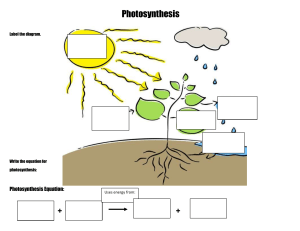
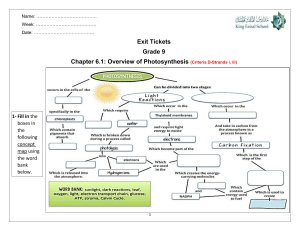
KS4 Biology Plant Nutrition 1 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Contents Plant Nutrition How do plants make food? What is photosynthesis? More about photosynthesis The rate of photosynthesis Minerals from the soil Multiple-choice quiz 2 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 How do plants get the food they need? All living organisms need food to grow and survive. Plants are known as producers because they provide food for many other organisms. Plants cannot move very much, so how do they get the food that they need? 3 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Nutrition in green plants Green plants are amazing because they actually make their own food! Green plants are the only living organisms that are able to do this. All other organisms rely on plants because of the food that the plants make. What is the name of the process by which plants make their own food? 4 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 What is photosynthesis? Plants make their own food by photosynthesis. This process is a chemical reaction that uses light energy. light energy The word photosynthesis comes from the Greek language: “photo” means “light” “synthesis” means “putting together” Photosynthesis just means “putting together with light”. What do green plants “put together” to make their food? 5 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Contents Plant Nutrition How do plants make food? What is photosynthesis? More about photosynthesis The rate of photosynthesis Minerals from the soil Multiple-choice quiz 6 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Photosynthesis: raw materials The raw materials for photosynthesis come from the air and the soil. What are these raw materials called? What else do plants need to turn carbon dioxide and water into food? 7 of 57 carbon dioxide water © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Photosynthesis: energy for the reaction Photosynthesis is a chemical reaction between carbon dioxide and water. light energy Energy is needed for this reaction to take place. Where do plants get this energy from? carbon dioxide water 8 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Photosynthesis: where it happens Plants use light energy from the Sun to power photosynthesis. light energy Where in the leaf does this reaction take place? Photosynthesis takes place in what part of plant cells? carbon dioxide water 9 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Photosynthesis: where it happens Photosynthesis takes place in plant cells with chloroplasts. light energy Chloroplasts contain the green chemical called chlorophyll. Chlorophyll absorbs the energy from sunlight that allows carbon dioxide and water to react. What are the products of this reaction? 10 of 57 chlorophyll carbon dioxide water © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Photosynthesis: products of the reaction The products of the reaction between carbon dioxide and water are glucose and oxygen. light energy chlorophyll Which of these products is used by plants? What happens to the ‘waste’ product? carbon dioxide oxygen glucose water 11 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Photosynthesis: products of the reaction Glucose is the useful product for plants. Some glucose is used straightaway by plant cells, some is converted to starch for storage and later used for food. light energy chlorophyll carbon Oxygen is the ‘waste’ dioxide product. This gas is transported out of the leaf into the air. Why is this important for humans and other living things? 12 of 57 oxygen glucose water © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Photosynthesis: summary Summarize the process of photosynthesis in one sentence. Photosynthesis is a chemical reaction that takes place in the chloroplasts in green plant cells, where light energy is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. Photosynthesis is a chemical reaction which means it can also be summarized in a word equation. What is the word equation for this vital chemical reaction? 13 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Photosynthesis: word equation light energy carbon dioxide water glucose oxygen chlorophyll light energy chlorophyll carbon dioxide oxygen glucose water 14 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Photosynthesis: word equation activity 15 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Photosynthesis: chemical formulae? Photosynthesis is a chemical reaction involving molecules. light energy carbon dioxide water glucose oxygen C6H12O6 O2 chlorophyll CO2 H2O The chemical formula of a glucose molecule is C6H12O6. What are the chemical formulae of the simple molecules that make up carbon dioxide, water and oxygen? 16 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Word equation to chemical equation 17 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Photosynthesis multiple-choice quiz 18 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Contents Plant Nutrition How do plants make food? What is photosynthesis? More about photosynthesis The rate of photosynthesis Minerals from the soil Multiple-choice quiz 19 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Leaves: maximizing photosynthesis Leaves are the most efficient solar panels on Earth! Why can they be called this? Light energy is absorbed by the chlorophyll in leaves and used to carry out photosynthesis. Leaves come in all shapes and sizes but what features do they have in common to maximize photosynthesis? 20 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Structure of a leaf How are leaves designed to maximize photosynthesis? Leaves are wide and flat Leaves are thin so gases to create a large surface can reach cells easily. area and to absorb as much light as possible. Leaves have lots of veins to carry water to the cells and carry glucose away. 21 of 57 Leaves have holes, called stomata, on their underside through which gases move in and out. © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Structure of a leaf activity 22 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Take a look inside a leaf 23 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 What happens to the glucose? 24 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Testing leaves for starch – procedure 25 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Testing leaves for starch – experiment 26 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Photosynthesis and respiration Only green plants photosynthesize, but respiration occurs in the cells of all living things to release energy. Photosynthesis (energy needed) light energy carbon dioxide water glucose oxygen chlorophyll Respiration (energy released) carbon glucose oxygen dioxide water Compare the reactants, products and energy results of these two chemical reactions. How are they connected? 27 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Photosynthesis and respiration How will the amounts of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the air vary over 24 hours? amount of oxygen amount of gas in the air amount of carbon dioxide 12 a.m. 12 p.m. 12 a.m. What overall effect do photosynthesis and respiration have on the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the air? 28 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Contents Plant Nutrition How do plants make food? What is photosynthesis? More about photosynthesis The rate of photosynthesis Minerals from the soil Multiple-choice quiz 29 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 The rate of photosynthesis Photosynthesis is a chemical reaction and so has a rate. light energy carbon dioxide water glucose oxygen chlorophyll Is the rate of photosynthesis always the same? The rate of photosynthesis varies depending on three main factors: light carbon dioxide temperature How do these factors affect the rate of photosynthesis? 30 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Light and the rate of photosynthesis Light energy has to be absorbed by chlorophyll for photosynthesis to take place. light energy carbon dioxide water glucose oxygen chlorophyll The brighter the light, the more light energy there is, so will photosynthesis be faster or slower? More light energy means that photosynthesis will be faster. If light intensity is too high plant cells can be damaged. How is photosynthesis affected if this happens? 31 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Investigating photosynthesis – apparatus 32 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Investigating photosynthesis – experiment 33 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Investigating photosynthesis – results 34 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Carbon dioxide and the rate of photosynthesis Carbon dioxide is one of the raw materials used by plants to make their food. light energy carbon dioxide water glucose oxygen chlorophyll The concentration of carbon dioxide in the air (0.03%) is actually quite low. Why is the concentration of carbon dioxide in commercial greenhouses often raised to about 0.1%? More carbon dioxide means more photosynthesis, so plants make more food and grow quicker. 35 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Temperature and the rate of photosynthesis Photosynthesis is controlled by enzymes. Enzymes usually work best at warmer temperatures. light energy carbon dioxide water glucose oxygen chlorophyll Why is the rate of photosynthesis slower on a sunny day in winter compared to in summer? If the temperature gets too hot (above 40 °C), plant enzymes begin to break down and are destroyed or denatured. Why does photosynthesis stop under such conditions? 36 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 What is a limiting factor? What is the ideal combination of factors for the maximum rate of photosynthesis? enough light enough carbon dioxide ideal temperature (not too hot or cold) How is the rate affected if one of these factors is restricted? If one of the factors is restricted, the rate of photosynthesis will be below the maximum possible rate. The restricted factor controls how quickly photosynthesis occurs and so limits the rate. It is called the limiting factor. 37 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Photosynthesis and light – limiting factors rate of photosynthesis How does the amount of light affect the rate of photosynthesis on this labelled graph? As the amount of light increases, so does the rate. The limiting factor is light. 2 Here, increasing the amount of light has no affect on the rate. The limiting factor is now carbon dioxide or temperature. 2 1 light intensity 38 of 57 1 What must be increased for the rate to increase? © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Photosynthesis and carbon dioxide – limiting factors rate of photosynthesis How does the amount of carbon dioxide affect the rate of photosynthesis on this labelled graph? As the amount of carbon dioxide goes up, so does the rate. The limiting factor is carbon dioxide. 2 Here, increasing the amount of carbon dioxide has no affect on the rate. Light or warmth is now the limiting factor. 2 1 concentration of carbon dioxide 39 of 57 1 What must be increased for the rate to increase? © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Photosynthesis and temperature – limiting factors rate of photosynthesis How does temperature affect the rate of photosynthesis on this labelled graph? 2 1 0oC temperature 45oC 40 of 57 11. As temperature increases, so does the rate because photosynthetic enzymes work best in the warmth. Here, the limiting factor is temperature. 2 Most plant enzymes are destroyed at about 45°C. Here, photosynthesis stops and the rate falls to zero. What is the limiting factor? © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Limiting factors activity 41 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Limiting factors in the greenhouse 42 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Contents Plant Nutrition How do plants make food? What is photosynthesis? More about photosynthesis The rate of photosynthesis Minerals from the soil Multiple-choice quiz 43 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 What do plants need for a balanced diet? Plants need carbon dioxide and water for photosynthesis. Do they need any other nutrients to keep healthy? Just like humans, plants need a balanced diet that includes small amounts of mineral elements. What mineral elements do they need? 44 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 What minerals do plants need? Plants need mineral elements for healthy growth. Some of the most important minerals needed by plants are: nitrogen nitrates phosphorus phosphates potassium potassium ions magnesium magnesium ions How do plants obtain these minerals? The mineral elements are found in salts dissolved in water. Plants obtain minerals when they absorb water from the soil. What type of salt are each of these elements found in? 45 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 What are minerals needed for? How do plants use these mineral elements? Mineral element How mineral is used in plants nitrogen (N) phosphorus (P) potassium (K) magnesium (Mg) 46 of 57 making leaves making roots making flowers and fruit making chlorophyll © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Plant and minerals – summary activity 47 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Where do minerals come from? What are the sources of minerals in the soil? Rocks: The minerals in rocks are slowly dissolved by slightly acidic rainwater. These minerals are washed into the soil. Natural fertilizers: Animal faeces and the decay of dead plants and animals return minerals to the soil. Artificial fertilizers: These contain a ready-made mixture of the minerals needed by plants. Why do farmers add fertilizers to their soil? 48 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Not enough minerals! What happens if plants do not get enough minerals? Plants do not grow properly if they are deprived of minerals and begin to look unhealthy. If a plant does not get enough of a mineral it is said to have a mineral deficiency. Do mineral deficiencies affect a plant in the same way? 49 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Mineral deficiency – no nitrogen! Nitrogen is used for making leaves and is probably the most important mineral for plant growth. What is the effect of nitrogen deficiency? upper leaves pale green lower leaves yellow and dead weak stem 50 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Mineral deficiency – no phosphorus! Phosphorus is used for making roots and is important for all the other minerals used by plants. What is the effect of phosphorus deficiency? purple leaves small roots 51 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Mineral deficiency – no potassium! Potassium is used for making flowers and fruit, so crops are given extra potassium before they start to fruit. What is the effect of potassium deficiency? poor flower and fruit growth yellow leaves with dead spots 52 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Mineral deficiency – no magnesium! Magnesium is used for making chlorophyll and so is vital for the process of photosynthesis. What is the effect of magnesium deficiency? upper leaves normal (leaves turn yellow from bottom upwards) lower leaves pale green or yellow 53 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Mineral deficiency experiment 54 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Plant and minerals summary Complete this table of plant mineral needs and deficiencies. Mineral Use in plant Deficiency signs nitrogen making leaves stunted growth and yellow leaves phosphorus making roots potassium making flowers and fruits poor roots and purple leaves yellow leaves with dead spots magnesium making chlorophyll leaves turn yellow from the bottom 55 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Contents Plant Nutrition How do plants make food? What is photosynthesis? More about photosynthesis The rate of photosynthesis Minerals from the soil Multiple-choice quiz 56 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004 Multiple-choice quiz 57 of 57 © Boardworks Ltd 2004