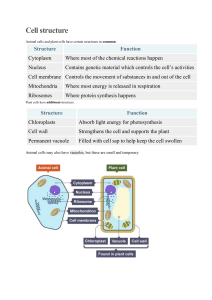
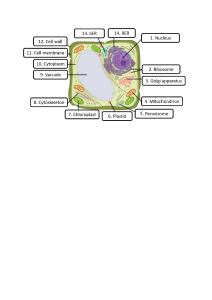
Cells and Organisation (Foundation) Revision Mat Label the cells using words from the boxes. a Complete the table to identify which sub-cellular structures are found in animal cells. Sub-Cellular Structure Animal Cell c Label the light microscope using the words in the f box. Plant Cell Biconcave shape to give it a large surface area for the diffusion of oxygen. nucleus circular DNA cell membrane mitochondria cell wall cytoplasm mitochondria permanent vacuole nucleus chloroplast Long fibres to carry electrical impulses up and down the body. chloroplasts cell wall cell membrane eyepiece lens stage cytoplasm light source flagellum cytoplasm circular DNA cell wall flagellum plasmid Name the sub-cellular structure that carries out each function. Explain why animal cells do not need chloroplasts. stage clips base fine adjustment knob coarse adjustment knob Cilia to waft mucus along the airways. Describe how you would use the microscope to view a pre-prepared slide of blood cells. plasmids b arm objective lens permanent vacuole cell membrane Contains bands of protein that change shape to contract and relax. d Controls the movement of substances into and out of the cell. A jelly-like substance that fills the cell, where most chemical reactions occur. Controls the activities of the cell. It contains genetic material (DNA), which is packaged into structures called chromosomes. h Name each type of cell, then draw one line from each cell to its adaptation. Contains lots of chloroplasts for photosynthesis. Compare how genetic material is packaged in plant cells and in bacterial cells. e Muscle cells and sperm cells both contain lots of mitochondria. Explain why. g Long protrusion to fit between grains of soil to absorb water. Tail-like structure and lots of mitochondria to release energy for movement. 1 of 2 Cells and Organisation (Foundation) Revision Mat The illustrations show four structures that make up the circulatory system. i Label the parts of the skeleton using the words from the box. k l Describe the four functions of the skeleton. the body you would find each type. 1. Support: circulatory system heart Joint: c blood vessel red blood cell n Name each joint and give an example of where in Example in body: Name each level of organisation in the correct order from smallest to largest. 2. Protection: Joint: smallest c Example in body: 3. Movement: o Complete the sentences using words from the box. antagonistic biomechanics contracts push shrink expands relaxes pull 4. Making blood cells: largest Muscles can’t Name each organ system and complete the descriptions of their function. j only , they can . A pair of muscles that work together are called Name: m Name and describe the function of each part of the joint. Function: Takes in muscles. is a from the air and removes strong, smooth tissue that . covers the ends of the bones from the blood. to Name: Function: Breaks down and absorbs . cranium sternum radius clavicle ribs tibia ulna patella mandible scapula humerus vertebrae pelvis carpals femur fibula talus When one muscle in the joint hold muscle , the other . The joint is pulled in keeps the one direction causing movement. slippery to The combination of muscles, bones and joints making us move is called . 2 of 2