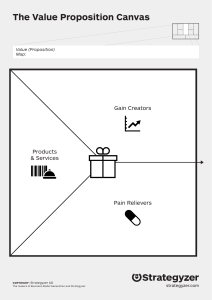
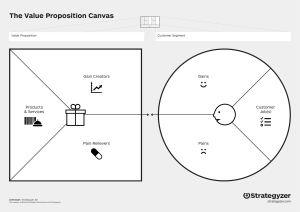
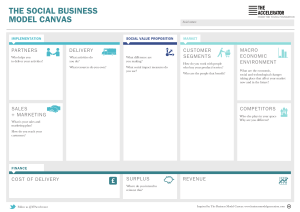
Chapter 1 - Innovation Management and New Business Development Purpose of the chapter • After this class, you will be able to: Describe innovation and differentiate innovation management from new business development Explain the skillset of an innovation manager Distinguish the idea development from the implementation phase in the innovation process Illustrate the role of uncertainty in the innovation process Categorize and define different types of innovation Implement the business model canvas in specific cases Assess the role of innovation in the economy and on public policy Describe what it means for countries to be innovative Where are we? What is innovation? • • • • • iPhone Online banking Electric bicycles Uber Artificial intelligence for marketing purposes New product New service New market New business model New process • And: a new way of looking at things!(see Volvo video) https://www.media.volvocars.com/global/en-gb/media/videos/244515/this-is-not-a-car Definition of new business development “The creation and development of new products, services, business models or processes in firms or other organizations” Why do firms have to innovate? Survival of firms: Nokia Why innovation? Effect on competition Definitions Innovation • Schumpeter, 1934 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. The introduction of a new good The introduction of a new method of production The opening of a new market The application of a new source of supply of raw materials A new organization of an industry • Garud et al., 2013 • the invention, development, and implementation of new ideas by people within an organizational context • This book / course • the creation and development of new products, services, business models or processes in firms or other organizations What is innovation? • New-to-the-world • Creation of new product line(s) • Addition to existing product line • Targeting new markets • Similar performance at lower cost • Improvements We include the whole surface in our definition of innovation Innovation management • Innovation management concerns the management of the creation and development of new products, services, business models or processes in firms or other organizations New business development • Sorensen, 2012 • Business development refers to the tasks and processes concerning analytical preparation of potential growth opportunities, the support and monitoring of the implementation of growth opportunities, but does not include decisions on strategy and implementation of growth opportunities • This book / course • the creation and development of new products, services, business models or markets The difference Paradoxes What is business model innovation? DriveNow: business model innovation • • • • Car sharing service in municipal areas DriveNow owned the cars Initiators: BMW (car manufacturer) and Sixt (leasing company) Business model innovation: • User was not owner of the car • The value proposition was: mobility (not: a car) • New customer channel (internet), customer relations (membership), key activities (booking system, maintenance system) and partners (BMW, Sixt) What is a business model? • System of interconnected and interdependent activities that determines the way the company ‘Does business’ with its customers, partners and vendors (Amit and Zott, 2012, p. 42). • A business model describes the rationale of how an organization creates, delivers, and captures value (Osterwalder and Pigneur, 2010) • A story around who do we serve, what is the value proposition (what), and how we make money Business model canvas (Osterwalder and Pigneur, 2006) Business model canvas (Osterwalder and Pigneur, 2006) Examples: supermarket Business model innovation • What is it? • A major change in business model • Examples • iPhone: major change in value proposition • Easyjet: small changes in many elements of the business model, which together make a big leap Structure: 2 sided market Classification of innovations Technology-market matrix Modularity matrix Innovation and society Why innovation: economic benefits • Innovation has positive and negative externalities (external effects): • Positive • Economic growth • Competitiveness of countries • Solution to societal problems (e.g. Health care, sustainability) • Negative • Loss of jobs (on the short term) • Pollution, use of resources Long term economic waves (Rursus, 2009) Be careful: no proof that the waves are caused by technology Government policy • Governments support innovation because of its expected positive externalities • Direct subsidies: involve a payment to an organization or person, dependent on the execution of a specific activity • Indirect subsidies: financial compensations to an organization or individual for a specific activity but that do not involve direct payments, e.g. tax deductions Innovativeness of countries How well do countries do? Global Innovation Index 2020: https://www.wipo.int/edocs/pubdocs/en/wipo_pub_gii_2020.pdf The European Innovation Index: https://ec.europa.eu/docsroom/documents/42981 Measurement https://ec.europa.eu/docsroom/documents/42981