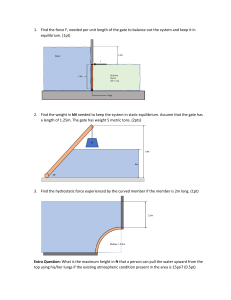
CHAPTER 3 TOTAL HYDROSTATIC FORCE ON SURFACES CURVED SURFACES Total hydrostatic force on Curved Surface The easiest way to determine the resultant hydrostatic force FR acting on a two-dimensional curved surface is to determine the horizontal and vertical components FH and FV separately. HYDROSTATIC FORCE ON CURVED SURFACE CHAPTER 3 Total hydrostatic force on Curved Surface Horizontal Component, FH 𝑭𝑯 = 𝒑𝒄𝒈 𝑨 Vertical Component, FV 𝑭𝑽 = 𝜸𝑳 𝑽 Resultant Force, FR 𝑭= (𝑭𝑯 )𝟐 +(𝑭𝑽 )𝟐 HYDROSTATIC FORCE ON CURVED SURFACE CHAPTER 3 CASE I: Liquid is above Curved Surface 𝑳𝑺 𝑭𝑯 = 𝒑𝒄𝒈 𝑨 𝒉 𝑭𝑯 𝑭𝑯 HYDROSTATIC FORCE ON CURVED SURFACE CHAPTER 3 CASE I: Liquid is above Curved Surface 𝑳𝑺 𝑭𝑽 𝑭𝑽 𝑭𝑽 = 𝜸𝑳 𝑽 HYDROSTATIC FORCE ON CURVED SURFACE CHAPTER 3 CASE II: Liquid is below Curved Surface 𝑳𝑺 𝑭𝑯 = 𝒑𝒄𝒈 𝑨 𝒉 𝑭𝑯 𝑭𝑯 HYDROSTATIC FORCE ON CURVED SURFACE CHAPTER 3 CASE II: Liquid is below Curved Surface 𝑳𝑺 𝑭𝑽 𝑭𝑽 = 𝜸𝑳 𝑽 HYDROSTATIC FORCE ON CURVED SURFACE CHAPTER 3 Example The given tank shown is 6m wide. Neglecting atmospheric pressure, compute the following: a. Horizontal Force on the curve panel AB. b. Vertical Force on the curve panel AB. c. Resultant Force. d. Angle that the resultant makes with the horizontal. e. Find the location of the FH and FV from C. f. Find the location of the point where the FR strikes the wall from A.. C HYDROSTATIC FORCE ON CURVED SURFACE CHAPTER 3 Example 𝑭 𝐴 The gate shown is a quarter circle 8 ft wide. Find the force F just sufficient to prevent rotation about hinge B. Neglect the weight of the gate. 𝐵 HYDROSTATIC FORCE ON CURVED SURFACE CHAPTER 3