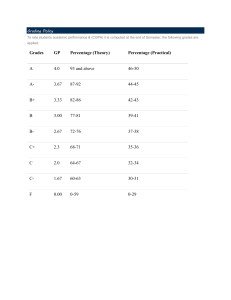
lOMoARcPSD|20887369 FIELD STUDY 1 EPISODE 13 Bsetle (Eulogio "Amang" Rodriguez Institute of Science and Technology) Studocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|20887369 LEARNING EPISODE FIELD STUDY 1 Assessment of Learning 13 (Summative Assessment) OBSERVE, ANALYZE, REFLECT Activity 13.1 Aligning Assessment Task with the Learning Outcome Resource Teacher:ARLENE TORRES School: SJCHS Grade/Year Level: GRADE 10 Teacher’s Signature: Subject Area:ENGLISH Date: February 02 OBSERVE Observe at least 3 classes – 1 Physical or Biological Science or Math, English, Filipino; 1 Social or Literature/Panitikan, EsP and 1 P.E / Computer / EPP/TLE Subject Learning Outcome/s Assessment Task (How did Teacher assess the learning outcome/s? Specify. EX: P.E / EPP/ TLE To dance tango Written quizEnumerate the steps of tango in order. Social Science, Literature/Panitikan, EsP Students perform news casting and debate By basing on the rubrics and make an reflection on what learning they have. Physical/Biological Science/Math English/Filipino To explore and create different experiments By making a rubrics and actual demonstration Is the If not aligned, assessment improve on it. tool / task aligned to the learning outcome/s? No Performance test – Let students dance tango. Yes Yes Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|20887369 ANALYZE 1. Are all the assessment task aligned to the learning outcome? - Yes all the assessment tasks of my resources teacher are aligned on the learning outcome objective they have. 2. What are possible consequences if teacher’s assessment tasks are not aligned to learning outcome/s? Does this affect assessment result? How? - The possible consequences if teachers assessment task are not aligned to learning outcomes is it may not be possible to be achieved the class. The effect of assessment results cannot be measure what the students learned from the lesson because it was not aligned in the intended learning outcomes. 3. Why should assessment tasks be aligned to the learning outcomes? - The assessment task should be aligned to the learning outcomes to attain the objectives of the lesson , And also to have an organized lesson and it will achieve only if the intended learning outcome are aligned in assessment learning process. REFLECT Reflect on past assessment you have been trough. Were they all aligned with what your teacher taught with learning outcomes? - As I reflect on the past assessments that I had been through, I remember all assessment that is given to us is aligned in the learning outcomes of our teacher. How dis this affect your performance? As a future teacher, what lesson do you learn from this past experience and from this observation? - It did not affect my performance because I remember all the assessment that I received was aligned on the intended learning outcomes of our teacher. - I learned that it is important to applied the steps in making the lesson plan . If we already know the steps on how to make the lesson plan then it will no longer be difficult for us to make a good intended learning outcomes that aligned to our assessment learning. Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|20887369 LINK Theory to Practice C. 1 Here is a learning outcome: Describe a person by the use of a metaphor Here is a test outcome: Describe a classmate or teacher by the way of a metaphor. Is the test item aligned to the learning outcome? A. No C. Yes B. Somewhat D. Yes, if teacher is not included A. 2 Learning outcome: Conduct an investigation to prove that plants can manufacture their own food. Test item: Can plants manufacture their own food? Explain your answer. Is the test item aligned to the learning outcome? A. No C. Yes B. Somewhat D. Yes, if explain your answer dropped A. 3 Learning outcome: Demonstrate the inductive method of teaching. Test: Outline the steps of the inductive method of teaching. Is the item aligned to the learning outcome? A. No C. Yes B. Somewhat D. Yes, if teacher is not included C. 4.Which assessment task is aligned to this learning outcome: Compute the menu if the scores are 50, 50, 50.48, 47, 46, 45, 44, 43, 42, 41, 40. A. What is mean? B. Is mean a measure of variability? C. What is the menu of 50, 50, 50.48, 47, 46, 45, 44, 43, 42, 41, 40. D. Is mean the same as average? A. 5 Learning outcome: To observe subject-verb agreement as one speaks. Test: Give the correct form of the verb. 1. Dogs (howl). 2. A cat (meow) 3. Birds (fly) Is the test aligned to the learning outcome? A. No C. Yes B. Somewhat D. Yes, there are 3 items on subject-verb agreement A. 6.Here is a lesson objective / intended learning outcome: “illustrate the law of supply and demand with your original concrete example”. For content validity, which test item is aligned? A. Define the law of supply and demand and illustrate it with an example. B. Illustrate the law of supply and demand with drawing. C. Illustrate the law of supply and demand with concrete, original example. D. Explain the law of supply and demand and illustrate it with diagram. Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|20887369 A. 7.Teacher B wrote this learning outcome: “To interpret a given quotation.” For content validity which should she ask? A. Interpret Nietzsche’s statement: “He who has a why to live for can bear with almost any how.” B. Do you believe in Nietzsche’s statement: “He who has a why to live for can bear with almost any how.”? C. What is true in Nietzsche’s statement: “He who has a why to live for can bear with almost any how.”? D. Nietzsche’s was an atheist. Do you believe that he can give this statement: “He who has a why to live for can bear with almost any how.”? A. 8. After teaching them the process of experimenting, Teacher J wanted his students to be able set up an experiment to find an answer to a scientific problem. Which will he ask his students to do? A. Set up and experiment to find out if aerial plants can also live o land. B. Can aerial plants also live on land? Research on experiments already conducted. Present your finding in class. C. Observe if aerial plants can survive when planted in soil. Note your observations and present them in the class. D. Research on the answers to this scientific problem: Can aerial plans survive when transferred in soil? C. 9. Here is an intended learning outcome of a Health teacher: “Identify skillrelated fitness and activities suitable for the individual”. Does her test item measure this particular outcome and therefore has content validity? Question 1. Identify the components of Physical fitness under skill-related activities. a. body composition c. flexibility b. agility d. organic vigor A. Yes, very much B. Yes, because it asks something about skill related activities. C. No. D. No, the opinions have nothing to do with skill related activities Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|20887369 Activity 13.2 Observing the Use of Traditional Assessment Tools Resource Teacher: ARLENE TORRES Teacher’s Signature: School: SJCHS Grade/Year Level: GRADE 10 Date: Subject Area: ENGLISH OBSERVE Observe classes and pay particular attention to the assessment tool used by the teacher With teachers permission, secure a copy of assessment tool. Direction: Put a check (/) on the test which teacher used. From your teacher’s test, give an example Type of traditional Assessment Tool/Paper and Pencil test Put a check (/) here Learning Outcome Assessed Sample test item of resource teacher Comments (Is the assessment tool constructed in accordance with established guidelines?) Explain your answer. Selected Response Type 1. Alternate response NOT OBSERVED NOT OBSERVED NOT OBSERVED 2. Matching type NOT OBSERVED NOT OBSERVED NOT OBSERVED 3. Multiple choice NOT OBSERVED NOT OBSERVED NOT OBSERVED 4.Others NOT OBSERVED NOT OBSERVED NOT OBSERVED Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|20887369 Type of traditional Assessment Tool/Paper and Pencil test Put a check (/) if Resource teacher used it. Learning Outcome Assessed Sample test item of resource teacher Comments (Is the assessment tool constructed in accordance with established guidelines?) Explain your answer. Constructed- Response Type 1. completion 2. Short answer type 3. Problem solving 4. Essay – restricted 5. Essay non – restricted 6.Others ANALYZE 1. Which assessment tools/task were most commonly used by teacher? Which ones were rarely used? Why were they rarely used? 2. Based on your answer found in the Tables above in which type of assessment tools and task were the Resource teacher most skilled in test construction? Least skilled? - NOT OBSERVED 3. Can an essay or other written requirement, even if it is a written paper-and-pencil test, be considered and authentic form of assessment? Explain your answer. Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|20887369 REFLECT How good are you at constructing traditional assessment tools? Which do you find most difficult to construct? Any lessons learned? LINK Theory to Practice 1. Which assessment task is aligned to the learning outcome given above? A. True-False test – an assessment task must be aligned to the learning outcome. B. Column 1 presents the learning outcome. Column 2 has the assessment task. Determine alignment of assessment with learning outcome. C. Here are 5 test items, Evaluate them on the basis of established guidelines in test construction. D. Is an essay more reliable than a multiple choice test? 2. What’s WRONG with this TRUE-FALSE test item? Filipinos are sociable but lazy. A. Opinionated C. Very short B. Not fit for a T-F test D. Sweeping 3. Is this item in accordance with rules on test construction? Write everything you learned from this course. A. No C. Somewhat B. Yes D. No, opinionated 4. In matching type of test, one option among 4 was not chosen by any examinee. What is TRUE of that option? A. Options C. Distracters B. Premises D. Jokers 5. In a multiple choice type of test, one option among 4 was not chosen by any examinee. What is TRUE of that option? A. Implausible C. Plausible B. Realistic D. Unattractive 6. The students were at a loss as to what answer to give in a completion type of test since there were so many blanks. Which is TRUE of the test item? A. Too complex C. Over mutilated B. Unattractive D. Implausible Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|20887369 Activity 13.3 Observing the Use of Non-Traditional Assessment Tools and Scoring Rubrics Resource Teacher: Teacher’s Signature: School: Grade/Year Level: Subject Area: Date: OBSERVE Observe classes in at least 3 different subjects and pay particular attention to the assessment tool used by the teacher. With teacher's permission, secure a copy of the assessment tool. Study the assessment tool then accomplish Observation Sheet. Did your Resource Teacher explain the rubric to the students? Which type of rubric did the Resource Teacher use-analytic or holistic? Authentic Assessment NonTraditional/ Alternative Learning Outcome Assessed Sample of Product/ Performance Assessed How a product/ performance was assessed One example of a product assessed. (Put a photo of the product/ documented performance in My Teaching Artifacts. INCLUDE THE RUBRIC IN MY TEACHING ARTIFACTS. Describe how the product/ performance was assessed. Which was used analytic rubric or holistic rubric? INCLUDE THE RUBRIC IN MY TEACHING ARTIFACTS 1. Product 2. Performance Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com) Comments (Is the scoring rubric constructed according to standards lOMoARcPSD|20887369 ANALYZE 1. Between analytic and holistic rubrics which one was more used? Why do you think that type of rubric was used more? 2. Based on your answers in # 1, what can you say about the scoring rubrics made and used by the Resource Teachers? 3. Will it make a difference in assessment of student work if teacher would rate the product or performance without scoring rubrics? Explain. 4. If you were to improve on one scoring rubric used, which one and how? 5. Can an essay or other written requirements, even if it is a written paper-and-pencil test, be considered an authentic form of assessment? Explain your answer. 6. Can rubrics help make students to become self-directed or independent learners? Do rubrics contribute to assessment AS learning (self-assessment?) What if there were no rubrics in assessment? LINK Theory to Practice A. 1. To pinpoint which part of the lesson needs more explanation, which scoring rubric can help? I. Analytic II. II. Holistic A. I only B. I and II C. II only D. No need for rubric B. 2. I want to know how skilled the students have become in research report. Which assessment task will be valid? A. Make students defend research report before a panel. Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|20887369 B. Make students write the research report. C. Group the students for research report writing. D. make students conduct an action research. C. 3. I want to get a global view of a student's performance. Which rubric is most fit? A. Analytic C. Holistic B. Itemized D. Analytic and holistic A. 4. Which can prove that students are now capable of sewing after a 200-hour course? A. Presentation of a product they have sewn B. Operation of the sewing machine C. Drawing a pattern for a set of pajamas D. Labeling the parts of a sewing machine A. 5. Which is the most reliable way of determining whether or not the student can now dance tango? A. Performance test C. Written test on steps of tango B. Oral test D. Written test illustrating the steps Activity 13.4 Scrutinizing the Types and Parts of a Portfolio Resource Teacher:ARLENE TORRES School: SANJOSE HIGHSCHOOL Grade/Year Level:GRADE 10 Date: Teacher’s Signature: Subject Area:ENGLISH OBSERVE 1. Ask your Resource Teacher for samples of portfolio, if any. If there are, select one best portfolio from what you examined. 2. If none, research for a sample portfolio and include them in My Learning Artifacts 3. Based on the sample portfolio given by your Resource Teacher/researched by you, accomplish Observation Sheet # 4. Put a check in the right column. What a Portfolio Includes Elements of a Portfolio 1. Clear objectives - The Present? Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com) Missing? lOMoARcPSD|20887369 objectives of the lesson/unit/course are clear which serve as bases for selection 2. Explicit guidelines for selection - What, when, where, how are products/documented performances selected? 3. Comprehensible criteria- the criteria against which the portfolio is graded must be understood by the learners 4. Selective significant pieces The portfolio includes only the selected significant materials. 5. Student's reflection - There is evidence that students reflected on their learning. 6. Evidence of student participation in selection of content of portfolio - There is proof that students took part in the selection of the content of the portfolio. ANALYZE 1. With OBE in mind, which should be the basis for the selection of pieces of evidence to show that what the student was supposed to learn was learned? 2. Scrutinize the elements of this portfolio. Based on the parts, under which type of portfolio do this fall? Elements of a ___________ Portfolio (Which type of portfolio? 1. Cover Letter- "About the Author" and "What My Portfolio Shows About My Progress as a Learner” 2. Table of Contents with numbered pages 3. Entries-both core (required items) and optional items (chosen by students). 4. Dates on all entries to facilitate proof of growth over time. 5. Drafts of aural/oral and written products and revised revisions, i.e. (first drafts and corrected/revised versions) 6. Student's Reflections Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|20887369 3. Where and when does the teacher make use of each of the 3 types of portfolio? REFLECT Have portfolios made the learning assessment process more inconvenient? Is the effort exerted on portfolio assessment commensurate to the improvement of learning and development of learners' metacognitive process that result from the use of portfolio? LINK Theory to Practice A. 1. A portfolio is synonymous to a folder of files. Is this CORRECT? A. No C. Yes B. Somewhat D. Sometimes A. 2. Which is an essential part of a portfolio? A. Student's reflection on his portfolio B. Display portfolio for everyone to see student development C. Artistic design to show student's artistic talent. D. Student's self-rating A. 3. I need to prove that I have fully developed the skill at writing a research report. Which type of portfolio is MOST APPROPRIATE? A. Showcase portfolio C. Development portfolio B. Assessment portfolio D. Process portfolio B. 4. Which portfolio can prove that an improvement has taken place in the way students pronounce words? A. Showcase portfolio B. Development portfolio C. Assessment portfolio D. Process portfolio C. 5. I want to know if my students can now focus the microscope properly. With which portfolio am I concerns? Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|20887369 A. Showcase portfolio C. Assessment portfolio B. Development portfolio D. Process portfolio Activity 13.5 Determining the Level of Teacher’s Questions Resource Teacher: ARLENE TORRES Teacher’s Signature: School: SANJOSE HIGHSCHOOL Grade/Year Level: GRADE 10 Date: Subject Area: ENGLISH OBSERVE 1. Observe a teacher in the classroom. 2. Note his/her questions both oral and written. 3. Score him/her according to the level of questions that he/she asks from remembering to creating and metacognition and self-system thinking. You may also refer to written tests for samples of questions in the various levels. 4. Make tally, then get the total. Use Table 1 and Table 2 separately. Table 1. Number of Questions per Level Cognitive Processes (Bloom as revised by Anderson and Krathwohl) Rank Cognitive Processes (and Kendall and Marzano) Self-system Thinking Metacognition Creating Evaluating Analyzing /An Applying Understanding / Remembering / Rank 2 1-Lowest Total 6 5 6-Highest 5 4 3 Tally of Assessment Tasks/ Questions. NOT OBSERVED NOT OBSERVED / Analysis Knowledge Utilization Comprehension Retrieval / //// - Example 4 Table 2. Examples of Assessment Questions / Assessment Task Tally and Total Score of Cognitive Processes Rank Tally and Total Score of Cognitive Rank Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com) Example of Assessment Rank based lOMoARcPSD|20887369 (Bloom as revised by Anderson and Krathwohl) Example: Creating = / Evaluating = / Processes (and Kendall and Marzano) Self-system thinking 6-Highest Metacognition 5 6-Highest Analyzing /An = // Applying = /// 5 4 3 Understanding = // Remembering = ///// 2 1-Lowest Tasks / Questions Given by Resource Teacher e.g. Teacher asked students Why is the lesson important to you? on use NOT OBSERVED Analysis Knowledge Utilization Comprehension Retrieval = /// 3 4 NOT OBSERVED NOT OBSERVED NOT OBSERVED 2 1-Lowest NOT OBSERVED NOT OBSERVED / / Rank Rank NOT OBSERVED ANALYZE 1. Which cognitive skill had the highest number of assessment questions? lowest number? - The cognitive skill had the highest number of assessment questions is remembering because the type of those questions are the way to checked the teacher if his/her students has recall their lessons that they discussed. 2. What do these (lowest and highest number of assessment questions) reveal about Resource Teacher's level of questions? - Based on the lowest and highest number of assessment questions that made by the Resource teacher’s , it reveal the level of questions balance because it’s based on remembering and analysing. Remembering where the students will recall only on what they discussed on their past lesson and analysing because students required to use their higher order thingking skills just to analyse the correct answer. 3. Based on Kendall's and Marzano's taxonomy, which are the highest cognitive skills? Give example of an assessment question for each of the two highest cognitive skills- metacognitive skills and self-system thinking. - Based on Kendall’s and Marzano’s taxonomy , the highest cognitive skills is retrieval wherein it is all about recalling the lesson from permanent memory. Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|20887369 REFLECT If you were to rate yourself on HOTS where will you be from a scale of 1 to 5 (52 highest) where will you be? - If im going to rate my HOTS , I will rate my self on a scale of 3 because I know myself that I need to learn more to develop HOTS. As a future teacher, reflect on how will you contribute to the development of learners HOTS? - As a future teacher I will contribute to the development on my learners HOTS by giving them a fair questions in their exams or quizzes. I will always use the cognitive skills of Bloom’s taxonomy to distribute properly the questions . LINK Theory to Practice C. 1. "Is my thinking CORRECT?" asks a student to himself. In which level of cognitive process is he? A. Self-system C. Metacognition B. Analysis D. Application A. 2. Formulate a 5-item imperfect matching type of test; is a test item in the level of which cognitive process? A. Creating C. Self-system thinking B. Analyzing D. Evaluating A. 3. Which one demonstrates self-system thinking? A. Ask the question "What has this lesson to do with me? B. Critic your thinking process. C. Come up with a solution to the given problem. D. Relate your present lesson to past lessons. B. 4. Paraphrase the first stanza of Rizal's "My Last Farewell" calls for _______. Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|20887369 A. analyzing C. evaluating B. understanding D. applying B. 5. How would you rate students' ability to reason out logically is a question to students' ability to A. engage in metacognition C. do self-system thinking B. analyze D. evaluate Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|20887369 Activity 13.6 Analyzing a Table of Specifications Resource Teacher:ARLENE TORRES School: SANJOSE HIGH SCHOOL Grade/Year Level: Teacher’s Signature: Subject Area: ENGLISH Date: FEBRUARY 02,2022 ANALYZE 1. What parts must a TOS contain to ensure test content validity? - To ensure the test content validity , a TOS must contain the equal distribution of questions in every item of cognitive level. 2. Why is there a need for number of items per cognitive level? - To maintain the fairness of questions in every cognitive level and also to be fair in every students. 3. With OBE in mind, is it correct to put learning outcome not topic in the first column? Why or why not? - In my own opinion, it is important to put first the learning outcomes because it is need to consider the output of my students. 4. Can a teacher have a test with content validity even without making a TOS? - Yes, the teacher can have a test question with content validity even without making tos but it is not reliable REFLECT Read this conversation and reflect on teachers' assessment practices. Write your reflections here. Student A: Saan naman pinulot ni Teacher ang kaniyang tanong? Ni-isang tanong sa tinuro, wala! (Where did Teacher get her test? Not one of what she taught came out!) Student B: Oo nga.! Nakakaiinis! (You are right! How annoying!") Did you have a similar experience? Reflect on it. Will the required use of Table of Specifications as guide in test construction solve the problem of misaligned tests? Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|20887369 - Yes I have the same experience during my highschool days I experienced during exams that there are some questions that are not connected to the lesson which teacher discussed. So to finish the exam I just answered it by my stock knowledge without knowing if it is correct or not. SHOW Your Learning Artifacts Accomplished Observation Sheet Analysis Reflection Completed Sample TOS LINK Theory to Practice A. 1. In Teacher R's Table of Specifications (TOS), 60 percent of the 1st grading test items are applying questions based on Bloom's taxonomy. A review of her test shows that 50% are remembering items, 20% are analyzing questions and 30% are applying questions. Is Teacher's test aligned with her TOS? A. No. B. No, her analyzing questions is supposed to be 60% C. Yes. D. Yes, her applying questions are also analyzing questions, too. A. 2. What is a function of a TOS? To ensure the __________. A. content validity of a test C. reasonable length of a test B. predictive validity of a test D. predictive validity of a test A. 3. A TOS ensures alignment of test with learning outcomes. Is the statement TRUE? A. Very true B. Sometimes true C. False D. Sometimes true, sometimes false Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|20887369 B. 4. In a TOS, the number of hours spent on a learning outcome determines the number of test items to be asked. Is this CORRECT? A. No C. Not always B. Yes D. Depends on the level of the questions asked A. 5. The following are found in a TOS EXCEPT _______. A. Teaching-learning activities B. Number of hours devoted to a topic C. Cognitive level of test item D. Number of test items A. 6. "It's just not fair. I studied everything we discussed in class about the Philippines and the things she made a big deal about, like comparing the Philippines And to think all she asked was 'What's the capital of Singapore? What does the conversation imply about the kind of test they took? A. Lacks content validity B. Has content validity. C. Lacks reliability D. Lacks construct validity Activity 13.7 Computing Students Grades Based on DepEd Grading System Resource Teacher: ARLENE TORRES School: Grade/Year Level: GRADE 10 Teacher’s Signature: Subject Area: ENGLISH Date: FEB 05,2022 OBSERVE A. Sample Students' Report Card 1. Secure a sample of a Students' Report Card from your Resource Teacher. 2. Study a sample of an unused Student's Report Card. Observe its contents. Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|20887369 3. Ask permission from your Resource Teacher for an interview with him/her and with a group student regarding the new grading system. B. Interview of Resource Teacher 1. What are the new features of the latest grading system? What things are you required to do with this new grading system which you were not asked before? - According to my resource teacher, the new grading system is favor to the students because it is no longer zero based while the teacher it’s favor too because they were able to come up with the grades that are suitable in every students performance. 2. Which do you prefer the old or the new grading system? Why? - According to my resource teacher , she preferred the new grading system because it is not hassle for them because they use an electronic grading system C. Interview of 5 Students 1. What do you like in the new grading system? - The most they like in the new grading system is that no longer zero based. Because of that there is no chance they get a failing grade as long as they will study as they can. 2. Do you have problems with the new grading system. If there is, what? - They have no problems in the new grading system because it is favor to all of them. 3. Does the new grading system give you a better picture of your performance? Why or why not? - According to them it’s a yes , the new grading system gives a better picture of their performances because they are not worrying about the failing grades because as they mentioned it is no longer zero based. 4. Which do you prefer the old or the new grading system? Why? - They preffered the new grading system because it give them a chance to get higher grades than before. D. Review of DepEd Order # 8, s. 2015 Read DepEd Order # 8 s. 2015. You may refer to Appendix A. Based on DepEd Order 8, s, 2015, answers the following: 1. What are the bases for grading? - All grades will be based on the weighted raw score of the learners summative assessments. The minimum grade needed to pass a specific learning area. Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|20887369 2. How do you compute grades per quarter for Grades 1 to 10 and Grades 11 to 12. Give an example. - In a grading period , there is one Quarterly Assestment but there should be instances for students to produce written work and to demonstrate what they know and can do through performance task. 3. How do you compute grades at the end of the school year? - According to my resi=ource teacher, she will going to sum up the quarterly grades of her students from first to fourth grading to compute the final grades of every students in different subjects. 4. What descriptors and grading scale are used in reporting progress of learners? - The learner’s report card 5. What are the bases for learners' promotion and retention at the end of the school year? - The basis for learners promotion is when the students get higher grades after computing the overall of her grades from 1st to last quarter but if he/she’s not going to promote. 6. What is the report on learners' observed values? - The report on learners observed values will depend on the behaviour of every students inside or outside the classroom. E. Grade Computation Show sample computations of a grade: in a subject of your choice from Grades 1 to 6 (if you are a future elementary teacher) in your specialization if you are a high school teacher) Show the percentage contributions of written work, performance tasks and quarterly assessment. Then give the descriptor. Refer to DepEd Order # 8, s. 2015. ANALYZE Analyze data and information gathered from the interview and from your review of an unused Student's Report Card and the DepEd grading system. 1. Do teachers and students like the new grading system? Why or why not? Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|20887369 - As I interviewed both students and teachers as I look like they want the new grading system because for the teacher it is easy to them in computing their grades because they used an electronic grading system . While the students , it is favor to them because it is easy to them to achive their goals which is getting high grades. 2. What are the good points of the new grading system according to teachers? According to students? -For the teacher he/she don’t have any reason to failed the students that have low performance and for the students they had a small chance to get failed grades because of the new grading system. 3. What are teachers challenged to do by this new grading system? -The teacher challenged by giving a corresponding point to his/her students even the answer is not really connected to the question given by the teacher . 4. Do you favor the distribution of percentages of written work, performance tasks and quarterly assessment? - Yes I am favor on the distribution of percentage of written work ,performance, tasks and quarterly assestment but it depends on the subjects. 5. Did you like the experience of computing grades? Why or why not? - I really like it because it is really exciting when you compute your students grades. You really feel that you are teacher. REFLECT In an era where the emphasis is self-directed learning and demonstration of competencies - knowledge, skills and values learned (outcomes-based education)- do grades really matter? - For me grades really matter because all of the students really study hard just to get the grades that they want. LINK Theory to Practice B. 1. Which is the percentage contribution of quarterly assessment to the grade of the student from Grades 1 to 10? A. 15% C. 25% Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|20887369 B. 20% D. 30% B. 2. Does quarterly assessment have the same percentage weights for all the subjects, for all the tracks in Grades 11-12? A. Yes C. Yes, only for the academic track B. No D. It depends on schools. C. 3. Which is the percentage contribution of written work to the grade of the Grade 1-10 student in Science and Math? A. 50% C. 40% B. 20% D. 30% A. 4. In MAPEH and TLE, which contribute/s heaviest to the student grade? A. Performance tasks C. Quarterly assessment B. Written work D. Quarterly assessment and performance tasks C. 5. Based on percentage contribution to the grade, what can be inferred from the DepEd's emphasis on learning and assessment? A. The emphasis depends on the grade level of the subjects. B. All components are being emphasized. C. The emphasis for all Grades 1-10 subjects is on performance tasks. D. The emphasis is on quarterly assessment. A. 6. A student gets a numerical grade of 80. What is his descriptor for his level of proficiency? A. Satisfactory C. Very Satisfactory B. Fairly Satisfactory D. Did not meet expectations D. 7. I get a grade of 90. What is its descriptor? A. Very satisfactory C. Advanced B. Beginning D. Outstanding A. 8. Which is described as "did not meet expectations? A. Below 75% C. Below 74% B. Below 76% D. Below 72% Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|20887369 D. 9. If a student failed to meet standards, which descriptor applies? A. Developing C. Poor B. Beginning. D. Did not meet expectations A. 10. How is the final grade per subject for Grades 11 and 12 obtained? A. Get the average of the grades for the 2 Quarters B. Get the average of the grades for the 4 Quarters C. Get the average of the grades of all subjects for the 2 semesters D. Get the average of the grades of all subjects for the 4 semesters. A. 11. Which is/are TRUE of MAPEH when it comes to grade computation? I. The quarterly grade is the average of the quarterly grades in the four areas-Music, Arts, Physical Education and Health (MAPEH) II. Individual grades are given to each area (MAPEH) III. There is one grade for Music and Arts, PE and Health because they are related. A. I only C. 1 and III B. I and II D. II only C. 12. Which is TRUE of Kindergarten grades? A. Grades are computed like the grades in Grade 1. B. There are numerical grades with descriptions. C. There are no numerical grades. D. Remarks like Passed, and Failed are used. D. 13. At the end of the school year, which is/are TRUE of grades? I. the General Average is computed by dividing the sum of all final grades by the total number of learning areas. II. Each learning area has equal weight in computing for the General Average. III. The Final Grade per learning area and the General Average are reported as whole numbers. A. I and II C, I and III B. II and III D. I, II and III Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|20887369 A. 14. Who is retained in the same grade level for Grades 1 to 10? Any students who did not meet expectations A. in three or more learning areas C. in four learning areas B. in 2 learning areas D. as shown in the general average B. 15. What happens when a student in Grade 1 to 10 did not meet expectations in two learning areas? A. Retained in the same grade level B. Promoted to the next grade level after passing remedial classes for learning areas with failing mark C. Promoted in the next grade level but has back subjects in the lower grade level D. Is not accepted for enrollment in the school Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|20887369 Activity 13.8 Reporting Student’s Performance Resource Teacher: ARLENE TORRES School: SANJOSE COMMUNITY HIGHSCHOOL Grade/Year Level: GRADE 10 1,2022 Teacher’s Signature: Subject Area: ENGLISH Date: FEB OBSERVE Proceedings in a Card Distribution Day 1. Observe how cards are distributed on Card Distribution Day. Describe how cards are - NOT OBSERVED 2. Describe how the Resource Teachers communicated learners' assessment results and grades to parents. -NOT OBSERVED 3. Did parents raise questions or concerns? If yes, what were their questions/concerns? -NOT OBSERVED 4. How did the Resource Teacher handle their questions and concerns? What answers did he she gives? - She handle it very well and answer will all of her learnings in the specific question. Interview with Resource Teacher 1. How do you give feedback to your students regarding their performance? When do you give feedback? - The resource teacher give feedback to the learner about their performance before she compute their grade so that the students will be aware if they have missed quizzes of projects incomplete. Teacher always remind those students because it will affect their grades if they did not complete all their misses in their academic performance 2. How do you report students' performance to parents? Does the school have a regular way of reporting grades to parents? - According to my resource teacher , she report her students performance by having a short meeting to their parents 3. What problems on grade reporting did you encounter with parents? How did you address it/them? -Not observed Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|20887369 Interview with Students 1. Do you see the meaning of your grades in the School Report Card? - Yes if it is high the I conclude that I study hard to get high grades but if it is low maybe I have something missed projects. 2. Does knowing your grade motivate you to work harder? -Yes because the higher the grades I will got motivate me to study hard. Interview with Parents 1. Does your child's Report Card give you a clear picture of how your child is performing? Why? - Yes if I saw the report card of my children I already know how her performance in the school. 2. If you were asked what else should be found in the Report Card, which one? - For me there is no need to be added on the report card because it is all enough to see the performance of every students. 3. Do you find the Card Distribution Day important? Why or why not? -Yes, card distribution is important because this is the only way to monitor the performance of my children. 4. Any suggestion on how to make Card Distribution more meaningful? - I don’t have any suggestion about the distribution of card becauase teachers did it in a proper way ANALYZE 1. What were the most common issues raised on students' performance? - The most common issue raised on students performance was low grades or failing grades. 2. Based on your observations and findings, what practices must be a) maintained and b) improved to make grades and reporting meaningful? Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|20887369 - In my opinion , I think to make it more meaningful the distribution of report card is that students should also there in order to see their grades together with their parents . And if there is a problem on the grade they may give some advice their children to make better grades . REFLECT 1. Grades are often a source of misunderstanding. How should I do reporting so that it will result to effective learning? To prevent the misunderstanding the teacher should explain the grading system to the parents and also he/she should show how the things that they considered in computing their grades . LINK Theory to Practice. D. 1. Why must grades be reported to parents? I. Promote ongoing formative feedback to students II. Ensure alignment of curriculum, instruction, and assessment III. Promote, to parents and students, credible and useful feedback A. I only C. II only B. I and III D. I, II and III C. 2. What must be done to make grade reporting meaningful? I. The grading system must be clear to all concerned. II. The standards and competencies are known and understood by all. I II. The grading system must be numerical. A. I and II C. I, II and III B. II only D. III only C. 3. To make grade reporting meaningful, which must be done? A. Announce names of students who need to help. B. Rank the Report Cards from highest to lowest then distribute the same according to rank. C. Explain how the grades were computed. Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|20887369 D. Console parents whose are non-performing by telling them that nobody fails. A. 4. What is an essential step in reporting grades to parents? I. Explain that grades give a picture of students' performance. II. Explain that grades compare students' performance against the established standards. III. Explain that grades compare students' performance against other students' performance. A. I and II C. I, II and III B. II only D. III only B. 5. What does criterion -referenced grading mean? A. Grading on the curve B. Grading against standards C. Comparing grades with average grade D. Interpreting grades based on Mean A. 6. What must be done to make grades meaningful? A. Interpret grades against standards. C. Compare individual grades against mean. B. Compute grades accurately. D. Compare grades of boys and girls. Downloaded by Mharilyn Batallia (giannaganer@gmail.com)