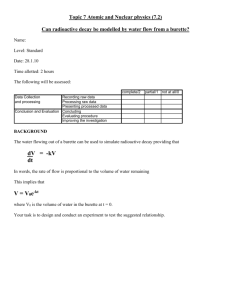
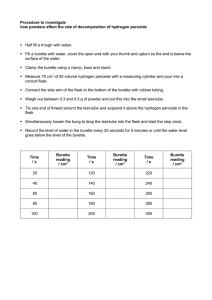
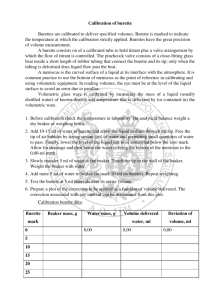
SCH 3U1 Acid- Base Titration Lab Purpose: To determine the concentration of a solution of hydrochloric acid by acid-base titration. Task: Titrate the given standard solution of sodium hydroxide against the given solution of hydrochloric acid of unknown concentration. Use your results to calculate the concentration of the acid and complete the write up portion below. Apparatus: Goggles 2- 150 mL beakers 1- 50 mL burette Burette clamp graduated cylinder retort stand 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask Materials: Standard solution of sodium hydroxide (1 mol/L) Unknown solution of hydrochloric acid Phenolphthalein solution (indicator) Procedure: 1. Using a graduated cylinder, obtain 50 mL of sodium hydroxide in a beaker and 25 mL of hydrochloric acid in a separate beaker. 2. Burette preparation: rinse the burette with distilled water and let the water drain out. Add 10 mL of titrant to the burette and slowly turn the burette so that it is horizontal. Roll the burette to make sure the titrant touches every part inside the burette. Drain the titrant. Attach your burette to the retort stand using a clamp. 3. Add 50 mL of titrant to your burette using a funnel. Place the 50 mL waste beaker under the burette tip. Open the stopcock to allow the titrant to fill the tip of the burette then close the valve. Record the initial volume reading of the burette for your trial. TAKE THE READING FROM THE BOTTOM OF THE MENISCUS! 4. Add 10 mL of hydrochloric acid to the Erlenmeyer flask and add two drops of phenolphthalein indicator to your hydrochloric acid. Place the flask under the tip of the burette so that the burette tip is just inside the mouth of the flask. Put a blank sheet of white paper under your Erlenmeyer flask to better observe the colour change of the indicator. 5. Open the valve slowly to titrate the acid and swirl the flask vigorously as base is being added. 6. When the colour of the acid begins to change (pink colour lingers), close the the valve and open it only slightly until the base is released in a dropwise fashion. Swirl the flask after each drop. 7. STOP adding titrant when the colour change from clear to pale pink is permanent. Dark pink means you have missed the endpoint! Exclude trials that are hot pink from your calcuations. 8. Record the final volume reading of your burette. 9. Repeat steps 3 (reading the initial volume of titrant) – step 8 until you have 3 trials that have no more than a 0.2 mL difference in the amount of base added. SCH 3U1 WRITE UP Group members: Date: Observation Table: Concentration of the standard solution, base NaOH __________________mol/L Trial 1 2 3 4 Average volume of base added Final base burette reading (mL) Initial base burette reading (mL) Volume of base added (final-initial) Questions: 1. Calculate the average volume of titrant used to titrate the unknown solution of hydrochloric acid and record your answer in the observation table above. (1) 2. Write a balance chemical equation for the titration including states of matter. (3) 3. Use your lab results and the balance equation to calculate the concentration of the acid (3) 4. What is an endpoint? What is an equivalence point? (2) 5. Was your solution totally neutralized? Explain (hint: review the pH range that phenolphthalein will operate at) (2) 6. Discuss any sources of error that your group encountered during this experiment. (2) Conclusion: Summarize your results and background knowledge needed to understand how to complete this lab.