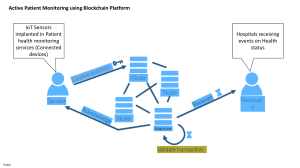
Attacks in Blockchain, its counter measures and effectiveness Reference Attack Basic Theory Countermeasure Effectiveness S. Singh et al [1] Liveliness Attack Attack used to delay the confirmation time of a transaction as much as possible by going through its three phases: preparation, denial and retarder phase. Two different block Feasible solution generation strategies encoded by Conflux’s consensus protocol. One gives an optimal solution by quick confirmation of consensus and other provides a high throughput and confirmation in blockchain systems. A. Begum et al [2] Double Spending Attack In this attack, a successful transaction is duplicated with the same fund creating a flaw that no two tokens can be spent twice in digital ledger. MSP (Multistage Secure Pool) framework which allows the pool to authenticate the transactions. The proposed framework includes four stages to overcome this attack are 1) detection stage, 2) confirmation stage, 3) Forwarding stage, and 4) broadcast stage. Effectively controls double spending but other vulnerability like 51% attack leads to double spending problem. Thus, open to provide solution. S. Sayeed et al [3] 51% Vulnerability Attack Applies on PoW based blockchain when a single minor hash function occupies more than 50% of the total blockchain hash function and can manipulate and reverse the transaction, stops others mining operations and hinder transaction verification. Two Phase Proof-of-Work prevents the pool from increasing beyond the alarming size by shrinking the incentive for miner in the pool. 2P-PoW prevents from creating hegemony by either outsourcing a major chunk of their hash rate or exposing the private keys of pool operator. Infeasible solution as by increasing the block size might be not sufficient since a powerful adversary can still overload the network by generating the dust transaction. Thus, open to solution. S. Singh et al [1] Private Key Security Attack An attacker detect vulnerability in elliptical curve digital signature to acquire User’s private key to access funds and verify transaction of the user. A public key infrastructure Effective solution in used to authenticate the cryptography for identity ensuring the secure public keys. integrity of a blockchain network and a group key management to secure communication to achieve confidentiality. S. Singh et al [1] Privacy Leakage Blockchain is traceable and even though measures are taken to ensure privacy, there are still some leakages of confidential information that is acquired by the attackers to perform malicious operation. HAWK framework used to provide privacy for smart contracts which allows codeless private contracts to enhance the security. Hawk divides a system into private and public part which stores financial information as private and other codes as public. Effective solution but still not used in overall blockchain network because overall change in structure of blockchain will be required. Attacks in Blockchain, its counter measures and effectiveness Reference Attack Basic Theory Countermeasure Effectiveness S. Solat et al [6] Selfish Mining Attack Some miners try to waste other legitimate miner’s mining power. Attacker attempt to fork the private chain and maintain a longer private chain and hold more blocks. Zero Block, prevents this attack by using a novel timestamp-free technique that exploits the Poisson nature of the proof-ofwork and the current knowledge on the propagation of information in Bitcoin. Much effective than previous solutions which were inefficient to forgeable timestamping techniques. But still require feasible solution. M. Saad et al [4] BGP Hijacking Attack Attacker intercepts the blockchain network by manipulating the BGP, after which data can be routed and modified by the attacker. The BGPsec protocol is used to fix vulnerabilities like fake routing updates incurring traffic hijacking and interception by attesting routing updates. Infeasible solution as it is unable to ensure correct packet delivery on the internet. S. Singh et al [1] Balance Attack Attacker introduces a delay between valid subgroups with the same mining power and executes the transaction. These attacks can be easily countered by patching vulnerabilities in programming platform and using secure programming Effective solution as major attack is due to careless programming practice. Y. Chen et al [5] Sybil Attack Forging an identity in a peerto-peer network of a reputation system, thus destroying the reputation. NetFlow algorithm selects a credible node of a network node based on transaction information to ensure that the authorized agent lost part of the revenue for the block. Effective solution References: [1] S. Singh, A. S. M. S. Hosen and B. Yoon, "Blockchain Security Attacks, Challenges, and Solutions for the Future Distributed IoT Network," in IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 13938-13959, 2021, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3051602. [2] A. Begum, A. H. Tareq, M. Sultana, M. K. Sohel, T. Rahman, and A. H. Sarwar, ‘‘Blockchain attacks, analysis and a model to solve double spending attack,’’ Int. J. Mach. Learn. Comput., vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 1–6, 2020. [3] S. Sayeed and H. Marco-Gisbert, ‘‘Assessing blockchain consensus and security mechanisms against the 51% attack,’’ Appl. Sci., vol. 9, no. 9, p. 1788, Apr. 2019. [4] M. Saad et al., "Exploring the Attack Surface of Blockchain: A Comprehensive Survey," in IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, vol. 22, no. 3, pp. 1977-2008, third quarter 2020, doi: 10.1109/COMST.2020.2975999. [5] Yourong Chen, Hao Chen, Yang Zhang, Meng Han, Madhuri Siddula, Zhipeng Cai, A survey on blockchain systems: Attacks, defenses, and privacy preservation, High-Confidence Computing, Volume 2, Issue 2, 2022,100048, ISSN 2667-2952, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hcc.2021.100048. [6] S. Solat and M. Potop-Butucaru, “Zeroblock: Preventing selfish mining in bitcoin.” axXiv preprint arXiv:1605.02435,2016 Submitted by: Himanshu Gautam (2021IS42)