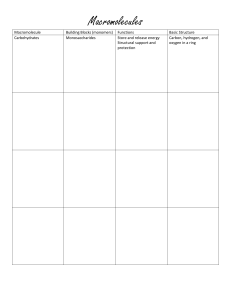
Chapter 2 Chemistry of Life Study Guide 1. Chemical reactions that absorb more energy than they release are called ___________________________. 2. The first carbon compounds that scientists studied are called ______________ compounds because they came from living organisms. (This word means it contains “carbon”) 3. DNA and RNA are two types of ______________________. (type of macromolecule) 4. What is the process that changes one set of chemicals into another set of chemicals? 5. When salt is dissolved in water, water is the ______________________. 6. Enzymes affect chemical reactions in living organisms by _________________ the activation energy of a reaction. 7. What atoms make up a molecule of water? How many hydrogen and oxygen? 8. The three particles that make up an atom are called protons, ___________________, and ________________. 9. What type of ion forms when an atom loses electrons? (positive/negative) 10. What are the four main groups of carbon-based molecules (macromolecules)? 11. The activation energy needed for a chemical reaction is decreased by a ____________________. (another name for an enzyme) 12. ________________________ is a term that describes a substance formed by the combination of two or more elements in a definite proportion. 13. The most abundant compound in most living things is _____________________. 14. What category of carbon-based molecules (macromolecules) includes sugars and starches? 15. Fats, oils, and cholesterol are all types of _________________________. 16. Identify the reactants in the following chemical equation: 6 H2O + 6 CO2 C6H12O6 + 6O2 17. Chemical reactions change substances into different substances by _______________________ and chemical bonds. 18. A very strong based might have a pH of _______________. 19. The effect of a catalyst on a chemical reaction _______________________ the activation energy. (increase/decrease) 20. When hydrogen and oxygen combine to form water, water is the (product/reactant). 21. __________________ are the smallest basic units of matter. 22. The attraction among molecules of different substances is called (example: water sticking to other substances) __________________________. 23. ______________________________________ is the term for the amount of energy that needs to be added for a chemical reaction to start. 24. This type of macromolecule, __________________________, is the main source of energy for living things. 25. _____________________ are the basic building blocks of proteins (monomer). 26. A monosaccharide is the monomer of _______________________. 27. True of False. Proteins store and transmit hereditary information. 28. A substance with a pH of 6 is called _________________________. 29. A covalent bond is formed as the result of ___________________________. 30. A ______________________ is a single unit (1 brick), while a _________________ is many units attached together (more than one brick). 31. Cell membranes are made up of _________________________________. 32. The place where the enzyme and the substrate react together is called _________________________. 33. _____________________ are macromolecules that are important in muscle contraction and transporting oxygen in the blood. 34. ____________________ are macromolecules that store genetic information in cells. 35. ____________________ are commonly called fats and oils and is a major component of cell membranes. 36. Glucose, sucrose, starch, and cellulose are examples of ______________________________. 37. ____________________ are catalytic molecules that help speed up reactions.