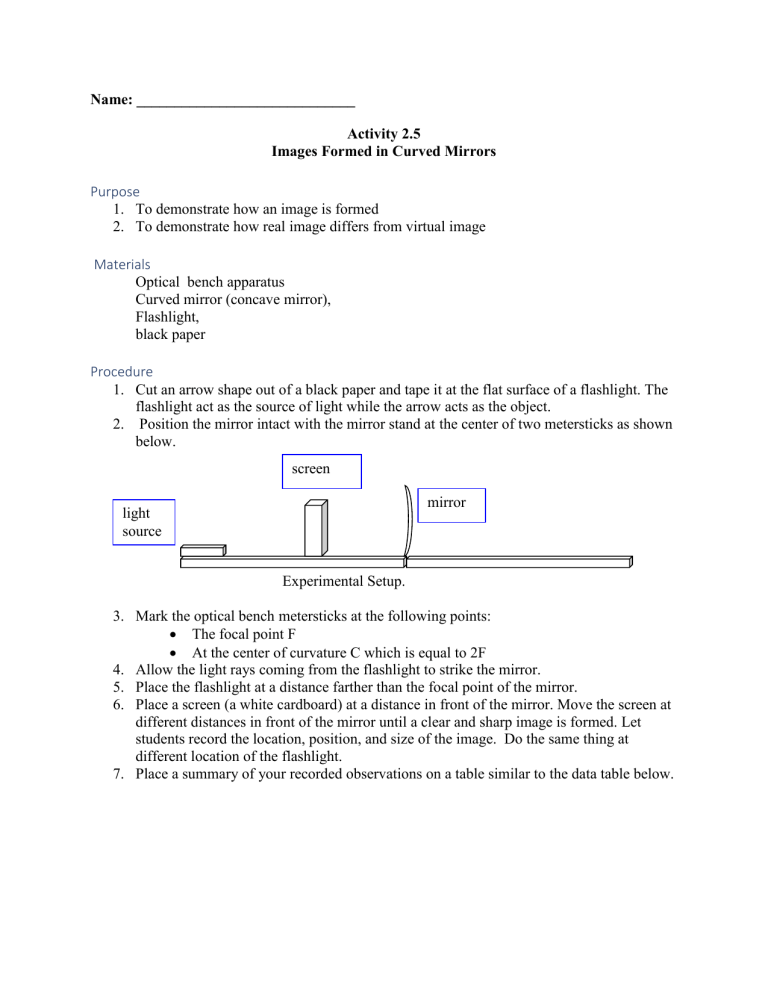
Name: _____________________________ Activity 2.5 Images Formed in Curved Mirrors Purpose 1. To demonstrate how an image is formed 2. To demonstrate how real image differs from virtual image Materials Optical bench apparatus Curved mirror (concave mirror), Flashlight, black paper Procedure 1. Cut an arrow shape out of a black paper and tape it at the flat surface of a flashlight. The flashlight act as the source of light while the arrow acts as the object. 2. Position the mirror intact with the mirror stand at the center of two metersticks as shown below. screen mirror light source Experimental Setup. 3. Mark the optical bench metersticks at the following points: The focal point F At the center of curvature C which is equal to 2F 4. Allow the light rays coming from the flashlight to strike the mirror. 5. Place the flashlight at a distance farther than the focal point of the mirror. 6. Place a screen (a white cardboard) at a distance in front of the mirror. Move the screen at different distances in front of the mirror until a clear and sharp image is formed. Let students record the location, position, and size of the image. Do the same thing at different location of the flashlight. 7. Place a summary of your recorded observations on a table similar to the data table below. Data Table Location of Object Location of Image Kind of image (real or virtual) Position of image (erect or inverted) Size of Image (reduced or enlarged) A. CONCAVE At infinity Farther than the Center of Curvature At the center of Curvature Between the Center of curvature and the Focal point At the focal point Between the focal point and the center of the lens B. CONVEX All locations Guide Questions 1. Describe the image changes in size and location as the object approaches the mirror. 2. Differentiate a real image from a virtual image. 3. Describe the images formed by curved mirrors (convex and concave mirrors). Activity 2.0 Focal length of the lens Purpose To determine the focal length of the convex lens Materials Convex lens Optical Bench Procedure 1. Look for any object (tree, etc.) outside your window. 2. Hold up the lens facing the window. 3. Move a sheet of paper (screen) behind it. See figure on the right. 4. Adjust the paper until a clear image of the distant object (tree, etc.) outside the window is observed on the paper. 5. Measure the distance from the image to the lens. This is the focal length of the lens. Guide Question: 1. What is the focal length of your lens? 2. If you take an object that is farther than the first one, do you think you will have the same measurement? Find it out by considering another object. Activity 2.1 Image Formed in lenses Purpose To locate and describe the image formed by concave and convex lenses Materials Concave les Convex lens Flashlight / Candle Optical Bench Candle Screen Lens Procedure 1. Start with a convex lens. Get its focal length 2. Position the candle on the following: (these are the object distances) 1.1 before the focal length of the lens (between 1F and the lens), 1.2 at the focal length F, 1.3 between F and 2F, 1.4 at 2F, and 1.5 beyond 2F 3. In all cases adjust the screen until a clear image is seen. 4. Measure the distance from the image to the lens. This is the image distance. Describe also the nature of the image and enter in the data table. 5. Repeat steps 1-4 using a concave lens. Table 2.11 Location of Object (object distance) A. CONVEX between 1F and the lens at the focal length F between F and 2F at 2F beyond 2F B. CONCAVE between 1F and the lens Location of Image (image distance) Kind of image Position of image at the focal length F between F and 2F at 2F beyond 2F Guide Question 1. Compare the nature of the image at different object distances for 1.1 Convex lens 1.2 Concave lens Size of Image