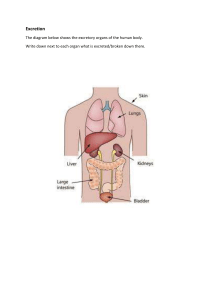
Section 3: Excretory System The kidneys maintain homeostasis by removing wastes and excess water from the body and by maintaining the pH of blood. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions • • • What is the function of the kidney in the body? What are the steps of the excretion of wastes from the Bowman’s capsule to the urethra? What is the difference between filtration and reabsorption in the kidneys? Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education Excretory System Vocabulary Review New • • • pH Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education kidney urea Excretory System 17-1-23 CH-34.3-EXCRETORY SYSTEM • L.O- To analyse the structure and function of human excretory system and nephron [Pg.1005-1006] Parts of the Excretory System • • • • The excretory system removes toxins and wastes from the body. Regulates the amount of fluid and salts in the body.[osmoregulation] Maintains the pH of the blood The components that make up the excretory system include the lungs, skin, and kidneys. Tim Fuller Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education Excretory System The Kidneys • • • • Bean shaped organs that filter out wastes, water, and salts from the blood Renal cortex Renal medulla Renal pelvis Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education Excretory System The Kidneys Nephron Filtration • • • Each kidney contains approximately one million filtering units called nephrons. The renal artery transports nutrients and wastes to the kidney. Urea is nitrogenous waste product. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education Excretory System Kidney Filtration Go to your ConnectEd resources to play Animation: Kidney Filtration. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education Excretory System 21-9-21 CH-34.3-EXCRETORY SYSTEM • L.O- To describe steps in urine formation and kidney disorders [ Pg. 1006-1007] The Kidneys Nephron Filtration • • • Each kidney contains approximately one million filtering units called nephrons. The renal artery transports nutrients and wastes to the kidney. Urea is nitrogenous waste product. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education Excretory System The Kidneys1.Ultrafiltration-Blood is filtered through the glomerulus into Bowman’s capsule, due to high blood pressure in glomerulus. [Ultrafiltration] The filtrate moves through convoluted tubules, loop of Henle and collecting tubule[ called together as renal tubule] 2.Reabsorption and the Formation of Urine • • • Glucose, some water and minerals are reabsorbed back into the capillaries surrounding the renal tubule. Urine, which is excess fluids and wastes[like urea and excess salts], leaves the kidneys through ducts called the ureters. Urine is stored in the urinary bladder and exits the body through the urethra. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education Excretory System Kidney Disorders • • • Infections Nephritis-inflammation of the glomeruli Kidney stones-crystallized solid that forms in the kidney Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education Excretory System Common Excretory Disorders Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education Excretory System Review Essential Questions • • • What is the function of the kidney in the body? What are the steps of the excretion of wastes from the Bowman’s capsule to the urethra? What is the difference between filtration and reabsorption in the kidneys? Vocabulary • kidney • urea Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education Excretory System