each student bring an empty cereal or other type of box to cut into a net. Clarify that more than one net or pattern can be drawn for a given solid. learning style: tactile Top Right 3 Create a foundation drawing for the isometric drawing in Additional Example 1. 11 English Language Learners ELL L4 Ri Right Real-World Foundation drawing: t gh nt Make a foundation drawing for the isometric drawing at the left. 2 1 Right 3 ht Rig 1 Front 11 Guided Instruction 2 1 Nets for Three-Dimensional Figures PowerPoint A net is a two-dimensional pattern that you can fold to form a threedimensional figure. A net shows all of the surfaces of a figure in one view. Additional Examples 4 Is the pattern a net for a cube? If so, name two letters that will be on opposite faces. yes; A and A C, B and E, D and F B D E F 4 Identifying Solids From Nets EXAMPLE Multiple Choice The net at the left shows all the surfaces of a three-dimensional figure. Which figure can you fold from the net? C 5 Draw a net for the figure with a square base and four isosceles triangular faces. Label the net with its dimensions. 10 The black triangle is shown on the largest side of the figure instead of the smallest in choices C and D. Those choices cannot be correct. The black triangle will be at the same end as the two diagonal lines when the net is folded into a box. Choice B is correct. cm 1 4 5 A A B B 8 cm m 0c D C C D E E A Test-Taking Tip B C D E The number of surfaces on a solid must match the number of regions in its net. 1 Package designers can use nets to help design containers. 5 Drawing a Net EXAMPLE Packaging Draw a net for the graham cracker box. Label the net with its dimensions. Resources • Daily Notetaking Guide 1-2 L3 • Daily Notetaking Guide 1-2— L1 Adapted Instruction 14 cm GRAHAM CRACKERS 20 cm Closure 7 cm 20 cm 7 cm 14 cm Explain how isometric, orthographic, and foundation drawings are alike and how they are different. Sample: All show three-dimensional figures on a two-dimensional surface; isometric drawings show three faces, orthographic drawings show the outlines of three views, and foundation drawings use the top view of orthographic drawings to show the height of each part of the figure. Quick Check 5 Draw a net for the solid shown. Label the net with its dimensions. See margin. 10 cm 10 cm 7 cm 12 12 F E D C B E D C B A 3 E D C B A 2 E D C B A 4 The net at the right folds into the cube shown beside it. Draw the cube and show which letters will be on its front and top. E, C D 8 cm Quick Check Chapter 1 Tools of Geometry 4 cm EXERCISES For more exercises, see Extra Skill, Word Problem, and Proof Practice. 3. Practice Practice and Problem Solving Assignment Guide A Practice by Example Example 1 GO for Help On isometric dot paper, make an isometric drawing of each cube structure. 1–3. See margin. 1. 2. 3. (page 10) 1 A B 1-10, 17-22, 28-30 2 A B 11-16, 23-27, 31-32 C Challenge 33-34 Test Prep Mixed Review Examples 2, 3 (page 11) For each figure, make (a) an orthographic drawing, and (b) a foundation drawing. 4–6. See back of book. 4. 5. Homework Quick Check To check students’ understanding of key skills and concepts, go over Exercises 4, 14, 18, 22, 26. 6. ht Fro Rig nt Exercises 1–3 If possible, provide ht Rig Fro nt 35-38 39-45 Fro nt wooden cubes so that students can model each cube structure. ght Ri How many cubes would you use to make each of the following? Example 4 7. the structure in Exercise 4 6 8. the structure in Exercise 5 6 9. the structure in Exercise 6 8 10. a model of the Sears Tower on page 11 713 GPS Guided Problem Solving L2 Reteaching L1 Adapted Practice Match each three-dimensional figure with its net. Practice Name (page 12) C 11. A 12. L3 L4 Enrichment B 13. Class L3 Date Practice 1-2 Points, Lines, and Planes Refer to the diagram at the right for Exercises 1–15. * ) 1. Name AB in another way. 2. Give two other names for plane Q. 3. Why is EBD not an acceptable name for plane Q? A Q Are the following sets of points collinear? * ) * ) A. B. C. D E 4. AB and C 5. B and F 6. EB and A 7. F and plane Q Are the following sets of points coplanar? * ) * ) F 9. DB and FC 11. AE and DC * ) 12. F, A, B, and C 13. F, A, B, and D 14. plane Q and EC 15. FB and BD * ) * ) C * ) * ) 8. E, B, and F 10. AC and ED * ) B * ) Find the intersection of the following lines and planes in the figure at the right. * ) * ) 16. GK and LG H G 17. planes GLM and LPN L K 18. planes GHPN and KJP M J 19. planes HJN and GKL N P © Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. * ) * ) 20. KP and plane KJN 21. KM and plane GHL Refer to the diagram at the right. Example 5 (page 12) 22. Name plane P in another way. Draw a net for each figure. Label the net with its dimensions. 14–16. See back of book. 14. 15. 16. 7m D 23. Name plane Q in another way. 24. What is the intersection of planes P and Q? 25. Are A and C collinear? C B A Q 26. Are D, A, B, and C coplanar? 27. Are D and C collinear? * ) P * ) 28. What is the intersection of AB and DC ? 2 in. 2 in. 4 in. 30 mm 10 m 12 mm 17. Answers may vary. Sample: a. 6m Apply Your Skills 17. a. Open-Ended Make an isometric drawing of a structure that can be built using 8 cubes. a–b. See margin. b. Make an orthographic drawing of this structure. c. Make a foundation drawing for this structure. See left. Lesson 1-2 Drawings, Nets, and Other Models 1. 2. Fro nt ht Rig * ) 30. Are AB and plane Q coplanar? 31. Are B and C collinear? 8m 36 mm B 29. Are planes P and Q coplanar? 13 Front Right b. 3. Fr on t ht Rig Fro nt Front ht Rig Right Top 13 4. Assess & Reteach For each foundation drawing, make (a) an isometric drawing on dot paper, and (b) an orthographic drawing. 18–20. See back of book. 2 1 19. 1 Front Use the figure below for Exercises 1–3. 2 3 2 1 20. Front 1 3 2 3 2 1 Right 3 Right Lesson Quiz 3 Right 18. GPS PowerPoint Front Read the comic strip and complete Exercises 31 and 32. Fro ht nt Rig 1. Make an isometric drawing of the cube structure. Fro 21. orthographic top view 22. Answers may vary. Sample: You may want a bird’s-eye view for a tourist map showing locations of attractions. ht nt Rig Visualization Think about how each net can be folded to form a cube. What is the color of the face that will be opposite the red face? blue green orange purple 23. 24. 25. 26. 2. Make an orthographic drawing. Front Top Right 3. Is the pattern a net for a cube? If so, name two letters that will be on opposite faces. no 27b. Answers may vary. Sample: the net shown in Exercise 23; it is easy to cut and fold. F A 21. What type of drawing that you’ve studied in this lesson is a “bird’s-eye view”? See left. 22. Writing Photographs of the Washington Monument are typically not taken from a bird’s-eye view. Describe a situation in which you would want a photo showing a bird’s-eye view. See left. B C 27. There are eleven different nets for a cube. Four of them are shown above. a. Draw as many of the other seven as you can. (Hint: Two nets are the same if you can rotate or flip one to match the other.) See margin. b. Writing If you were going to make 100 cubes for a mobile, which of the eleven nets would you use? Explain why. See left. D Make an orthographic drawing for each isometric drawing. E yes; A and C, B and D, E and F 28. GO Homework Help Visit: PHSchool.com Web Code: aue-0102 4. Draw a net for the figure. 29. 30. nline Fro nt ht Rig t Fro 28–30. See back of book. nt h Rig ht Fro nt Rig 31. Draw a net for a cylinder. (Hint: The net needs to show three regions: two circles and a rectangle.) See margin. Sample: 32. There are eight different nets for a pyramid with a square base. Draw as many of them as you can. See margin. 14 Chapter 1 Tools of Geometry 31. Answers may vary. Sample: 27. Answers may vary. Sample: 14 32. C Alternative Assessment Challenge 33. Visualization Use the orthographic drawing at the right. a. Make an isometric drawing of the structure. b. Make an isometric drawing of the structure from part (a) Top after it has been turned on its base 908 counterclockwise. c. Make an orthographic drawing of the stucture from part (b). d. Turn the structure from part (a) 1808. Repeat parts (b) and (c). a-c. See margin. d. See back of book. Front 34. The net at the left is folded into a cube. Sketch the cube so that its front face is shaded as shown at the right. See margin. Right Give each student 10 cubes. Instruct students to use all their cubes to build a structure. Then have students draw isometric, orthographic, and foundation drawings of their structures, and have partners check that the drawings correctly describe the structure. Have students dismantle the cubes, then exchange drawings with new partners who use the drawings to rebuild the same structure. Test Prep Test Prep Multiple Choice 35. A three dimensional figure is made with 11 cubes. The top view of the figure shows 5 squares. Which of the following is the greatest possible number of cubes in a stack represented by one of the five squares? D A. 4 B. 5 C. 6 D. 7 Resources For additional practice with a variety of test item formats: • Standardized Test Prep, p. 75 • Test-Taking Strategies, p.70 • Test-Taking Strategies with Transparencies 36. Which of the following shows a top, front, and right view of a threedimensional shape? G F. an isometric drawing G. an orthographic drawing H. a foundation drawing J. a net Short Response 37. Draw a net for the rectangular box. Label the net with its dimensions. See margin. 7m 37. [2] correct net and labels 1m 5m Extended Response 1m 5m 38. Make drawings to show the top view, the front view, and the right-side view of the figure at the right. See back of book. 7m [1] mislabeled net 39. Mixed Review GO for Help n 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 39. Reasoning What is the last digit of 345? To answer, make a table, look for a pattern, and use inductive reasoning. Explain the pattern. See margin. Lesson 1-1 Find a pattern for each sequence. Use the pattern to show the next two terms. 40. A, C, E, G, . . . I, K 41. 2, 6, 12, 20, 30, . . . 42, 56 42. 4, 16, 64, 256, . . . 1024, 4096 43. 100, 95, 85, 70, 50, . . . 25, –5 Last digit of 3n 3 9 7 1 3 9 7 1 11R1 4 45 The pattern 3, 9, 7, 1 repeats 11 times for n ≠ 1 to 44. For n ≠ 45, the last digit is 3. Skills Handbook x 2 Algebra Evaluate each expression for the given values. 44. a2 + b2 for a = 3 and b = -5 34 Lesson 1-2 Drawings, Nets, and Other Models lesson quiz, PHSchool.com, Web Code: aua-0102 33. a. b. c. Fro nt t h Rig nt 15 34. Answers may vary. Sample: Top Fro 45. 12 bh for b = 8 and h = 11 44 Front Right ht Rig 15