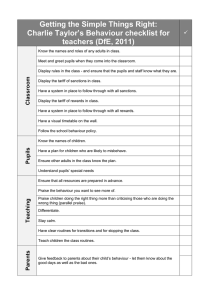
Marie Daubé Unit 2 – Developing Teaching, Learning and Assessment in Education and Training 2.3.3 Explain how the student’s own practice in creating and maintaining a safe, inclusive teaching and learning environment has taken account of theories of behaviour management. Before discussing how I create and maintain a safe and inclusive teaching and learning environment, I think it is important to define what it might look like. According to the 7th of the 14 teacher’s standards called “manages behaviour effectively to ensure a good and safe learning environment”, safe and inclusive teaching and learning environment manifests when the teacher: At Secure Expert Has clear rules and routines for Has extensive knowledge and Has a critical understanding of the behaviour in classrooms, and takes understanding of how to use and most effective teaching, learning and responsibility for promoting good and adapt a range of teaching, learning behaviour management strategies courteous behaviour both in and behaviour management strategies classrooms and around the school, in accordance with the school’s behaviour policy Has high expectations of behaviour, Able to personalise learning and Demonstrates how to select and use and establishes a framework for behaviour codes to provide approaches that personalise learning discipline with a range of strategies, opportunities for all learners to to provide opportunities for all using praise, sanctions and rewards achieve their potential. learners to achieve their potential Manages classes effectively, using Manages classes very effectively, Models management of classes approaches appropriate to pupils’ using approaches appropriate to effectively, using approaches needs in order to involve and motivate pupils’ needs in order to fully involve appropriate to pupils’ needs in order them and motivate them to involve and motivate all Maintains good relationships with Maintains excellent relationships with Models and coaches others to pupils, exercises appropriate pupils, exercises appropriate exercise appropriate authority and to authority, and acts decisively when authority; acts decisively act decisively consistently and fairly necessary Page 1|5 There are several ways in which I try to implement the above in my practice and this is what I shall discuss in this essay. Motivation, inner-drive and basic needs As mentioned in previous essays, Abraham Maslow postulated that a person will be motivated when his needs are fulfilled. The need starts from the lowest level basic needs and keeps moving up as a lower-level need is fulfilled. In my practice creating and maintaining a safe, inclusive teaching and learning environment, I met these needs in order by: 1. Physiological: Physical survival necessities such as food, water, and shelter -ensuring the optimum classroom conditions are met (such as heater, AC, opened windows) and that water is always available. 2. Safety: Protection from threats, deprivation, and other dangers - ensuring I conduct a risk assessment as I enter the classroom. 3. Social (belongingness and love): The need for association, affiliation, friendship, and so on -gage their interests, understand their friendships, help them deal with difficulties they may face in their relationships. 4. Self-esteem: The need for respect and recognition – I do this by listening to my students—and hear them, using positive humor, providing corrective feedback in ways that foster student effort, acknowledging student growth. 5. Self-actualization: The opportunity for personal development, learning, and fun/creative/challenging work. Self-actualization is the highest level need to which a human being can aspire according to Maslow and I make sure my relationship with pupils ensures a productive and inspiring learning environment. John Hattie proposed “that how learners see themselves, and what they perceive as most important in terms of their learning and their desired outcomes, will have a significant effect on their motivation to learn and Page 2|5 subsequent behaviour in class” (Bates, 2016, p156). Therefore, I use a lot of positive reinforcement in my language to support them feel safe and included. Rules and routines I sustain high expectations of behaviour which are integral to learning. I establish and maintain a framework for behaviour management, consistently and fairly, using a wide range of strategies including those mentioned by Vygotsky, incorporating the use of specific praise, sanctions and rewards. In the same way, as proposed by Lee Canter’s theory, I try my best to make sure that I set clear expectations for myself and the pupils. When coming into my class, pupils demonstrate a shared understanding of rules and routines for behaviour which are embedded and implemented consistently in accordance with the school’s behaviour policy. In addition, I actively encourage pupils to behave well in the classroom and around the school and display high levels of courtesy and cooperation. And as per Kounin’s “ripple effect” theory, I ensure that any matters relating to pupil behaviour are addressed immediately thus maximising their learning; all the while overlooking some as mentioned in Sue Cowley’s theory. Treat them as individuals and not just a group of people Robert Hare contends that almost certainly all human beings have psychopathic traits and as such, he created the PCL or Psychopathic Checklist as a means to diagnostic and deal with these individuals’ traits. According to Bob Bates, this applies in classroom too and teacher should be aware they are teaching students with different personality types and not packs of people who happen to have the same age. Bates advises (Bates, 2016, p163): “should you encounter people displaying these traits in your class, I would advise you to (…) have a strategy Page 3|5 (…) make sure that you follow the rules and regulations set down by your own organisation (…).” The reason for mentioning this because in order to deal with some types of behaviours we ought as adults to understand that students are individuals and that if we want promote inclusive and safe learning environment, we must first need to know and understand them (to the best of our ability), study age and stage related expectations as well as child development in order to support them with more challenging behaviours they themselves may not be in a position to understand. My classroom is a Judgement-Free Zone What constitutes safe and inclusive teaching and learning is when students feel free and safe to be able to express themselves. If they feel like any time they open their mouth to answer a question they might get judged negatively by their peers, they will stop opening themselves up and this is what I exert avoiding in my classroom. Teaching Humanities, we are prone to discuss sensitive issues and at times go into debate over them. To combat this potential avenue for mockery or judgement, I need to go out of your way to create an environment free from judgment. I let them know that differing opinions are a great thing and that being "wrong" isn't a bad thing. I remind them that failure is part of learning and often share about my own failures which demystifies the idea adults know it all and are free from mistakes or being judged by others and/or their peers. Lastly, I have an excellent knowledge and understanding of how to tackle derogatory language and inappropriate behaviour such as racism and homophobia; and other forms of bullying including the inappropriate use of social media. Page 4|5 Choice theory In my practice I keenly encourage learners to feel a responsibility. Most learners have a much higher level of investment into the group and their learning (reducing unwanted behaviour) when they are given a choice than when there is no specific expectations for participation, decision-making or direct involvement placed upon them. To conclude, it is apparent that the most effective behaviour management systems incorporate elements from various theories as behaviour and its subsequent management is a result of various factors such as the social interaction between individuals and the internal cognitive processes. I have only named a few but I implement various behaviour theories in my practice with the intent of creating a safe and inclusive learning environment where learners feel that they belong, where everyone is equal and that nobody is ostracized, and which, in turn, improves behaviour in lessons. Additionally, I use positive reinforcement is utilized in lessons through praise and encouragement, and when my learners are not allowed to say they can’t do something and always encouraged to try to do something to the best of their ability! References: Bates, B. (2016), Learning Theories simplified, London: Sage. The Knowledge Hut (no date), Motivation Theories [online]. Available from: https://www.knowledgehut.com/tutorials/project- management/motivation-theories (accessed July 2021) Page 5|5